3. For a mole of a perfect monoatomic gas, the internal energy, U, can be expressed as a function of the pressure and volume as 3 U = U(P,V) = PV a) Calculate explicitly the line integral of dU along the closed path ABCD shown as a black trace in the P – V graph below. D C 3P1 2P1 P1 -> A V V1 2V1 3V1 4V1 5V1 6V1 Problem 3a-3c b) Compute the following line integrals between the points B and C in the figure above: 1. S, PdV, along the path, h, described by P = 3P;V/(V – 3V1), shown in red in the figure above. 2. S, PdV, along the path, s, shown in black in the figure above. Use these results to demonstrate that &W = -PdV is not an exact differential. S.
3. For a mole of a perfect monoatomic gas, the internal energy, U, can be expressed as a function of the pressure and volume as 3 U = U(P,V) = PV a) Calculate explicitly the line integral of dU along the closed path ABCD shown as a black trace in the P – V graph below. D C 3P1 2P1 P1 -> A V V1 2V1 3V1 4V1 5V1 6V1 Problem 3a-3c b) Compute the following line integrals between the points B and C in the figure above: 1. S, PdV, along the path, h, described by P = 3P;V/(V – 3V1), shown in red in the figure above. 2. S, PdV, along the path, s, shown in black in the figure above. Use these results to demonstrate that &W = -PdV is not an exact differential. S.
Physical Chemistry
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781133958437
Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Chapter4: Gibbs Energy And Chemical Potential
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4.42E: Use the ideal gas law to demonstrate the cyclic rule of partial derivatives.
Related questions
Question
I need help with 3A and B. Please show me the detailed steps.
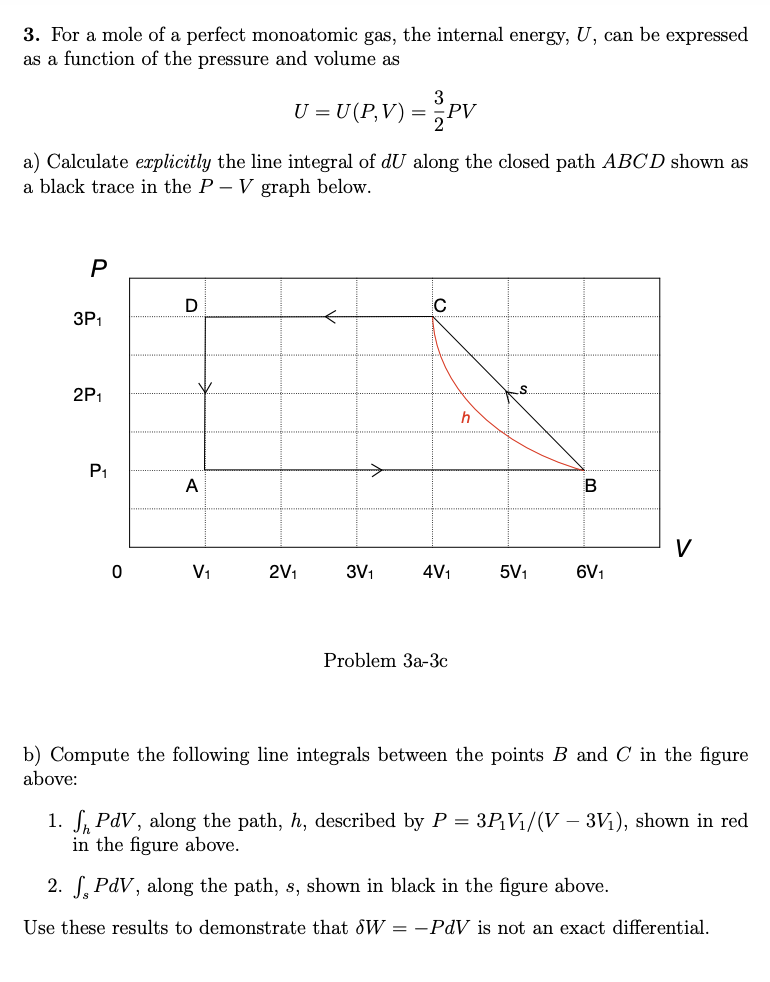
Transcribed Image Text:3. For a mole of a perfect monoatomic gas, the internal energy, U, can be expressed
as a function of the pressure and volume as
U = U (P,V) = PV
a) Calculate explicitly the line integral of dU along the closed path ABCD shown as
a black trace in the P – V graph below.
3P1
2P1
P1
A
V
V1
2V1
3V1
4V1
5V1
6V1
Problem За-3Зс
b) Compute the following line integrals between the points B and C in the figure
above:
1. S, PdV, along the path, h, described by P = 3P¡V1/(V – 3V1), shown in red
in the figure above.
2. S, PdV, along the path, s, shown in black in the figure above.
Use these results to demonstrate that dW = -PdV is not an exact differential.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,