(b) the activity of the malate-aspartate shuttle (MAS) system of isolated rat brain mitochondria suspended in an isotonic me- dium buffered to pH 7.4. Diagram A illustrates NADH fluo- rescence emission upon addition of Glutamate in the ab- sence and presence of Aspartate. Diagram B illustrates sim- ilarly NADH fluorescence emission upon addition of Gluta- mate in the presence of Aspartate followed by additions of Diagrams A and B on the right show changes in
(b) the activity of the malate-aspartate shuttle (MAS) system of isolated rat brain mitochondria suspended in an isotonic me- dium buffered to pH 7.4. Diagram A illustrates NADH fluo- rescence emission upon addition of Glutamate in the ab- sence and presence of Aspartate. Diagram B illustrates sim- ilarly NADH fluorescence emission upon addition of Gluta- mate in the presence of Aspartate followed by additions of Diagrams A and B on the right show changes in
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Chapter6: Energy, Enzymes, And Biological Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1ITD
Related questions
Question
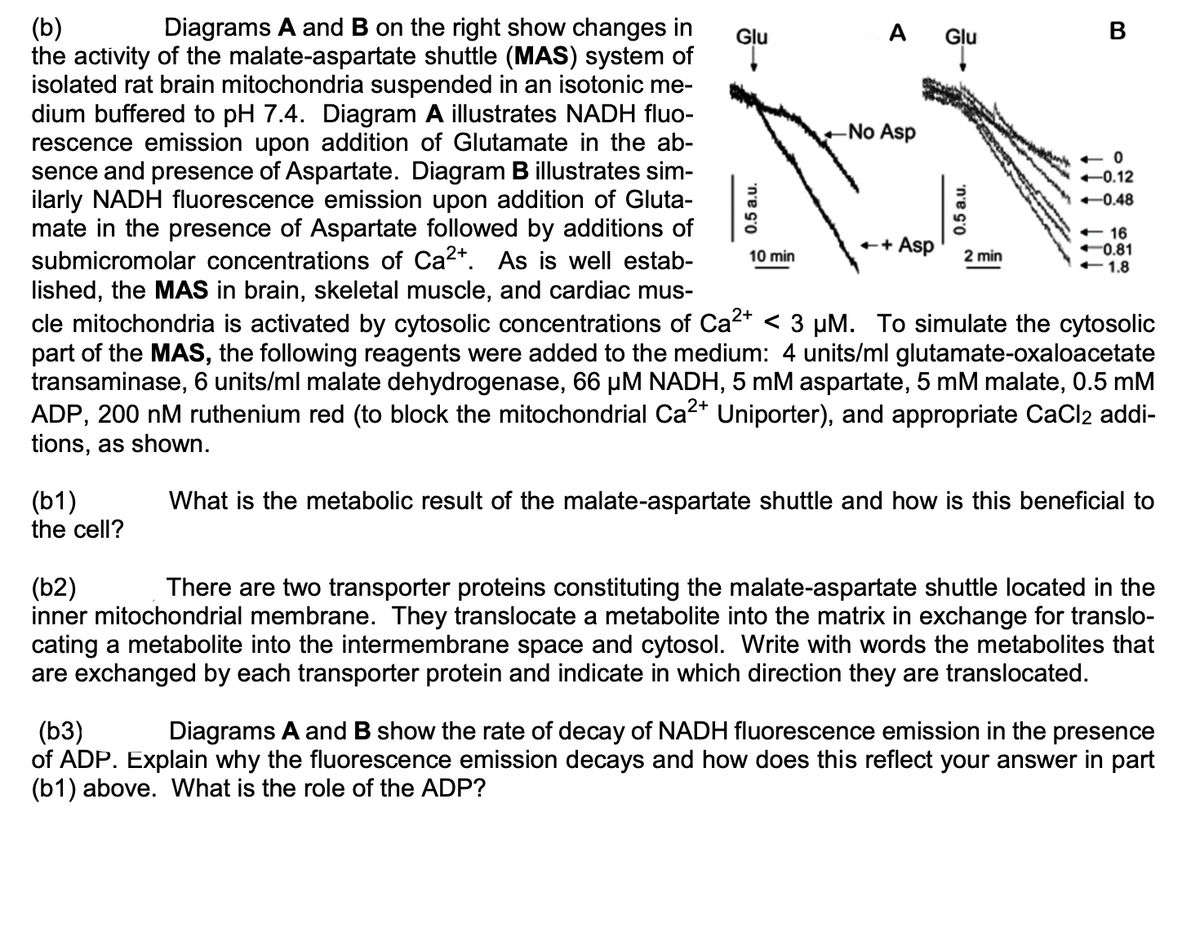
Transcribed Image Text:(b)
the activity of the malate-aspartate shuttle (MAS) system of
isolated rat brain mitochondria suspended in an isotonic me-
dium buffered to pH 7.4. Diagram A illustrates NADH fluo-
rescence emission upon addition of Glutamate in the ab-
sence and presence of Aspartate. Diagram B illustrates sim-
ilarly NADH fluorescence emission upon addition of Gluta-
mate in the presence of Aspartate followed by additions of
submicromolar concentrations of Ca2+. As is well estab-
lished, the MAS in brain, skeletal muscle, and cardiac mus-
Diagrams A and B on the right show changes in
Glu
A Glu
В
-No Asp
+ 0
+0.12
-0.48
+ 16
0.81
+1.8
++
Asp
10 min
2 min
cle mitochondria is activated by cytosolic concentrations of Ca2* < 3 µM. To simulate the cytosolic
part of the MAS, the following reagents were added to the medium: 4 units/ml glutamate-oxaloacetate
transaminase, 6 units/ml malate dehydrogenase, 66 µM NADH, 5 mM aspartate, 5 mM malate, 0.5 mM
ADP, 200 nM ruthenium red (to block the mitochondrial Ca2* Uniporter), and appropriate CaCl2 addi-
tions, as shown.
(b1)
the cell?
What is the metabolic result of the malate-aspartate shuttle and how is this beneficial to
(b2)
inner mitochondrial membrane. They translocate a metabolite into the matrix in exchange for translo-
cating a metabolite into the intermembrane space and cytosol. Write with words the metabolites that
are exchanged by each transporter protein and indicate in which direction they are translocated.
There are two transporter proteins constituting the malate-aspartate shuttle located in the
(b3)
of ADP. Explain why the fluorescence emission decays and how does this reflect your answer in part
(b1) above. What is the role of the ADP?
Diagrams A and B show the rate of decay of NADH fluorescence emission in the presence
0.5 a.u.
'n'e G'o
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning