At a potential of -1.0 V (versus SCE), carbon tetrachloride in methanol is reduced to chloroform at a Hg cathode: 2CCl4 + 2H+ + 2e + 2Hg (1) ⇒ 2CHCl3 + Hg2 Cl₂ (8) At -1.80 V, the chloroform further reacts to give methane: 2CHCl3 + 8H+ + Be + 6Hg(1)→ 2CH4 + 3Hg2Cl₂ (8) Several 0.850-g samples containing CC14, CHCl3, and inert organic species were dissolved in methanol and electrolyzed at -1.0 V until the current approached zero. A coulometer indicated the charge required to complete the reaction, as given in the second column of the following table. The potential of the cathode was then adjusted to -1.80 V. The additional charge required to complete the reaction at this potential is given in the third column of the table. Calculate the percent CCl4 and CHCI 3 in each mixture.
At a potential of -1.0 V (versus SCE), carbon tetrachloride in methanol is reduced to chloroform at a Hg cathode: 2CCl4 + 2H+ + 2e + 2Hg (1) ⇒ 2CHCl3 + Hg2 Cl₂ (8) At -1.80 V, the chloroform further reacts to give methane: 2CHCl3 + 8H+ + Be + 6Hg(1)→ 2CH4 + 3Hg2Cl₂ (8) Several 0.850-g samples containing CC14, CHCl3, and inert organic species were dissolved in methanol and electrolyzed at -1.0 V until the current approached zero. A coulometer indicated the charge required to complete the reaction, as given in the second column of the following table. The potential of the cathode was then adjusted to -1.80 V. The additional charge required to complete the reaction at this potential is given in the third column of the table. Calculate the percent CCl4 and CHCI 3 in each mixture.
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Chapter24: Coulometry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 24.8QAP
Related questions
Question
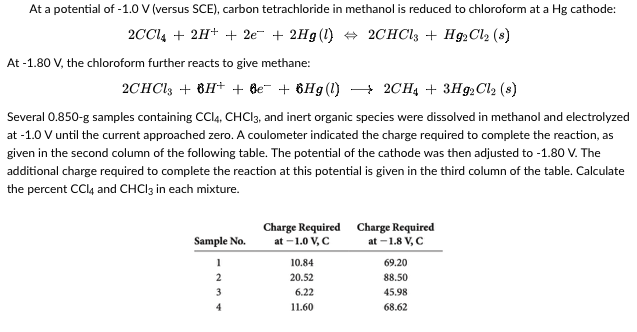
Transcribed Image Text:At a potential of -1.0 V (versus SCE), carbon tetrachloride in methanol is reduced to chloroform at a Hg cathode:
2CCl4 + 2H+ + 2e + 2Hg (1) ⇒ 2CHCl3 + H2Cl₂ (8)
At -1.80 V, the chloroform further reacts to give methane:
2CHCl3 + 8H+ + Be + 6Hg(1)→2CH4 +3Hg2 Cl₂ (8)
Several 0.850-g samples containing CC14, CHCI3, and inert organic species were dissolved in methanol and electrolyzed
at -1.0 V until the current approached zero. A coulometer indicated the charge required to complete the reaction, as
given in the second column of the following table. The potential of the cathode was then adjusted to -1.80 V. The
additional charge required to complete the reaction at this potential is given in the third column of the table. Calculate
the percent CCl4 and CHCl3 in each mixture.
Charge Required
at -1.0 V, C
Charge Required
at -1.8 V, C
Sample No.
1
10.84
69.20
2
20.52
88.50
3
6.22
45.98
4
11.60
68.62
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning