A data set includes data from 500 random tornadoes. The display from technology available below results from using the tornado lengths (miles) to test the claim that the mean tornado length is greater than 22 miles Use a 0.05 significance level. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, P-value, and state the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. A Click the icon to view the display from technology. Assuming all conditions for conducting a hypothesis test are met, what are the null and alternative hypotheses? O A. Ho: u= 2.2 miles O B. Ho: u= 2.2 miles H,:u<2.2 miles H,: u> 2.2 miles OC. Ho: u= 2.2 miles O D. Ho: u<2.2 miles H,:u= 2.2 miles H,:u#2.2 miles Identify the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Identify the P-value. (Round three decimal places as needed.) State the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. Ho. There is V evidence to support the claim that the mean tomado length is greater than 2.2 miles Fail to reject Reject
A data set includes data from 500 random tornadoes. The display from technology available below results from using the tornado lengths (miles) to test the claim that the mean tornado length is greater than 22 miles Use a 0.05 significance level. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, P-value, and state the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. A Click the icon to view the display from technology. Assuming all conditions for conducting a hypothesis test are met, what are the null and alternative hypotheses? O A. Ho: u= 2.2 miles O B. Ho: u= 2.2 miles H,:u<2.2 miles H,: u> 2.2 miles OC. Ho: u= 2.2 miles O D. Ho: u<2.2 miles H,:u= 2.2 miles H,:u#2.2 miles Identify the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Identify the P-value. (Round three decimal places as needed.) State the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. Ho. There is V evidence to support the claim that the mean tomado length is greater than 2.2 miles Fail to reject Reject
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.5: Comparing Sets Of Data
Problem 3BGP
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
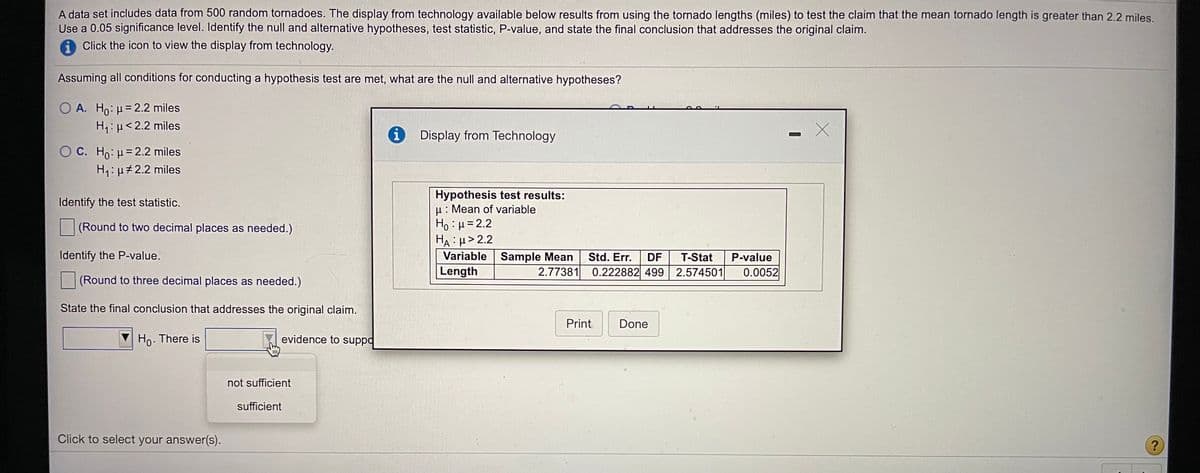
Transcribed Image Text:A data set includes data from 500 random tornadoes. The display from technology available below results from using the tornado lengths (miles) to test the claim that the mean tornado length is greater than 2.2 miles.
Use a 0.05 significance level. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, P-value, and state the final conclusion that addresses the original claim.
Click the icon to view the display from technology.
Assuming all conditions for conducting a hypothesis test are met, what are the null and alternative hypotheses?
O A. Ho:H=2.2 miles
H,:p<2.2 miles
i Display from Technology
C. Ho: H= 2.2 miles
H1: μ+2.2 miles
Hypothesis test results:
u: Mean of variable
Ho:=2.2
HA:H> 2.2
Variable Sample Mean
Length
Identify the test statistic.
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Identify the P-value.
Std. Err.
DF
T-Stat
P-value
2.77381 0.222882 499 2.574501
0.0052
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
State the final conclusion that addresses the original claim.
Print
Done
Ho. There is
evidence to suppo
not sufficient
sufficient
Click to select your answer(s).
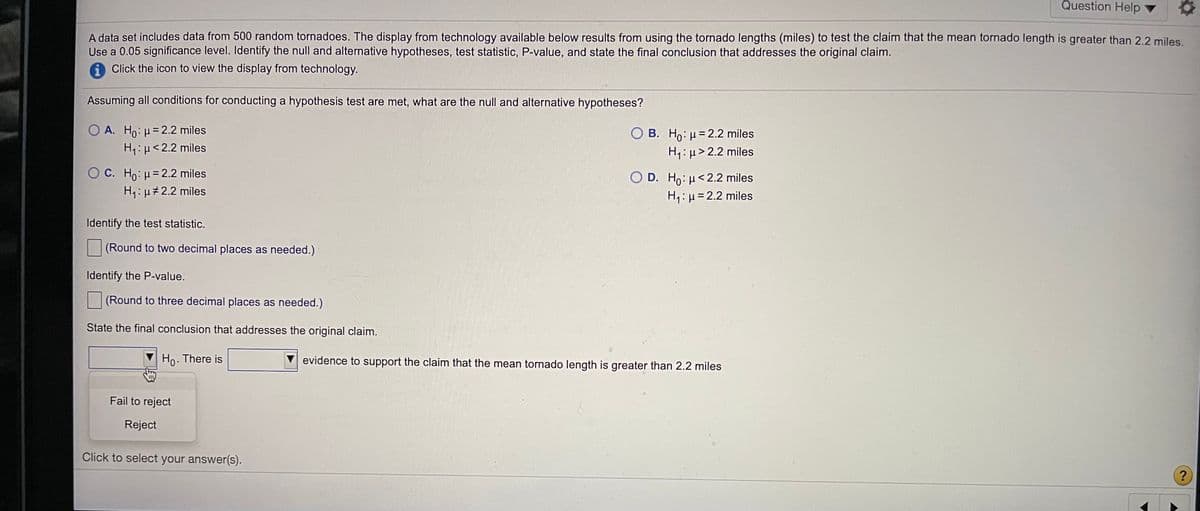
Transcribed Image Text:Question Help ▼
A data set includes data from 500 random tornadoes. The display from technology available below results from using the tornado lengths (miles) to test the claim that the mean tornado length is greater than 2.2 miles
Use a 0.05 significance level. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, P-value, and state the final conclusion that addresses the original claim.
Click the icon to view the display from technology.
Assuming all conditions for conducting a hypothesis test are met, what are the null and alternative hypotheses?
O A. Ho: u=2.2 miles
B. Ho: µ= 2.2 miles
H4: µ> 2.2 miles
H:µ<2.2 miles
O C. Ho: = 2.2 miles
H,: µ#2.2 miles
O D. Ho: µ<2.2 miles
H1: µ= 2.2 miles
Identify the test statistic.
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Identify the P-value.
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
State the final conclusion that addresses the original claim.
Ho. There is
evidence to support the claim that the mean tornado length is greater than 2.2 miles
Fail to reject
Reject
Click to select your answer(s).
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning