An experiment was conducted to determine whether giving candy to dining parties resulted in greater tips. The mean tip percentages and standard deviations are given in the accompanying table along with the sample sizes. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations, and do not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Complete parts (a) and (b). O A. Ho: H1 =H2 H: >H2 C. Ho: H =H2 The test statistic, t, is (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The P-value is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) State the conclusion for the test. A. Reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that giving candy does result in grea O B. Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that giving candy does result in greater C. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that giving candy does result D. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that giving candy does result in gi b. Construct the confidence interval suitable for testing the claim in part (a). (Round to two decimal places as needed.) clusion found with the hypothesis test?
An experiment was conducted to determine whether giving candy to dining parties resulted in greater tips. The mean tip percentages and standard deviations are given in the accompanying table along with the sample sizes. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations, and do not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Complete parts (a) and (b). O A. Ho: H1 =H2 H: >H2 C. Ho: H =H2 The test statistic, t, is (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The P-value is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) State the conclusion for the test. A. Reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that giving candy does result in grea O B. Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that giving candy does result in greater C. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that giving candy does result D. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that giving candy does result in gi b. Construct the confidence interval suitable for testing the claim in part (a). (Round to two decimal places as needed.) clusion found with the hypothesis test?
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.4: Distributions Of Data
Problem 19PFA
Related questions
Question
practice questions***
first 3 questions plz
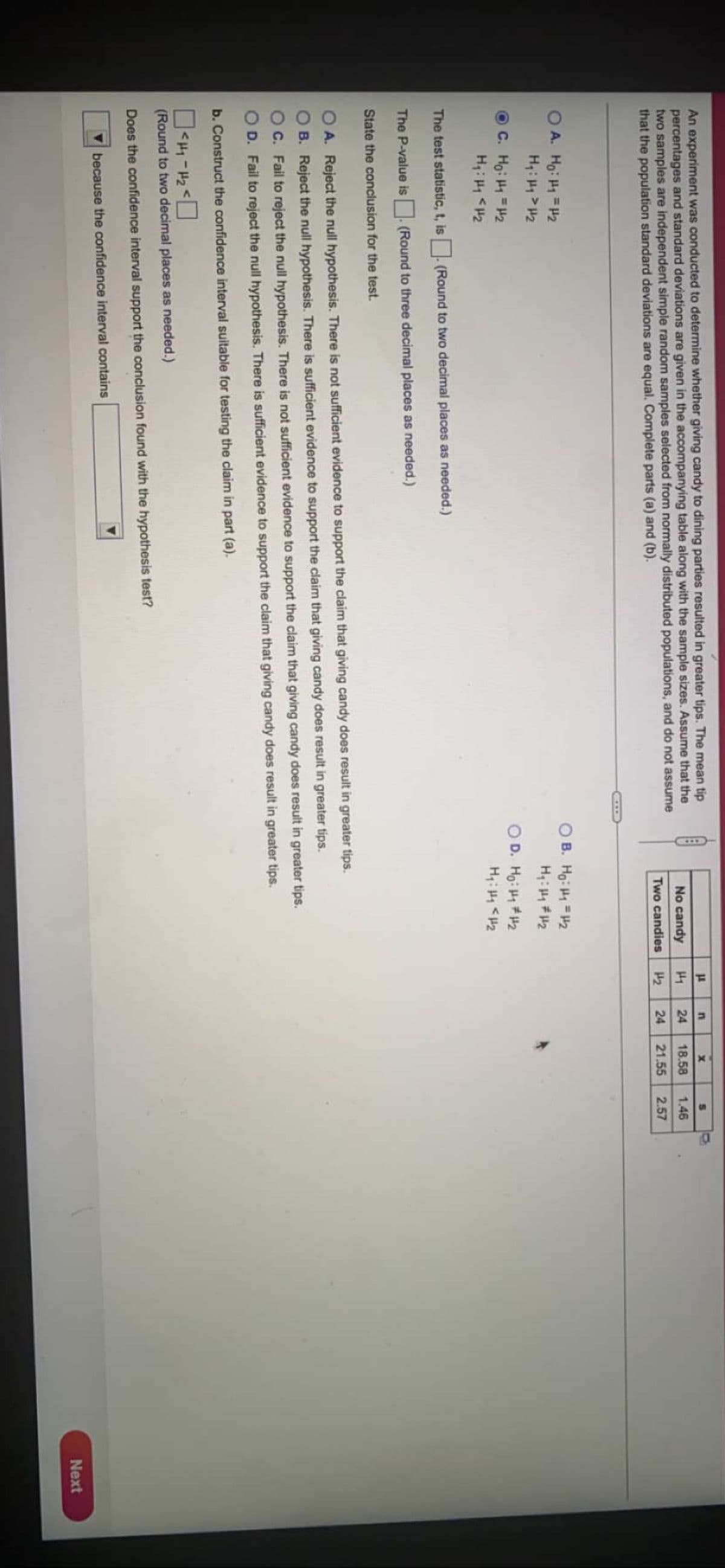
Transcribed Image Text:An experiment was conducted to determine whether giving candy to dining parties resulted in greater tips. The mean tip
percentages and standard deviations are given in the accompanying table along with the sample sizes. Assume that the
two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations, and do not assume
that the population standard deviations are equal. Complete parts (a) and (b).
No candy
24
18.58
1.46
Two candies
H2
24
21.55
2.57
A. Ho: H1 =H2
O B. Ho: H1 = 2
C. Hg: H = 2
O D. Ho: H H2
The test statistic, t, is (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
The P-value is (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
State the conclusion for the test.
A. Reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that giving candy does result in greater tips.
B. Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that giving candy does result in greater tips.
C. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that giving candy does result in greater tips.
D. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that giving candy does result in greater tips.
b. Construct the confidence interval suitable for testing the claim in part (a).
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Does the confidence interval support the conclusion found with the hypothesis test?
because the confidence interval contains
Next
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill