(a) Calculate the following planned overhead absorption rates: (i) A machine hour rate for the Cutting Department. (ïi) A rate expressed as a direct labour cost for the Assembling Department.
(a) Calculate the following planned overhead absorption rates: (i) A machine hour rate for the Cutting Department. (ïi) A rate expressed as a direct labour cost for the Assembling Department.
Managerial Accounting
15th Edition
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Chapter5: Support Department And Joint Cost Allocation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5E: Crystal Scarves Co. produces winter scarves. The scarves are produced in the Cutting and Sewing...
Related questions
Question
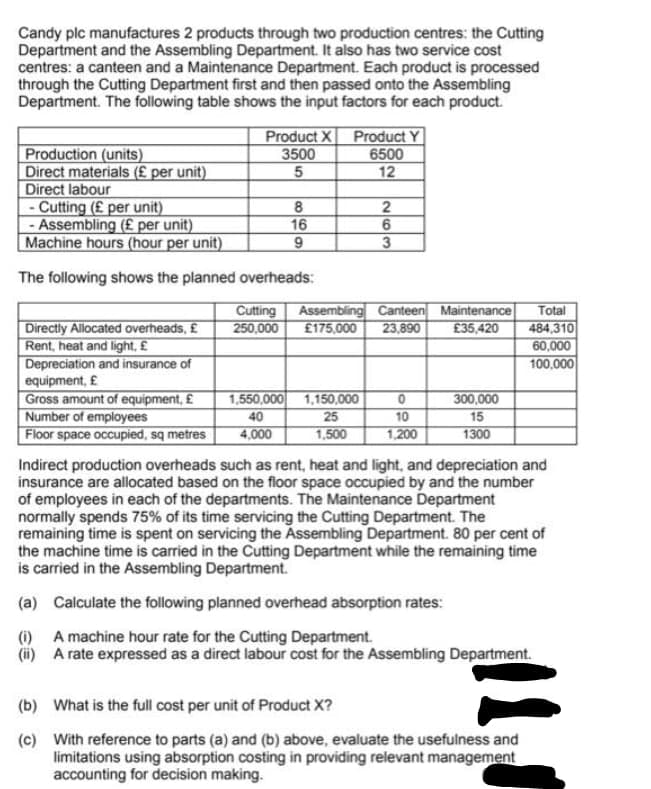
Transcribed Image Text:Candy plc manufactures 2 products through two production centres: the Cutting
Department and the Assembling Department. It also has two service cost
centres: a canteen and a Maintenance Department. Each product is processed
through the Cutting Department first and then passed onto the Assembling
Department. The following table shows the input factors for each product.
Product X
3500
Product Y
6500
12
Production (units)
Direct materials (£ per unit)
Direct labour
- Cutting (£ per unit)
- Assembling (£ per unit)
Machine hours (hour per unit)
16
The following shows the planned overheads:
Cutting
250,000
Assembling Canteen Maintenance
23,890
Total
484,310
60,000
Directly Allocated overheads, £
Rent, heat and light, £
Depreciation and insurance of
equipment, £
Gross amount of equipment, £
Number of employees
Floor space occupied, sq metres
£175,000
£35,420
100,000
1,150,000
300,000
1,550,000
40
25
10
15
4,000
1,500
1,200
1300
Indirect production overheads such as rent, heat and light, and depreciation and
insurance are allocated based on the floor space occupied by and the number
of employees in each of the departments. The Maintenance Department
normally spends 75% of its time servicing the Cutting Department. The
remaining time is spent on servicing the Assembling Department. 80 per cent of
the machine time is carried in the Cutting Department while the remaining time
is carried in the Assembling Department.
(a) Calculate the following planned overhead absorption rates:
(i) A machine hour rate for the Cutting Department.
(i) A rate expressed as a direct labour cost for the Assembling Department.
(b) What is the full cost per unit of Product X?
(c) With reference to parts (a) and (b) above, evaluate the usefulness and
limitations using absorption costing in providing relevant management
accounting for decision making.
N63
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning