A geneticist is using a three-point testcross to map three linked Drosophila recessive mutations called a, b, and c, where a is associated with anomalous gait, b is associated with buckled wings, and c is associated with curved bristles. She first crosses homozygous anomalous, buckled flies to homozygous curved flies. Next, she testcrosses the F1 progeny to anomalous, buckled, curved flies. She obtains 1000 progeny distributed as shown. From this data, calculate the map distance between b and c. Testcross progeny phenotype Number curved 281 map distance: m. u. anomalous, buckled 279 wild type 4 anamalous, buckled, curved buckled, curved 128 anomalous 132 anomalous, curved 83 buckled 87
A geneticist is using a three-point testcross to map three linked Drosophila recessive mutations called a, b, and c, where a is associated with anomalous gait, b is associated with buckled wings, and c is associated with curved bristles. She first crosses homozygous anomalous, buckled flies to homozygous curved flies. Next, she testcrosses the F1 progeny to anomalous, buckled, curved flies. She obtains 1000 progeny distributed as shown. From this data, calculate the map distance between b and c. Testcross progeny phenotype Number curved 281 map distance: m. u. anomalous, buckled 279 wild type 4 anamalous, buckled, curved buckled, curved 128 anomalous 132 anomalous, curved 83 buckled 87
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Chapter20: Chromosomes And Human Genetics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7CT: The following pedigree shows the pattern of inheritance of red-green color blindness in a family....
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
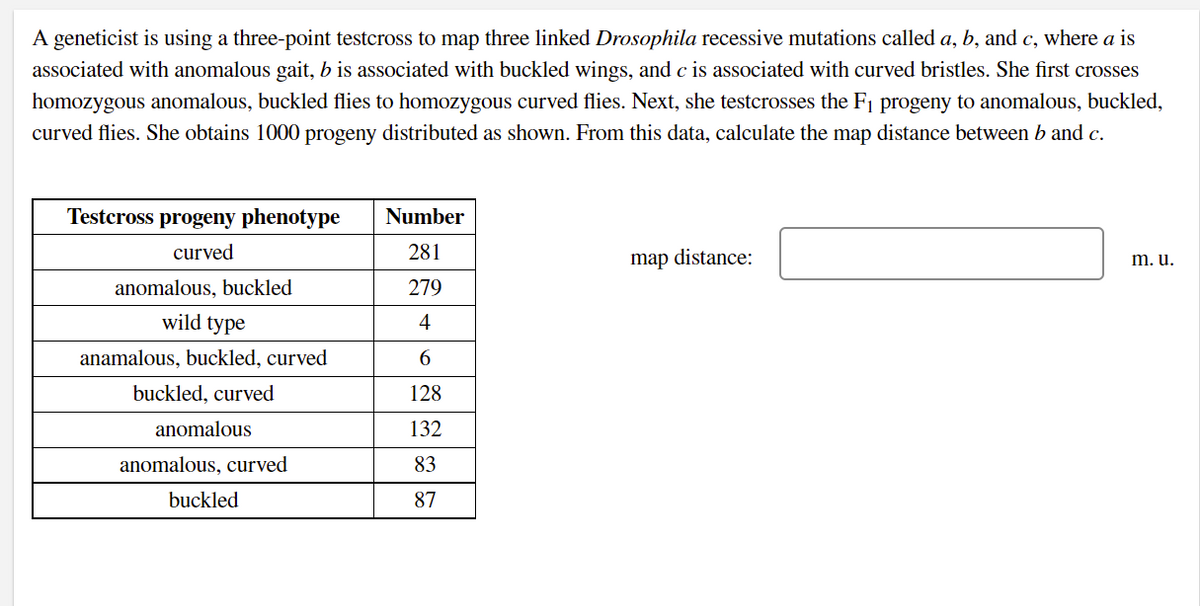
Transcribed Image Text:A geneticist is using a three-point testcross to map three linked Drosophila recessive mutations called a, b, and c, where a is
associated with anomalous gait, b is associated with buckled wings, and c is associated with curved bristles. She first crosses
homozygous anomalous, buckled flies to homozygous curved flies. Next, she testcrosses the F1 progeny to anomalous, buckled,
curved flies. She obtains 1000 progeny distributed as shown. From this data, calculate the map distance between b and c.
Testcross progeny phenotype
Number
curved
281
map distance:
m. u.
anomalous, buckled
279
wild type
4
anamalous, buckled, curved
buckled, curved
128
anomalous
132
anomalous, curved
83
buckled
87
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305112100
Author:
Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305112100
Author:
Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning