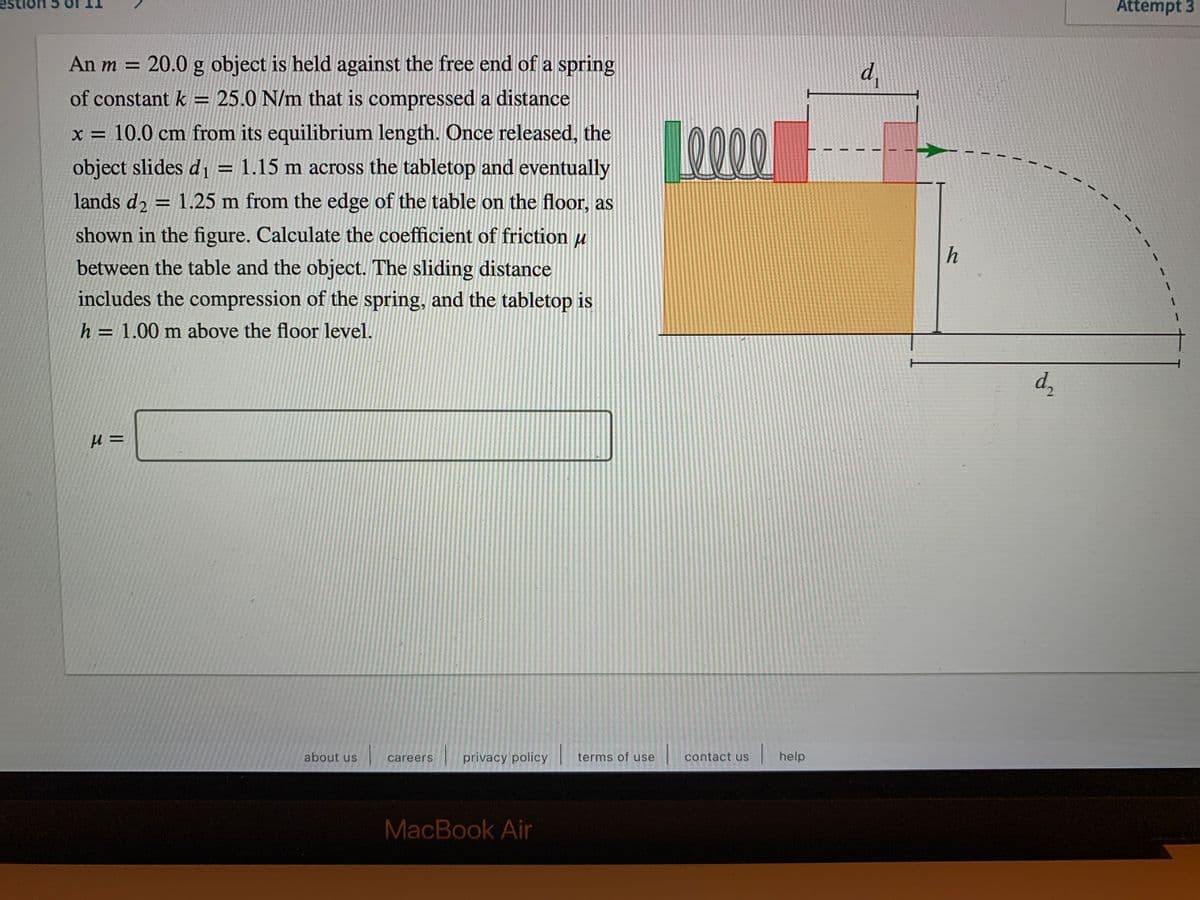
An m = 20.0 g object is held against the free end of a spring of constant k = 25.0 N/m that is compressed a distance LO00 x = 10.0 cm from its equilibrium length. Once released, the object slides d1 = 1.15 m across the tabletop and eventually lands d, = 1.25 m from the edge of the table on the floor, as shown in the figure. Calculate the coefficient of friction µ between the table and the object. The sliding distance includes the compression of the spring, and the tabletop is h h = 1.00 m above the floor level.
An m = 20.0 g object is held against the free end of a spring of constant k = 25.0 N/m that is compressed a distance LO00 x = 10.0 cm from its equilibrium length. Once released, the object slides d1 = 1.15 m across the tabletop and eventually lands d, = 1.25 m from the edge of the table on the floor, as shown in the figure. Calculate the coefficient of friction µ between the table and the object. The sliding distance includes the compression of the spring, and the tabletop is h h = 1.00 m above the floor level.
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter12: Oscillatory Motion
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 21P: A 50.0-g object connected to a spring with a force constant of 35.0 N/m oscillates with an amplitude...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Attempt 3
An m = 20.0 g object is held against the free end of a spring
d,
of constant k = 25.0 N/m that is compressed a distance
LO000
x = 10.0 cm from its equilibrium length. Once released, the
object slides d, = 1.15 m across the tabletop and eventually
%3D
lands d2 = 1.25 m from the edge of the table on the floor, as
%3D
shown in the figure. Calculate the coefficient of friction u
h
between the table and the object. The sliding distance
includes the compression of the spring, and the tabletop is
h = 1.00 m above the floor level.
%3D
d,
about us
privacy policy
terms of use
|help
careers
contact us
MacBook Air
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill