Background: You just finished teaching your first PSYCH 248 lab section, and it’s time to calculate the grades. Your wonderful teaching assistant created an Excel file with all of the students’ exam grades, homework grade, and lab grade as well as their gender. Your next steps are to calculate each student’s final grade, convert those scores to letter grades, and describe the distribution of scores. 2. In Excel, calculate the final Number Grade, Letter Grade, and Z-score for each student. a. To calculate the Number Grade, type a numerical equation after an = sign in a cell or use the =AVERAGE() formula; however, keep in mind that the =AVERAGE() formula will always give you the regular mean, not the weighted mean. Grades for this course are comprised of three parts: lecture exams (60%), homework (20%), and lab (20%). b. To calculate the Letter Grade, use the =IF() formulawith a series of logic statements or enter the data by hand. For this assignment, let’s convert Number Grade into Letter Grade using the following rubric: A (90-100), B (80-89), C (70-79), D (60-69), F (<60). c. To calculate the Z-score, use the =STANDARDIZE() formula on the Number Grade variable. This formularequires three components: x (i.e., one student’sNumber Grade), the sample mean, and the sample standard deviation. You can calculate the sample mean and standard deviation for Number Grade using the =AVERAGE() and =STDEV() formulas. i. Create a new column called Abs(Z-score). In this column, use the =ABS() formula on the Z-score variable you just created to get the absolute values of each Z-score. 3. Now that you have filled in your dataset, save your file and open it in JASP. a. In the Data View, apply value labels to the Gender variable by clicking on the title of the column and entering the labels accordingly (0=Woman, 1=Man). b. Make sure that each variable has the correct “column type” (i.e., nominal, ordinal, or scalar) 9. Descriptive Statistics a. Give the mean, median, mode, standard deviation, minimum, and maximum for the Number Grades variable (round to two decimal places). b. Look at these same descriptive statistics for Exam 1, Exam 2, and Exam 3. On average, which exam did students score best on?
Background: You just finished teaching your first PSYCH 248 lab section, and it’s time to calculate the grades. Your wonderful teaching assistant created an Excel file with all of the students’ exam grades, homework grade, and lab grade as well as their gender. Your next steps are to calculate each student’s final grade, convert those scores to letter grades, and describe the distribution of scores. 2. In Excel, calculate the final Number Grade, Letter Grade, and Z-score for each student. a. To calculate the Number Grade, type a numerical equation after an = sign in a cell or use the =AVERAGE() formula; however, keep in mind that the =AVERAGE() formula will always give you the regular mean, not the weighted mean. Grades for this course are comprised of three parts: lecture exams (60%), homework (20%), and lab (20%). b. To calculate the Letter Grade, use the =IF() formulawith a series of logic statements or enter the data by hand. For this assignment, let’s convert Number Grade into Letter Grade using the following rubric: A (90-100), B (80-89), C (70-79), D (60-69), F (<60). c. To calculate the Z-score, use the =STANDARDIZE() formula on the Number Grade variable. This formularequires three components: x (i.e., one student’sNumber Grade), the sample mean, and the sample standard deviation. You can calculate the sample mean and standard deviation for Number Grade using the =AVERAGE() and =STDEV() formulas. i. Create a new column called Abs(Z-score). In this column, use the =ABS() formula on the Z-score variable you just created to get the absolute values of each Z-score. 3. Now that you have filled in your dataset, save your file and open it in JASP. a. In the Data View, apply value labels to the Gender variable by clicking on the title of the column and entering the labels accordingly (0=Woman, 1=Man). b. Make sure that each variable has the correct “column type” (i.e., nominal, ordinal, or scalar) 9. Descriptive Statistics a. Give the mean, median, mode, standard deviation, minimum, and maximum for the Number Grades variable (round to two decimal places). b. Look at these same descriptive statistics for Exam 1, Exam 2, and Exam 3. On average, which exam did students score best on?
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
(REV)00th Edition
ISBN:9780395977224
Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Chapter9: Systems Of Linear Equations
Section9.7: Puzzle Problems
Problem 2OE
Related questions
Question
Background: You just finished teaching your first PSYCH 248 lab section, and it’s time to calculate the grades. Your wonderful teaching assistant created an Excel file with all of the students’ exam grades, homework grade, and lab grade as well as their gender. Your next steps are to calculate each student’s final grade, convert those scores to letter grades, and describe the distribution of scores.
2. In Excel, calculate the final Number Grade, Letter Grade, and Z-score for each student.
a. To calculate the Number Grade, type a numerical equation after an = sign in a cell or use the =AVERAGE() formula; however, keep in mind that the =AVERAGE() formula will always give you the regular mean, not the weighted mean. Grades for this course are comprised of three parts: lecture exams (60%), homework (20%), and lab (20%).
b. To calculate the Letter Grade, use the =IF() formulawith a series of logic statements or enter the data by hand. For this assignment, let’s convert Number Grade into Letter Grade using the following rubric: A (90-100), B (80-89), C (70-79), D (60-69), F (<60).
c. To calculate the Z-score, use the =STANDARDIZE() formula on the Number Grade variable. This formularequires three components: x (i.e., one student’sNumber Grade), the sample mean, and the sample standard deviation. You can calculate the sample mean and standard deviation for Number Grade using the =AVERAGE() and =STDEV() formulas.
i. Create a new column called Abs(Z-score). In this column, use the =ABS() formula on the Z-score variable you just created to get the absolute values of each Z-score.
3. Now that you have filled in your dataset, save your file and open it in JASP.
a. In the Data View, apply value labels to the Gender variable by clicking on the title of the column and entering the labels accordingly (0=Woman, 1=Man).
b. Make sure that each variable has the correct “column type” (i.e., nominal, ordinal, or scalar)
9.
a. Give the mean, median, mode , standard deviation, minimum, and maximum for the Number Grades variable (round to two decimal places).
b. Look at these same descriptive statistics for Exam 1, Exam 2, and Exam 3. On average, which exam did students score best on?
10. Descriptive Statistics by Group
a. Give the mean, median, mode, and standard deviationfor the Number Grades variable for men and for women separately.
b. On average, did men or women do better in the course? Do you think this difference is significant?
11. Boxplots
a. Create boxplots for Number Grade separately for men and for women; make sure to label outliers. Paste your boxplots below.
b. Is there more variability in the distribution for men or for women? How can you tell?
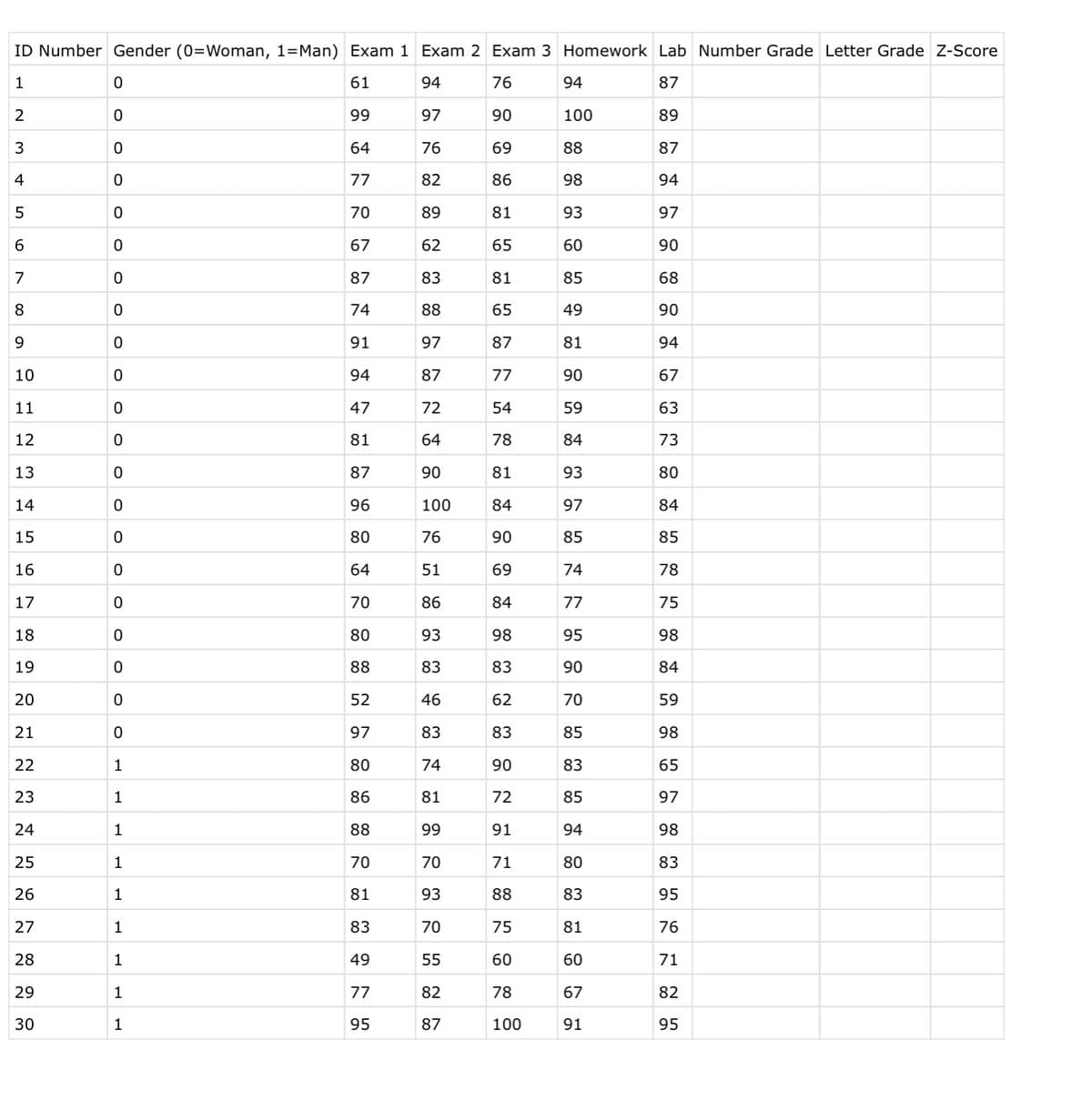
Transcribed Image Text:ID Number Gender (0=Woman, 1=Man) Exam 1 Exam 2 Exam 3 Homework Lab Number Grade Letter Grade Z-Score
1
61
94
76
94
87
2
99
97
90
100
89
3
64
76
69
88
87
4
77
82
86
98
94
70
89
81
93
97
67
62
65
60
90
87
83
81
85
68
8
74
88
65
49
90
91
97
87
81
94
10
94
87
77
90
67
11
47
72
54
59
63
12
81
64
78
84
73
13
87
90
81
93
80
14
96
100
84
97
84
15
80
76
90
85
85
16
64
51
69
74
78
17
70
86
84
77
75
18
80
93
98
95
98
19
88
83
83
90
84
20
52
46
62
70
59
21
97
83
83
85
98
22
1
80
74
90
83
65
23
1
86
81
72
85
97
24
1
88
99
91
94
98
25
1
70
70
71
80
83
26
1
81
93
88
83
95
27
1
83
70
75
81
76
28
1
49
55
60
60
71
29
1
77
82
78
67
82
30
1
95
87
100
91
95
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage