An Introduction to Physical Science
14th Edition
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Chapter15: Place And Time
Section15.3: Time
Problem 1PQ
Related questions
Question
Each object is composed of identical thin sticks of uniformly distributed mass 4.47 kg and length 0.489 m. What are the moments of inertia ?A , ?B , ?C , and ?D of the objects about a rotation axis perpendicular to the screen and passing through the black dot displayed on each object?
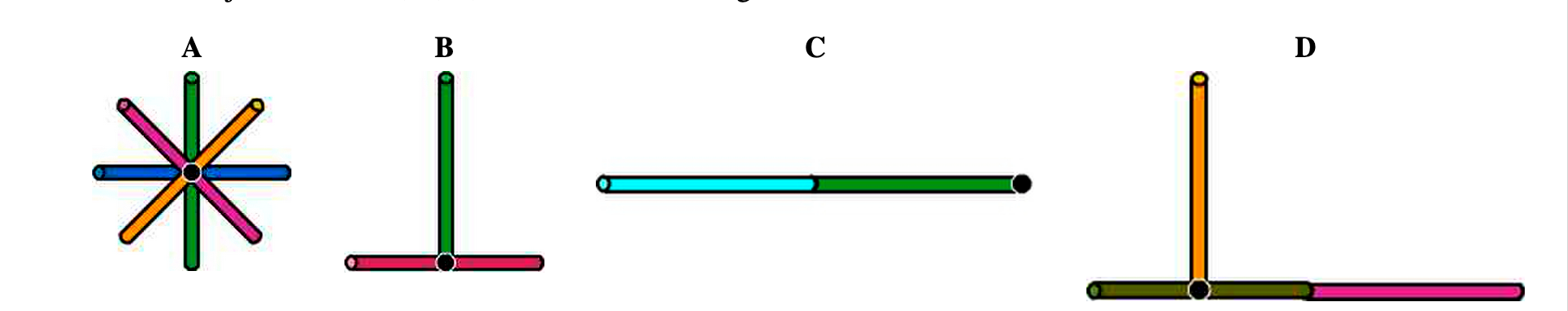
Transcribed Image Text:A
В
C
D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:
9781305079137
Author:
James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:
9781305079137
Author:
James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning