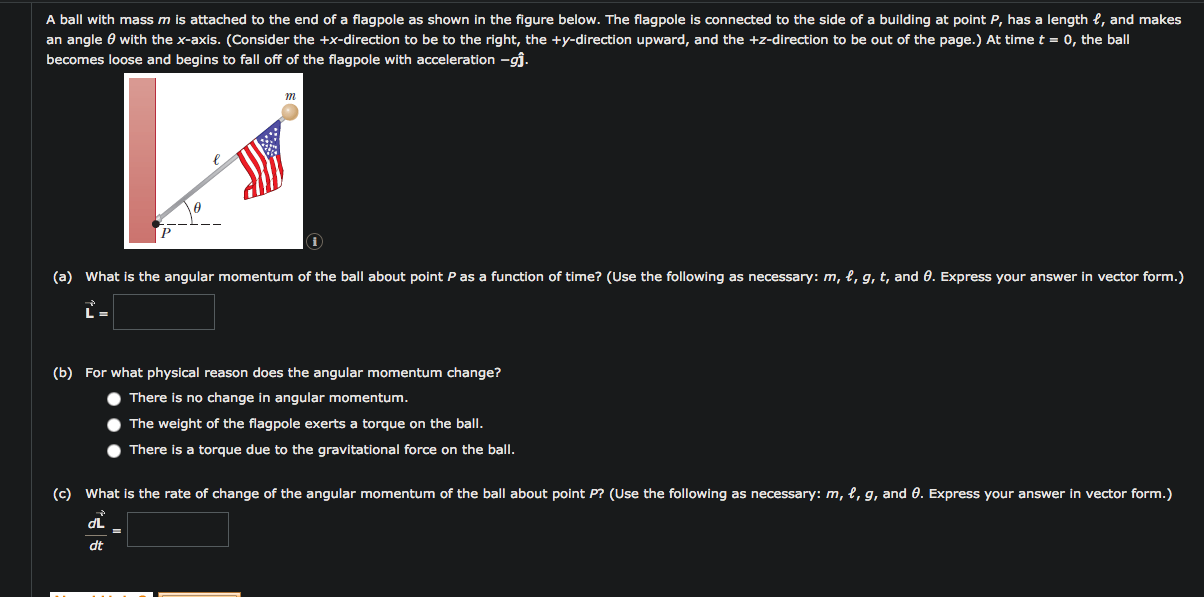
A ball with mass m is attached to the end of a flagpole as shown in the figure below. The flagpole is connected to the side of a building at point P, has a length e, and makes an angle 0 with the x-axis. (Consider the +x-direction to be to the right, the +y-direction upward, and the +z-direction to be out of the page.) At time t = 0, the ball becomes loose and begins to fall off of the flagpole with acceleration –gĵ. (a) What is the angular momentum of the ball about point P as a function of time? (Use the following as necessary: m, l, g, t, and 0. Express your answer in vector form.) (b) For what physical reason does the angular momentum change? There is no change in angular momentum. The weight of the flagpole exerts a torque on the ball. There is a torque due to the gravitational force on the ball. (c) What is the rate of change of the angular momentum of the ball about point P? (Use the following as necessary: m, l, g, and 0. Express your answer in vector form.) dL dt
Rigid Body
A rigid body is an object which does not change its shape or undergo any significant deformation due to an external force or movement. Mathematically speaking, the distance between any two points inside the body doesn't change in any situation.
Rigid Body Dynamics
Rigid bodies are defined as inelastic shapes with negligible deformation, giving them an unchanging center of mass. It is also generally assumed that the mass of a rigid body is uniformly distributed. This property of rigid bodies comes in handy when we deal with concepts like momentum, angular momentum, force and torque. The study of these properties – viz., force, torque, momentum, and angular momentum – of a rigid body, is collectively known as rigid body dynamics (RBD).
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images




