A galvanic cell consists of one half-cell that contains Ag( s) and Ag *(aq), and one half-cell that contains Pb( s) and Pb 2+( aq). What species are produced at the electrodes under standard conditions? Ag (aq) + e→ Ag( s) E = +0.80 V Pb 2+(aq) + 2 e Pb( s) E = -0.13 V O Pb2+(ag) is formed at the cathode, and Cu(s) is formed at the anode. O Ag(ag) is formed at the cathode and, Pb(s) is formed at the anode. Pb(s) is formed at the cathode, and Ag*(ag) is formed at the anode. Ag(s) is formed at the cathode, and Pb2+(aq) is formed at the anode.
A galvanic cell consists of one half-cell that contains Ag( s) and Ag *(aq), and one half-cell that contains Pb( s) and Pb 2+( aq). What species are produced at the electrodes under standard conditions? Ag (aq) + e→ Ag( s) E = +0.80 V Pb 2+(aq) + 2 e Pb( s) E = -0.13 V O Pb2+(ag) is formed at the cathode, and Cu(s) is formed at the anode. O Ag(ag) is formed at the cathode and, Pb(s) is formed at the anode. Pb(s) is formed at the cathode, and Ag*(ag) is formed at the anode. Ag(s) is formed at the cathode, and Pb2+(aq) is formed at the anode.
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter19: Principles Of Chemical Reactivity: Electron Transfer Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 84GQ
Related questions
Question
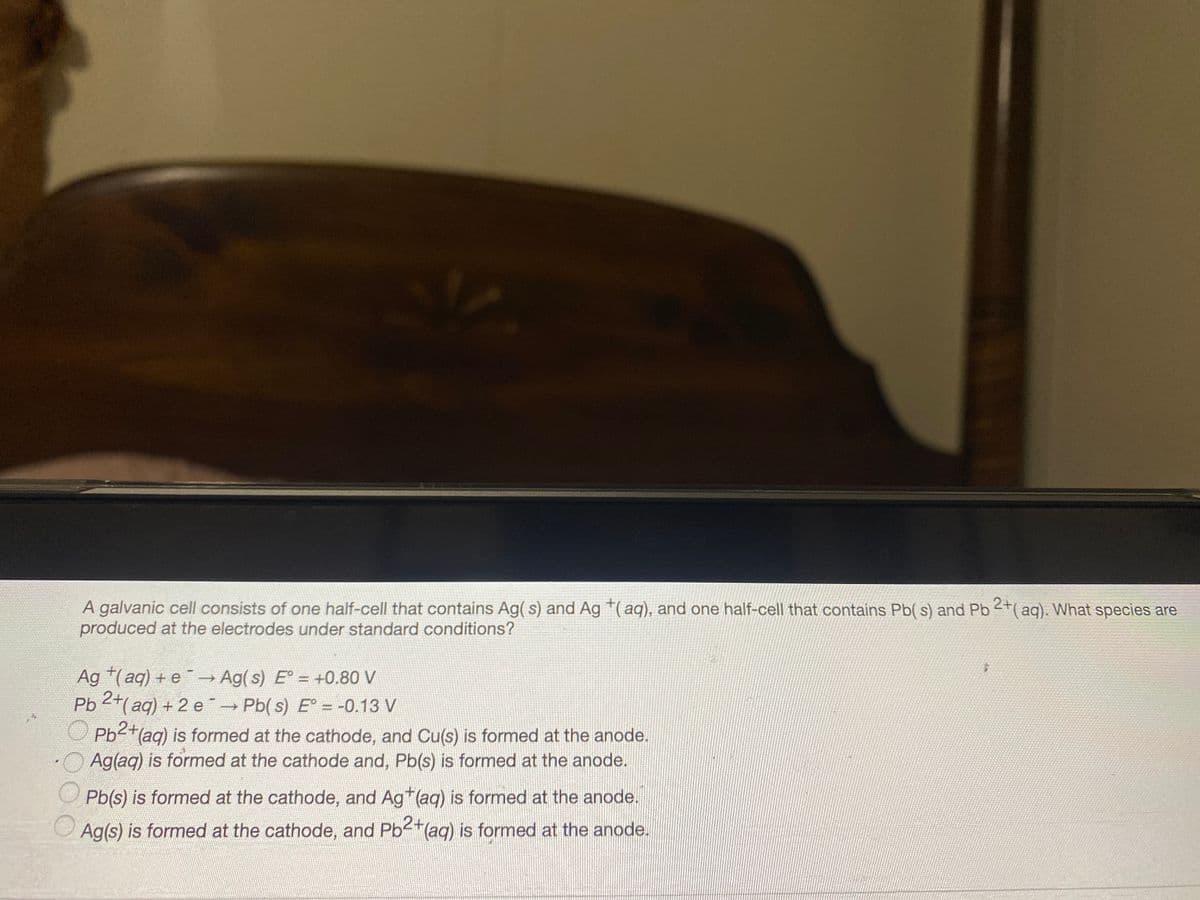
Transcribed Image Text:A galvanic cell consists of one half-cell that contains Ag( s) and Ag (aq), and one half-cell that contains Pb( s) and Pb 2+( aq). What species are
produced at the electrodes under standard conditions?
Ag (aq) + e-→ Ag(s) E° = +0.80 V
Pb 2+(aq) + 2 e
→ Pb( s) E° = -0.13 V
Pb²+(aq) is formed at the cathode, and Cu(s) is formed at the anode.
Ag(aq) is formed at the cathode and, Pb(s) is formed at the anode.
Pb(s) is formed at the cathode, and Ag (ag) is formed at the anode.
Ag(s) is formed at the cathode, and Pb2+(aq) is formed at the anode.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning