At -5.92 °C the pressure equilibrium constant K = 5.9 for a certain reaction. P Here are some facts about the reaction: • If the reaction is run at constant pressure, 127. kJ/mol of heat are released. • The constant pressure molar heat capacity C • The net change in moles of gases is -1. = 2.41 J mol -1. K¹. -1 р Yes. ☐ x10 Using these facts, can you calculate K at -27. °C? ○ No. If you said yes, then enter your answer at right. Round it to 2 significant digits. Р If you said no, can you at least decide whether K at -27. °C will be bigger or smaller than K, at −5.92 °C? П Yes, and K, will be р bigger. Yes, and K smaller. will be No. ☑
At -5.92 °C the pressure equilibrium constant K = 5.9 for a certain reaction. P Here are some facts about the reaction: • If the reaction is run at constant pressure, 127. kJ/mol of heat are released. • The constant pressure molar heat capacity C • The net change in moles of gases is -1. = 2.41 J mol -1. K¹. -1 р Yes. ☐ x10 Using these facts, can you calculate K at -27. °C? ○ No. If you said yes, then enter your answer at right. Round it to 2 significant digits. Р If you said no, can you at least decide whether K at -27. °C will be bigger or smaller than K, at −5.92 °C? П Yes, and K, will be р bigger. Yes, and K smaller. will be No. ☑
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Chapter16: Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 48E: At mom temperature, the equilibrium constant (Kw) for the self-ionization of water is 1.001014....
Related questions
Question
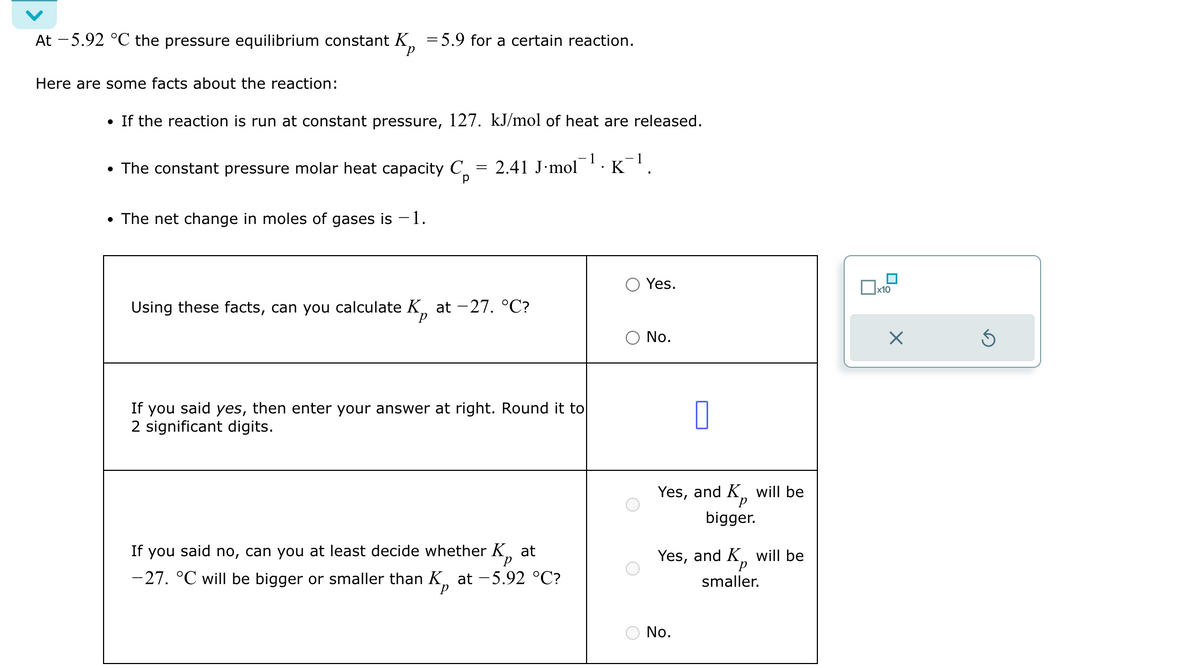
Transcribed Image Text:At -5.92 °C the pressure equilibrium constant K = 5.9 for a certain reaction.
P
Here are some facts about the reaction:
• If the reaction is run at constant pressure, 127. kJ/mol of heat are released.
• The constant pressure molar heat capacity C
• The net change in moles of gases is -1.
= 2.41 J mol
-1.
K¹.
-1
р
Yes.
☐ x10
Using these facts, can you calculate K at -27. °C?
○ No.
If you said yes, then enter your answer at right. Round it to
2 significant digits.
Р
If you said no, can you at least decide whether K at
-27. °C will be bigger or smaller than K, at −5.92 °C?
П
Yes, and K, will be
р
bigger.
Yes, and K
smaller.
will be
No.
☑
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning