2. The component shown always breaks at point C, which is just to the right of the contact point of the roller at B. Find the internal forces in terms of shear, normal and bending to show why this is. 150 mm -250 mm- 400 N A OB 125 mm 500 N 110 mm 80 N•m
2. The component shown always breaks at point C, which is just to the right of the contact point of the roller at B. Find the internal forces in terms of shear, normal and bending to show why this is. 150 mm -250 mm- 400 N A OB 125 mm 500 N 110 mm 80 N•m
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Chapter7: Analysis Of Stress And Strain
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7.7.19P: During a test of an airplane wing, the strain gage readings from a 45° rosette (see figure) are as...
Related questions
Question
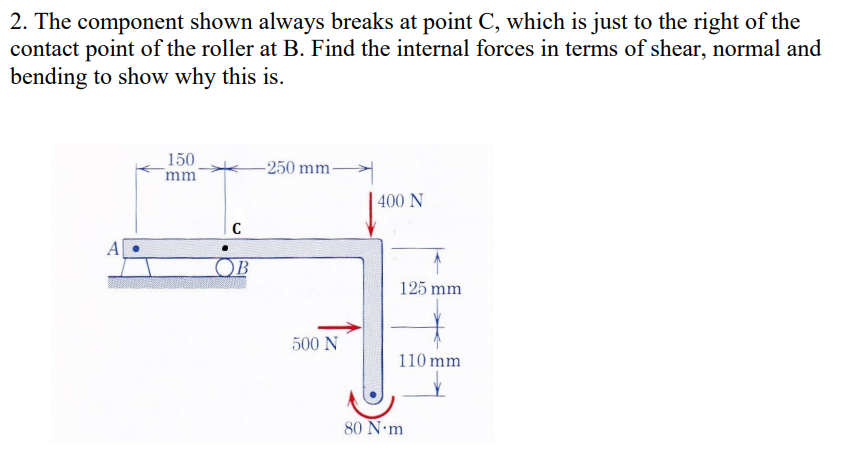
Transcribed Image Text:2. The component shown always breaks at point C, which is just to the right of the
contact point of the roller at B. Find the internal forces in terms of shear, normal and
bending to show why this is.
150
mm
-250 mm-
400 N
OB
125 mm
500 N
110 mm
80 N•m
Expert Solution
Step 1
The component always breaks at point C, which is just right of the contact point of the roller at B. So, draw the free-body diagram of the section which is just right of the contact point of the roller at B as follows:
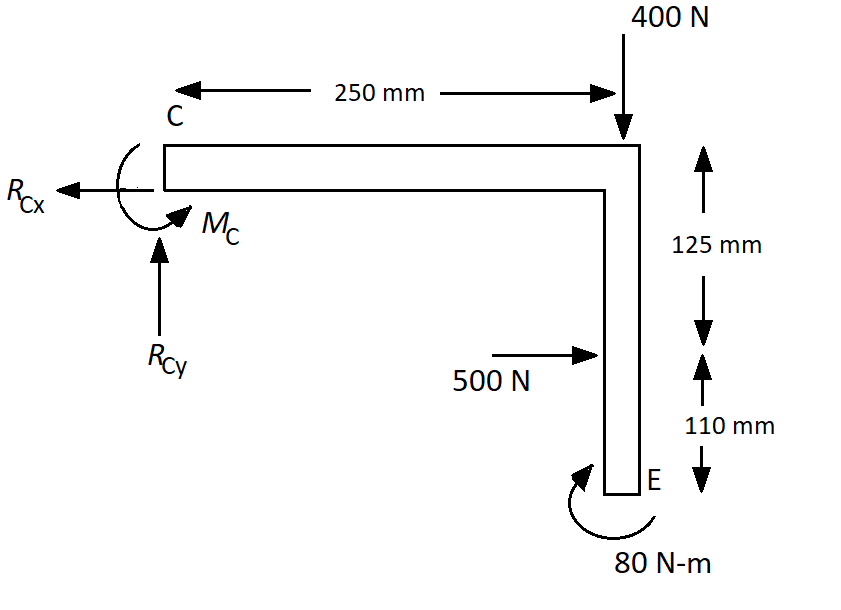
Here, the reaction force at C in the horizontal direction is RCx, the reaction force at C in the vertical direction is RCy and the moment reaction at C is MC.
Step 2
Consider the equilibrium of force in the horizontal direction,
Consider the equilibrium of force in the vertical direction,
Calculate the moment reaction at C,
Step 3
Therefore, the internal forces in terms of shear, normal, and bending are,
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning