A buffer solution was made by mixing 2.00 L of 1.500 M potassium nitrite with 1.00 L of 1.476 M Mitrous Ka (nitrous acid) 4.5*10-4 For all to the following questions, write your answer as a normal number to three significant figures (a) The molarity of the conjugate base in the solution at the instant of mixing is (b) The molarity of the weak acid in the solution at the instant of mixing is (c) The pH of the buffer after the mixing of the two solutions is Use the i
A buffer solution was made by mixing 2.00 L of 1.500 M potassium nitrite with 1.00 L of 1.476 M Mitrous Ka (nitrous acid) 4.5*10-4 For all to the following questions, write your answer as a normal number to three significant figures (a) The molarity of the conjugate base in the solution at the instant of mixing is (b) The molarity of the weak acid in the solution at the instant of mixing is (c) The pH of the buffer after the mixing of the two solutions is Use the i
Chapter15: Acid-base Equilibria
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13Q: An acid is titrated with NaOH. The following beakers are illustrations of the contents of the beaker...
Related questions
Question
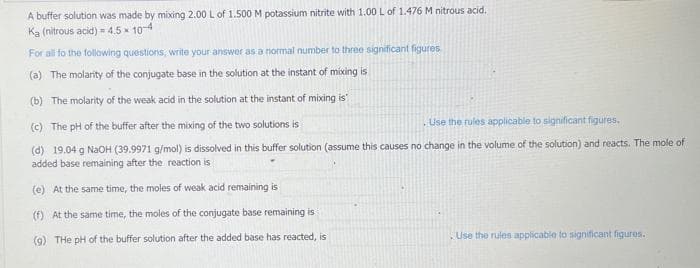
Transcribed Image Text:A buffer solution was made by mixing 2.00 L of 1.500 M potassium nitrite with 1.00 L of 1.476 M nitrous acid.
Ka (nitrous acid) = 4.5 x 10-4
For all to the following questions, write your answer as a normal number to three significant figures.
(a) The molarity of the conjugate base in the solution at the instant of mixing is
(b) The molarity of the weak acid in the solution at the instant of mixing is
(c) The pH of the buffer after the mixing of the two solutions is
Use the rules applicable to significant figures.
(d) 19.04 g NaOH (39.9971 g/mol) is dissolved in this buffer solution (assume this causes no change in the volume of the solution) and reacts. The mole of
added base remaining after the reaction is
(e) At the same time, the moles of weak acid remaining is
(f) At the same time, the moles of the conjugate base remaining is
(9) THe pH of the buffer solution after the added base has reacted, is
Use the rules applicable to significant figures.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning