Chemical Principles in the Laboratory
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305264434
Author:Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Publisher:Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Chapter32: Voltaic Cell Measurements
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2ASA
Related questions
Question
![Use the standard reduction potentials shown here
to answer the questions.
> View Avallable Hint(s)
Reduction hal-reaction E (V)
(Cu**] = 2x10-14 M
Cu" (aq) + 2e-Cu(s) 0.337
2H (aq) + 2e-H2(g) 0.000
Previous Answers
Correct
Because of the logarithm function, this answer actually has just one significant figure. It is expressed here with
three significant figures because it will be used in the calculation for Part B.
Part B
Based on these data, what is the value of the formation constant, Ke , of (Cu(NH,)4* ?
Express the formation constant numerically using one significant figure.
View Avallable Hint(s)
K - 1.5 • 104
Submit Previoun Answers
x Incorrect; Try Again
Provide Feedback](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F30e82296-4fd9-4bc6-bcfd-fd7607543f23%2Fb0cd8dc2-03ca-43e9-9c4e-7f2e3e9d685a%2Fq11auqi_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Use the standard reduction potentials shown here
to answer the questions.
> View Avallable Hint(s)
Reduction hal-reaction E (V)
(Cu**] = 2x10-14 M
Cu" (aq) + 2e-Cu(s) 0.337
2H (aq) + 2e-H2(g) 0.000
Previous Answers
Correct
Because of the logarithm function, this answer actually has just one significant figure. It is expressed here with
three significant figures because it will be used in the calculation for Part B.
Part B
Based on these data, what is the value of the formation constant, Ke , of (Cu(NH,)4* ?
Express the formation constant numerically using one significant figure.
View Avallable Hint(s)
K - 1.5 • 104
Submit Previoun Answers
x Incorrect; Try Again
Provide Feedback
Transcribed Image Text:Use the standard reduction potentials shown here
to answer the questions.
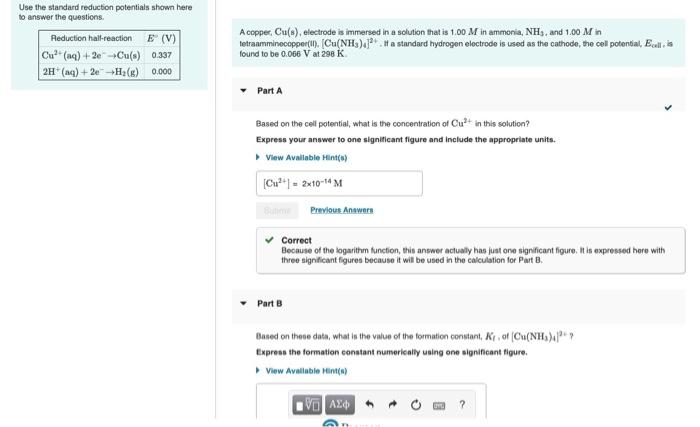
A copper, Cu(s), electrode is immersed in a solution that is 1.00 M in ammonia, NH3, and 1.00 M in
tetraamminecopper(). [Cu(NH3)4.If a standard hydrogen electrode is used as the cathode, the cel potential, Ecell, is
found to be 0.066 V at 298 K.
Reduction hal-reaction E (V)
Cu" (aq) + 2e-Cu(s) 0.337
2H (aq) + 2e-+H2(g) 0.000
Part A
Based on the cell potential, what is the concentration of Cu in this solution?
Express your answer to one significant figure and include the appropriate units.
> View Available Hint(s)
(Cu*") - 2x10-14 M
Rutm Prevlous Answers
v Correct
Because of the logarithm function, this answer actually has just one significant figure. It is expressed here with
three significant figures because it will be used in the calculation for Part B.
Part B
Based on these data, what is the value of the formation constant, Kr, of (Cu(NH,)"?
Express the formation constant numerically using one significant figure.
View Avallable Hint(s)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemical Principles in the Laboratory
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305264434
Author:
Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Publisher:
Brooks Cole

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemical Principles in the Laboratory
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305264434
Author:
Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Publisher:
Brooks Cole

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning