5. Phosphorus trichloride, PC, is a compound used in the manufacture of pesticides and gasoline additives. How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 96.7 g PC, from 31.7 C to 692 C? The specific heat of PCh is 0.874 Jig C. found to be toxic. What i
5. Phosphorus trichloride, PC, is a compound used in the manufacture of pesticides and gasoline additives. How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 96.7 g PC, from 31.7 C to 692 C? The specific heat of PCh is 0.874 Jig C. found to be toxic. What i
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter8: Bonding And Molecular Structure
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 91IL: A paper published in the research Journal Science in 2007 (S. Vallina and R. Simo, Science, Vol....
Related questions
Question
number 5
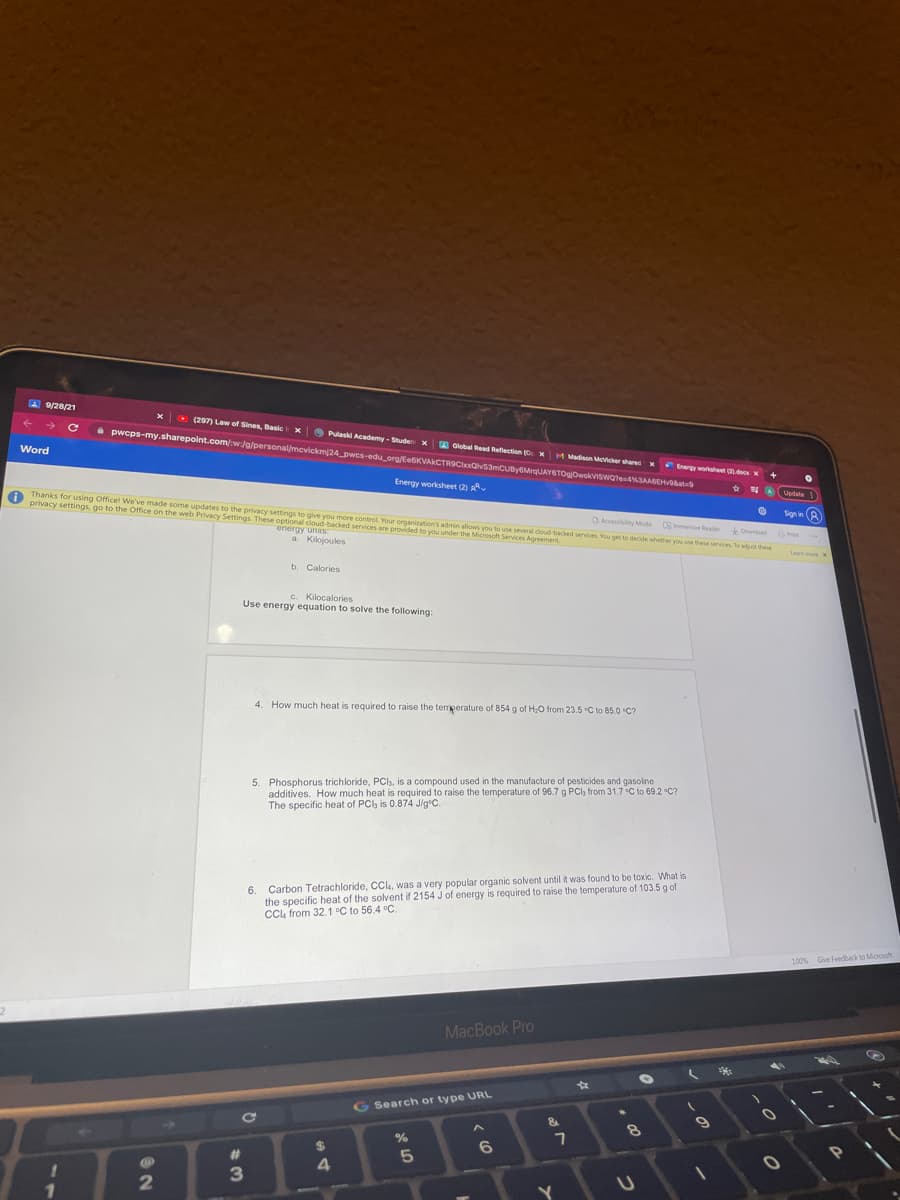
Transcribed Image Text:A 9/28/21
(297) Law of Sines, Basic
c x
O Pulaski Academy - Studen x
a pwcps-my.sharepoint.com/w:/a/personal/mcvickmj24 pwcs-edu_org/EeGKVAKCTRICioOlv3mCUByeMrgUAYSTOgowokVISwatesSAAGEHVat
Global Read Reflection (Ox
M Madison Mevicker shared x Energy workshee doc
Word
Energy worksheet (2)
Updala
Sign in A
Thanks for using Officel We've made some updates to the privacy settings to give you more control Your organization's admin allows you to use several doud-backed services You get to decide whether you use these serices To adt hese
privacy settings, go to the Office on the web Privacy Settings. These optional cloud-backed services are provided to you under the Microsoh Services Agreement.
DAccebliy Mode mer der
Oowad
P
energy unieS
a Kilojoules
Lean more X
b. Calories
c. Kilocalories
Use energy equation to solve the following:
4. How much heat is required to raise the temeerature of 854 g of H;O from 23.5 C to 85.0 "C?
5. Phosphorus trichloride, PCl, is a compound used in the manufacture of pesticides and gasoline
additives. How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 96.7 g PCl, from 31.7 C to 69.2 C?
The specific heat of PCl, is 0.874 J/g*C.
6. Carbon Tetrachloride, CC, was a very popular organic solvent until it was found to be toxic. What is
the specific heat of the solvent if 2154 J of energy is required to raise the temperature of 103.5 g of
CCL from 32.1 °C to 56.4 °C.
100% Give Feedback to Microsoft
MacBook Pro
G Search or type URL
%23
6.
%23
3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning