A very flexible helium-filled balloon is released from the ground into the air at 20. °C. The initial volume of the balloon is 5.00 L, and the pressure is 760. mmHg. The balloon ascends to an altitude of 20 km, where the pressure is 76.0 mmHg and the temperature is -50. °Č. What is the new volume, V2, of the balloon in liters, assuming it doesn't break or leak?
A very flexible helium-filled balloon is released from the ground into the air at 20. °C. The initial volume of the balloon is 5.00 L, and the pressure is 760. mmHg. The balloon ascends to an altitude of 20 km, where the pressure is 76.0 mmHg and the temperature is -50. °Č. What is the new volume, V2, of the balloon in liters, assuming it doesn't break or leak?
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
11th Edition
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Chapter5: Gases, Liquids, And Solids
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5.114P: 5-114 Carbon dioxide gas, saturated with water vapor, can be produced by the addition of aqueous...
Related questions
Question
100%
Transcribed Image Text:Item 5
5 of 16
>
I Review I Constants I Periodic Table
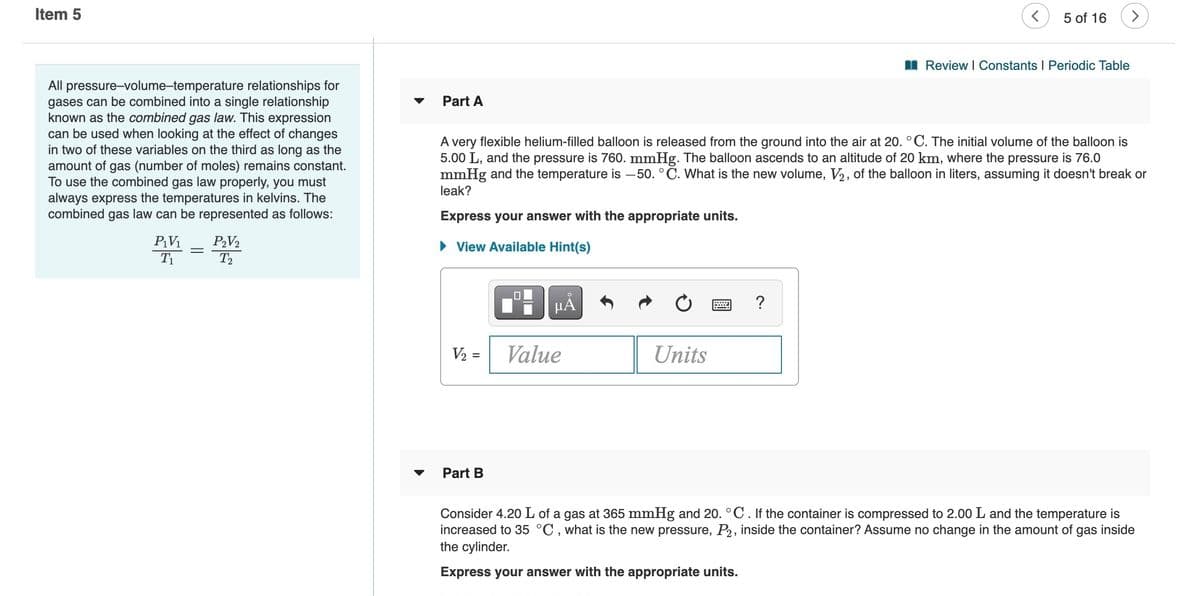
All pressure-volume-temperature relationships for
gases can be combined into a single relationship
known as the combined gas law. This expression
can be used when looking at the effect of changes
in two of these variables on the third as long as the
amount of gas (number of moles) remains constant.
To use the combined gas law properly, you must
always express the temperatures in kelvins. The
combined gas law can be represented as follows:
Part A
A very flexible helium-filled balloon is released from the ground into the air at 20. °C. The initial volume of the balloon is
5.00 L, and the pressure is 760. mmHg. The balloon ascends to an altitude of 20 km, where the pressure is 76.0
mmHg and the temperature is -50. °C. What is the new volume, V2, of the balloon in liters, assuming it doesn't break or
leak?
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
P2V2
T2
PV1
• View Available Hint(s)
T1
V2 =
Value
Units
Part B
Consider 4.20 L of a gas at 365 mmHg and 20. °C. If the container is compressed to 2.00 L and the temperature is
increased to 35 °C , what is the new pressure, P2, inside the container? Assume no change in the amount of gas inside
the cylinder.
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
Transcribed Image Text:Item 5
5 of 16
>
I Review I Constants I Periodic Table
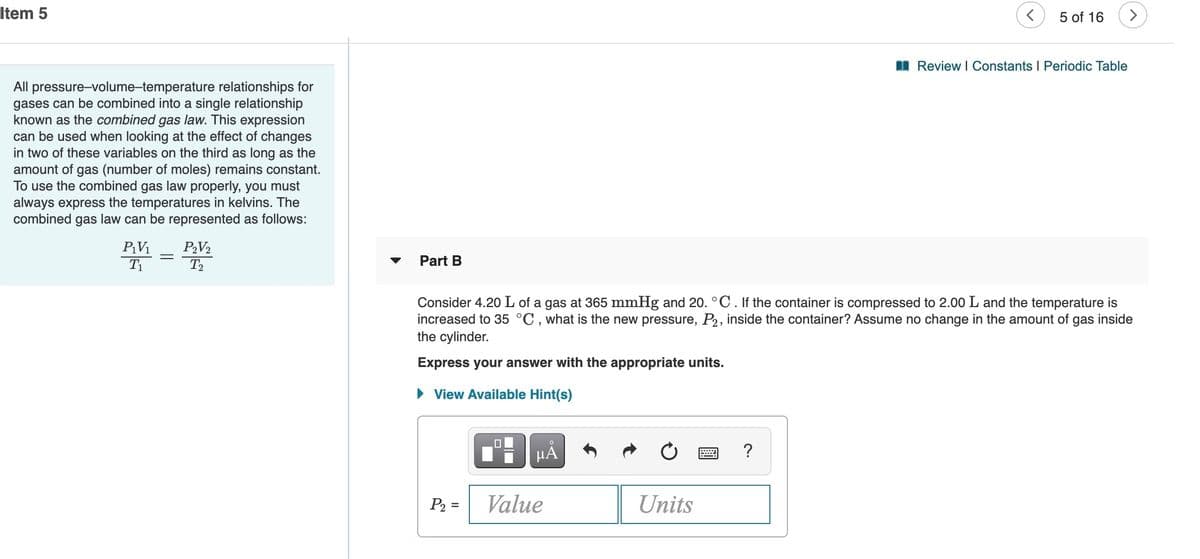
All pressure-volume-temperature relationships for
gases can be combined into a single relationship
known as the combined gas law. This expression
can be used when looking at the effect of changes
in two of these variables on the third as long as the
amount of gas (number of moles) remains constant.
To use the combined gas law properly, you must
always express the temperatures in kelvins. The
combined gas law can be represented as follows:
PV1
PV2
T2
T1
Part B
Consider 4.20 L of a gas at 365 mmHg and 20. °C. If the container is compressed to 2.00 L and the temperature is
increased to 35 °C , what is the new pressure, P2, inside the container? Assume no change in the amount of gas inside
the cylinder.
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
• View Available Hint(s)
μΑ
P2 =
Value
Units
%3D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285869759
Author:
Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285869759
Author:
Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133109655
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285853918
Author:
H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co