9. The figure shows an acceleration-versus-force graph for an object of mass m. Data have been plotted as individual points, and a line has been drawn through the points. Draw and label, directly on the figure, the acceleration- versus-force graphs for objects of mass a. 2m b. 0.5m Use triangles A to show four points for the object of mass 2m, then draw a line through the points. Use squaresI for the object of mass 0.5m. 10. A constant force applied to object A causes A to accelerate at 5 m/s2. The same force applied to object B causes an acceleration of 3 m/s². Applied to object C, it causes an acceleration of 8 m/s². 3 4 Force (rubber bands) a. Which object has the largest mass? b. Which object has the smallest mass? c. What is the ratio of mass A to mass B? (m,lmB) = 11. A constant force applied to an object causes the object to accelerate at 10 m/s?. What will the acceleration of this object be if a. The force is doubled? b. The mass is doubled? c. The force is doubled and the mass is doubled? d. The force is doubled and the mass is halved? Acceleration
9. The figure shows an acceleration-versus-force graph for an object of mass m. Data have been plotted as individual points, and a line has been drawn through the points. Draw and label, directly on the figure, the acceleration- versus-force graphs for objects of mass a. 2m b. 0.5m Use triangles A to show four points for the object of mass 2m, then draw a line through the points. Use squaresI for the object of mass 0.5m. 10. A constant force applied to object A causes A to accelerate at 5 m/s2. The same force applied to object B causes an acceleration of 3 m/s². Applied to object C, it causes an acceleration of 8 m/s². 3 4 Force (rubber bands) a. Which object has the largest mass? b. Which object has the smallest mass? c. What is the ratio of mass A to mass B? (m,lmB) = 11. A constant force applied to an object causes the object to accelerate at 10 m/s?. What will the acceleration of this object be if a. The force is doubled? b. The mass is doubled? c. The force is doubled and the mass is doubled? d. The force is doubled and the mass is halved? Acceleration
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter9: Linear Momentum And Collisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9.20P: Review. A force platform is a tool used to analyze the performance of athletes by measuring the...
Related questions
Question
Can you please do 9, 10, and 11
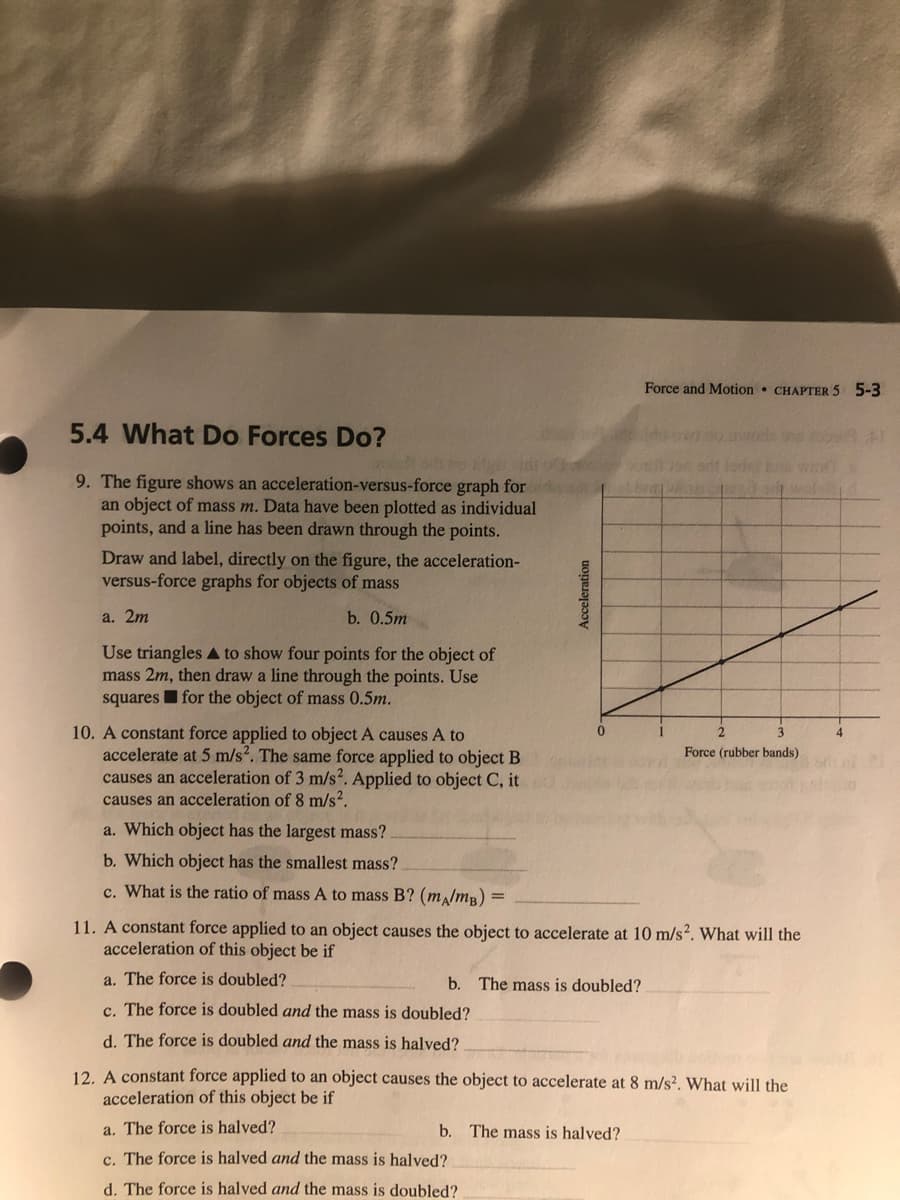
Transcribed Image Text:Force and Motion • CHAPTER 5 5-3
5.4 What Do Forces Do?
on sdt lod
9. The figure shows an acceleration-versus-force graph for
an object of mass m. Data have been plotted as individual
points, and a line has been drawn through the points.
Draw and label, directly on the figure, the acceleration-
versus-force graphs for objects of mass
a. 2m
b. 0.5m
Use triangles A to show four points for the object of
mass 2m, then draw a line through the points. Use
squaresI for the object of mass 0.5m.
10. A constant force applied to object A causes A to
accelerate at 5 m/s?. The same force applied to object B
causes an acceleration of 3 m/s2. Applied to object C, it
causes an acceleration of 8 m/s².
Force (rubber bands)
a. Which object has the largest mass?
b. Which object has the smallest mass?
c. What is the ratio of mass A to mass B? (malmB) =
11. A constant force applied to an object causes the object to accelerate at 10 m/s?. What will the
acceleration of this object be if
a. The force is doubled?
b. The mass is doubled?
c. The force is doubled and the mass is doubled?
d. The force is doubled and the mass is halved?
12. A constant force applied to an object causes the object to accelerate at 8 m/s?. What will the
acceleration of this object be if
a. The force is halved?
b. The mass is halved?
c. The force is halved and the mass is halved?
d. The force is halved and the mass is doubled?
Acceleration
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College