A political pollster is conducting an analysis of sample results in order to make predictions on election night. Assuming a two-candidate election, if a specific candidate receives at least 55% of the vole in the samble that candidate will be forecast as the winner of the election. You select a random sample of 100 voters. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. a. What is the probability that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 50.1%? The probability is that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 50.1%. (Round to four decimal places as needed.) b. What is the probability that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 60%? that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 60%. The probability is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) What is the probability that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 49% (and she will actually lose the election)? C. that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 49% I nlaces as needed.) The probability is this new sample size. Comment on the difference
A political pollster is conducting an analysis of sample results in order to make predictions on election night. Assuming a two-candidate election, if a specific candidate receives at least 55% of the vole in the samble that candidate will be forecast as the winner of the election. You select a random sample of 100 voters. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. a. What is the probability that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 50.1%? The probability is that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 50.1%. (Round to four decimal places as needed.) b. What is the probability that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 60%? that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 60%. The probability is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) What is the probability that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 49% (and she will actually lose the election)? C. that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 49% I nlaces as needed.) The probability is this new sample size. Comment on the difference
Chapter8: Sequences, Series,and Probability
Section8.7: Probability
Problem 50E: Flexible Work Hours In a recent survey, people were asked whether they would prefer to work flexible...
Related questions
Question
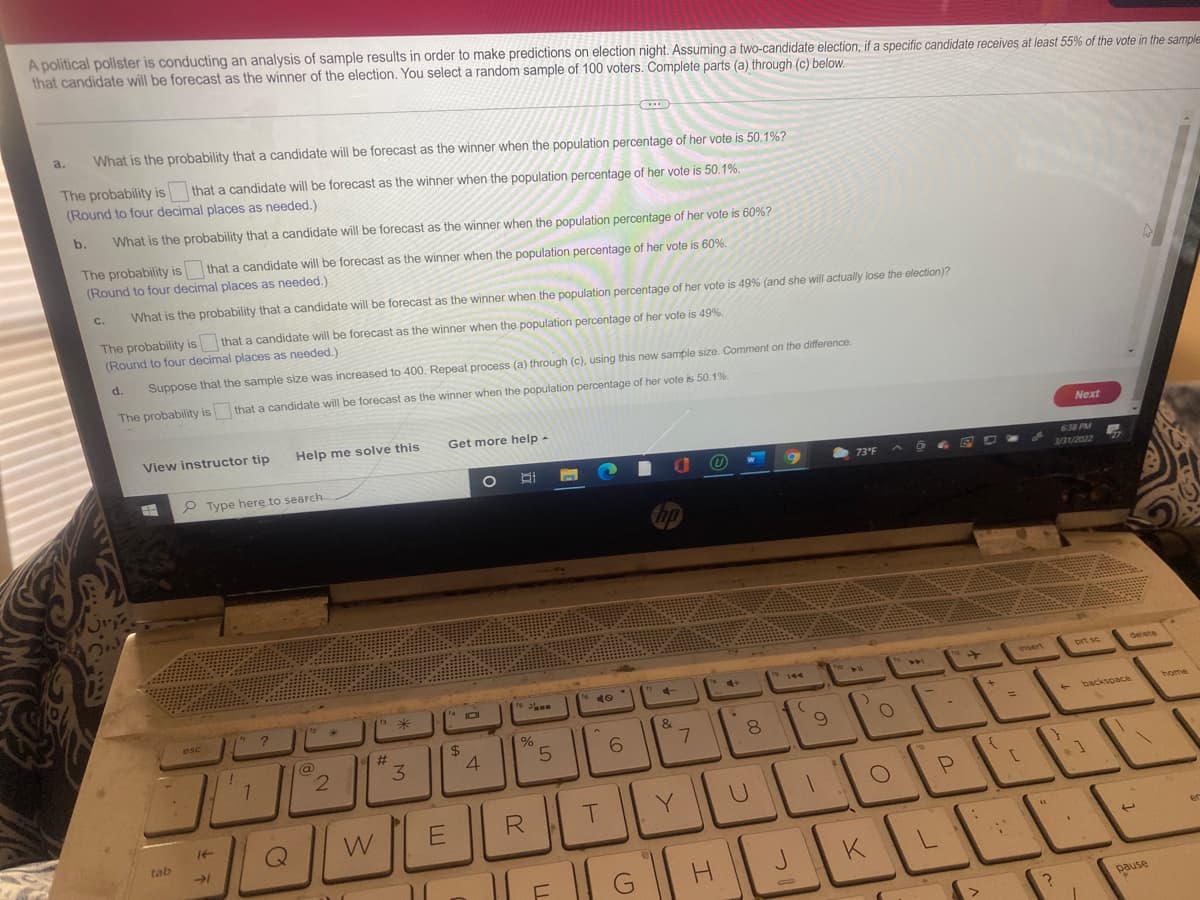
Transcribed Image Text:A political pollster is conducting an analysis of sample results in order to make predictions on election night. Assuming a two-candidate election, if a specific candidate receives at least 55% of the vote in the sample
that candidate will be forecast as the winner of the election. You select a random sample of 100 voters. Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
a.
What is the probability that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 50.1%?
The probability is
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
that a candidate will be forecast as the wihner when the population percentage of her vote is 50.1%.
b.
What is the probability that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 60%?
The probability is that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 60%.
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
C.
What is the probability that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 49% (and she will actually lose the election)?
The probability is that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 49%.
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
d.
Suppose that the sample size was increased to 400. Repeat process (a) through (c), using this new sample size. Comment on the difference.
The probability is that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 50.1%.
View instructor tip
Help me solve this
Get more help -
Next
638 PM
P Type here to search
1O
73°F
3/31/2022
hp
prt sc
delete
insert
144
44
40
esc
home
&
backspace
6.
2$
4
%23
6.
3
W
R
tab
Q
J
K
pause
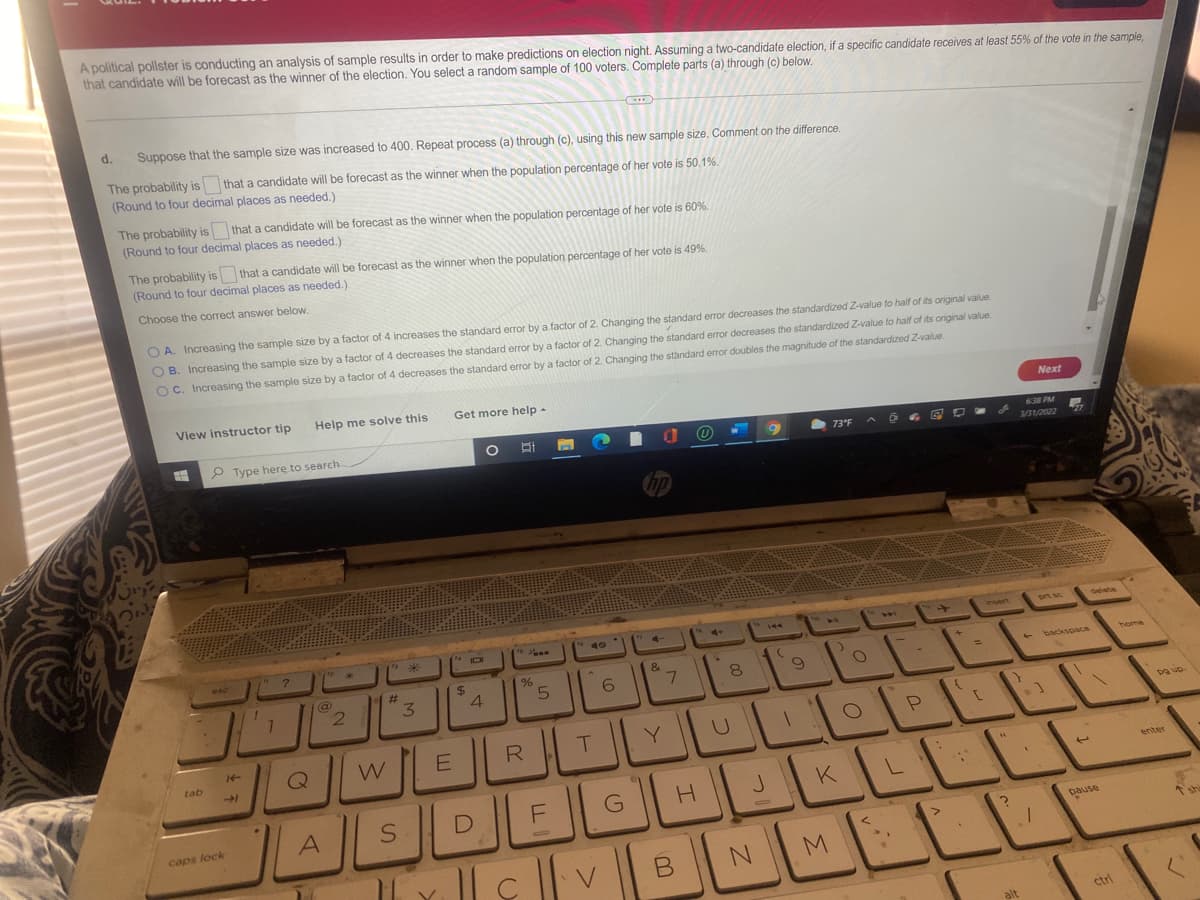
Transcribed Image Text:A political pollster is conducting an analysis of sample results in order to make predictions on election night. Assuming a two-candidate election, if a specific candidate receives at least 55% of the vote in the sample,
that candidate will be forecast as the winner of the election. You select a random sample of 100 voters. Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
d.
Suppose that the sample size was increased to 400. Repeat process (a) through (c), using this new sample size. Comment on the difference.
The probability is that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 50.1%.
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
The probability is that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 60%.
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
The probability is that a candidate will be forecast as the winner when the population percentage of her vote is 49%.
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
Choose the correct answer below.
O A. Increasing the sample size by a factor of 4 increases the standard error by a factor of 2. Changing the standard error decreases the standardized Z-value to half of its original value
OB. Increasing the sample size by a factor of 4 decreases the standard error by a factor of 2. Changing the standard error decreases the standardized Z-value to haif of its original value
OC. Increasing the sample size by a factor of 4 decreases the standard error by a factor of 2. Changing the standard error doubles the magnitude of the standardized Z-value.
View instructor tip
Help me solve this
Get more help -
Next
P Type here to search
73°F
638 PM
1/31/2022
27
hp
4+
prt sc
deleta
144
40
insert
144
esc
LL
%24
&
#3
3
backspace
home
7.
8
2.
ER
Y
an Bd
tab
Q
enter
K
caps lock
pause
shi
M.
alt
ctrl
4,
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you


Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning