Being a computer analyst, he wanted to be very thorough in organizing the facts concerning his family's physical traits. He remembered from his Biology class that one's outward appearance (phenotype) was determined by one's genotype (genetic makeup). He also remembered that each person carries 2 alleles for each trait, one allele from each parent. PART 1: Meet the Spud Family Mr. and Mrs. Spud are expecting their third tater tot. As they flip through their family photo album, they began to talk about what baby spud might look like. Would his/her hair be curly like the Curly Fries on mom's side or would it be straight like the French Fries on dad's side. Mr. Spud, remembering some of his college biology, decided to make some predictions as to what his child might look like. Being confident with his task at hand, he got out some paper and began writing down the traits of his entire family. following is his list. The TABLE 1. Phenotypes of the Spud Family. TRAIT 1* Child 2nd Child Mrs. Spud Mr. Spud (alleles) Ear Lobes (E, e) Mouth (L, V) Hair (С, С) Eye Color (B, b) Nose (X", X") Freckles (F, F') (girl) (boy) free free free attached full lips thin lips thin lips full lips wavy straight wavy straight blue brown brown blue long wide wide long red & black red & black red red As he started his list, Mrs. Spud ran to the kitchen and grabbed a potato from the pantry. She thought it would be fun to create a visual of her next child. But, Mr. Spud reminded her that first they must construct their family pedigree in order to determine which alleles they each had. He decided the easiest way to find out each person's genotype was to construct a separate pedigree for each trait. He started with each person's phenotype and then translated each phenotype into its corresponding genotype. He knew he be predict what the next "Spud" might look like. Meanwhile, Mrs. Spud went to the computer and got on the internet to determine the genetics behind each trait. Here is what she discovered about Potato Head genetics: 1. Free ear lobes (E) are dominant to attached ear lobes (e). 2. Thin lips (L) are dominant to full lips (1). able everyone's genotype but he was hoping that he would have enough information to determine his genotype as well as his wife's. Once he knew that, he could 3. Hair form is an example of incomplete dominance: C is curly hair and C' is straight. However, CC' is wavy hair. might not to determine 4. Brown eye color (B) is dominant to blue eye color (b). 132
Being a computer analyst, he wanted to be very thorough in organizing the facts concerning his family's physical traits. He remembered from his Biology class that one's outward appearance (phenotype) was determined by one's genotype (genetic makeup). He also remembered that each person carries 2 alleles for each trait, one allele from each parent. PART 1: Meet the Spud Family Mr. and Mrs. Spud are expecting their third tater tot. As they flip through their family photo album, they began to talk about what baby spud might look like. Would his/her hair be curly like the Curly Fries on mom's side or would it be straight like the French Fries on dad's side. Mr. Spud, remembering some of his college biology, decided to make some predictions as to what his child might look like. Being confident with his task at hand, he got out some paper and began writing down the traits of his entire family. following is his list. The TABLE 1. Phenotypes of the Spud Family. TRAIT 1* Child 2nd Child Mrs. Spud Mr. Spud (alleles) Ear Lobes (E, e) Mouth (L, V) Hair (С, С) Eye Color (B, b) Nose (X", X") Freckles (F, F') (girl) (boy) free free free attached full lips thin lips thin lips full lips wavy straight wavy straight blue brown brown blue long wide wide long red & black red & black red red As he started his list, Mrs. Spud ran to the kitchen and grabbed a potato from the pantry. She thought it would be fun to create a visual of her next child. But, Mr. Spud reminded her that first they must construct their family pedigree in order to determine which alleles they each had. He decided the easiest way to find out each person's genotype was to construct a separate pedigree for each trait. He started with each person's phenotype and then translated each phenotype into its corresponding genotype. He knew he be predict what the next "Spud" might look like. Meanwhile, Mrs. Spud went to the computer and got on the internet to determine the genetics behind each trait. Here is what she discovered about Potato Head genetics: 1. Free ear lobes (E) are dominant to attached ear lobes (e). 2. Thin lips (L) are dominant to full lips (1). able everyone's genotype but he was hoping that he would have enough information to determine his genotype as well as his wife's. Once he knew that, he could 3. Hair form is an example of incomplete dominance: C is curly hair and C' is straight. However, CC' is wavy hair. might not to determine 4. Brown eye color (B) is dominant to blue eye color (b). 132
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Michael Cummings
Chapter5: The Inheritance Of Complex Traits
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5QP: As it turned out, one of the tallest Potsdam Guards had an unquenchable attraction to short women....
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
How do you figure out the geno and phenotype from the info given? 2 pages out the lab but I figured once explained I’ll be able to do understand and do the rest!
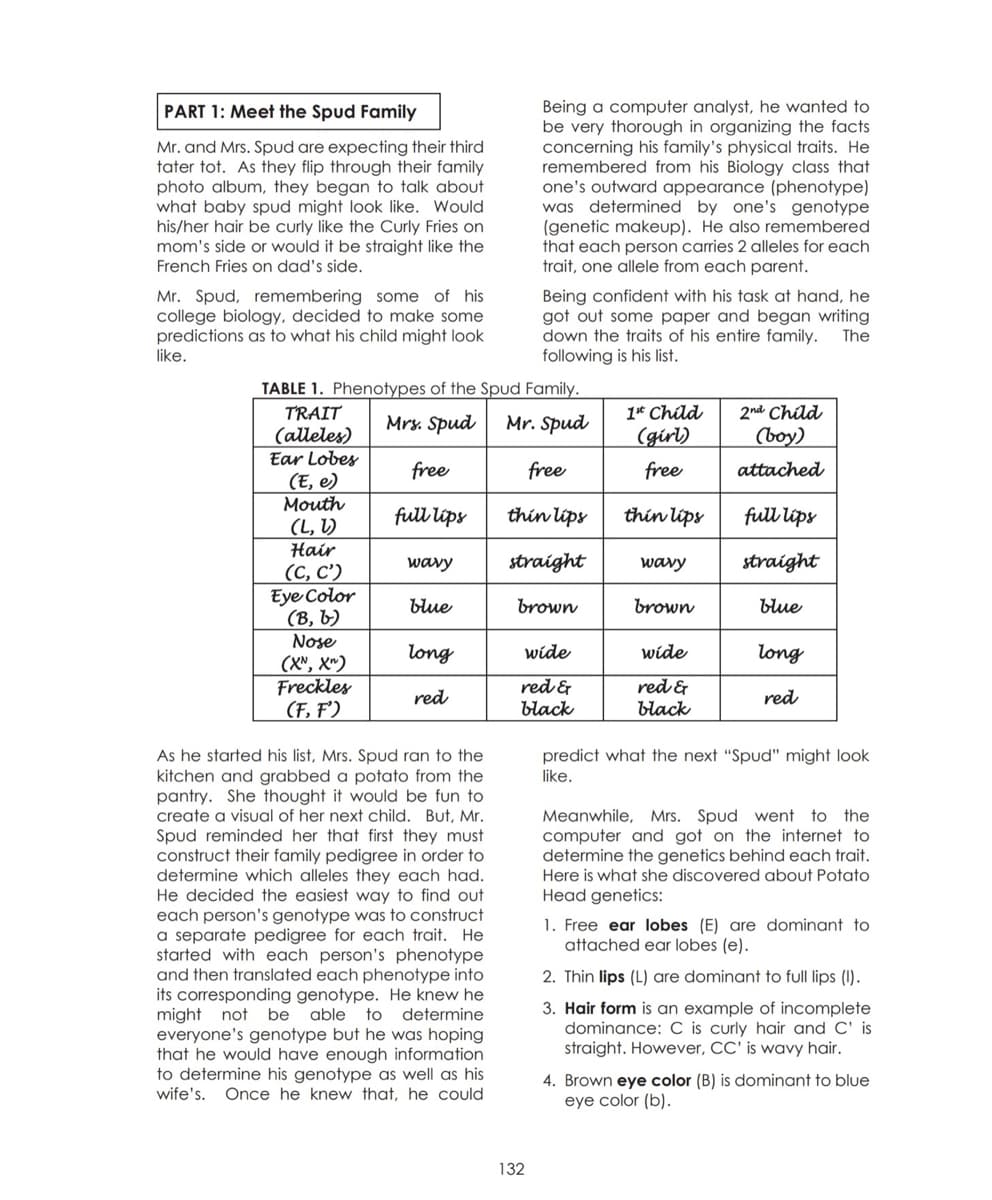
Transcribed Image Text:Being a computer analyst, he wanted to
be very thorough in organizing the facts
concerning his family's physical traits. He
remembered from his Biology class that
one's outward appearance (phenotype)
was determined by one's genotype
(genetic makeup). He also remembered
that each person carries 2 alleles for each
trait, one allele from each parent.
PART 1: Meet the Spud Family
Mr. and Mrs. Spud are expecting their third
tater tot. As they flip through their family
photo album, they began to talk about
what baby spud might look like. Would
his/her hair be curly like the Curly Fries on
mom's side or would it be straight like the
French Fries on dad's side.
Mr. Spud, remembering some of his
college biology, decided to make some
predictions as to what his child might look
like.
Being confident with his task at hand, he
got out some paper and began writing
down the traits of his entire family.
following is his list.
The
TABLE 1. Phenotypes of the Spud Family.
TRAIT
(alleles)
Ear Lobes
(E, e)
Mouth
(L, V)
Hair
(С, С)
Eye Color
(B, b)
1* Child
2nd Child
Mrs. Spud
Mr. Spud
(girl)
(boy)
free
free
free
attached
full lips
thin lips
thin lips
full lips
wavy
straight
wavy
straight
blue
brown
brown
blue
Nose
long
wide
wide
long
(X", X")
Freckles
(F, F')
red &
red &
black
red
red
black
As he started his list, Mrs. Spud ran to the
kitchen and grabbed a potato from the
pantry. She thought it would be fun to
create a visual of her next child. But, Mr.
Spud reminded her that first they must
construct their family pedigree in order to
determine which alleles they each had.
He decided the easiest way to find out
each person's genotype was to construct
a separate pedigree for each trait. He
started with each person's phenotype
and then translated each phenotype into
its corresponding genotype. He knew he
might not be
everyone's genotype but he was hoping
that he would have enough information
to determine his genotype as well as his
wife's. Once he knew that, he could
predict what the next "Spud" might look
like.
to the
Meanwhile, Mrs. Spud went
computer and got on the internet to
determine the genetics behind each trait.
Here is what she discovered about Potato
Head genetics:
1. Free ear lobes (E) are dominant to
attached ear lobes (e).
2. Thin lips (L) are dominant to full lips (1).
3. Hair form is an example of incomplete
dominance: C is curly hair and C' is
straight. However, CC' is wavy hair.
able to determine
4. Brown eye color (B) is dominant to blue
eye color (b).
132
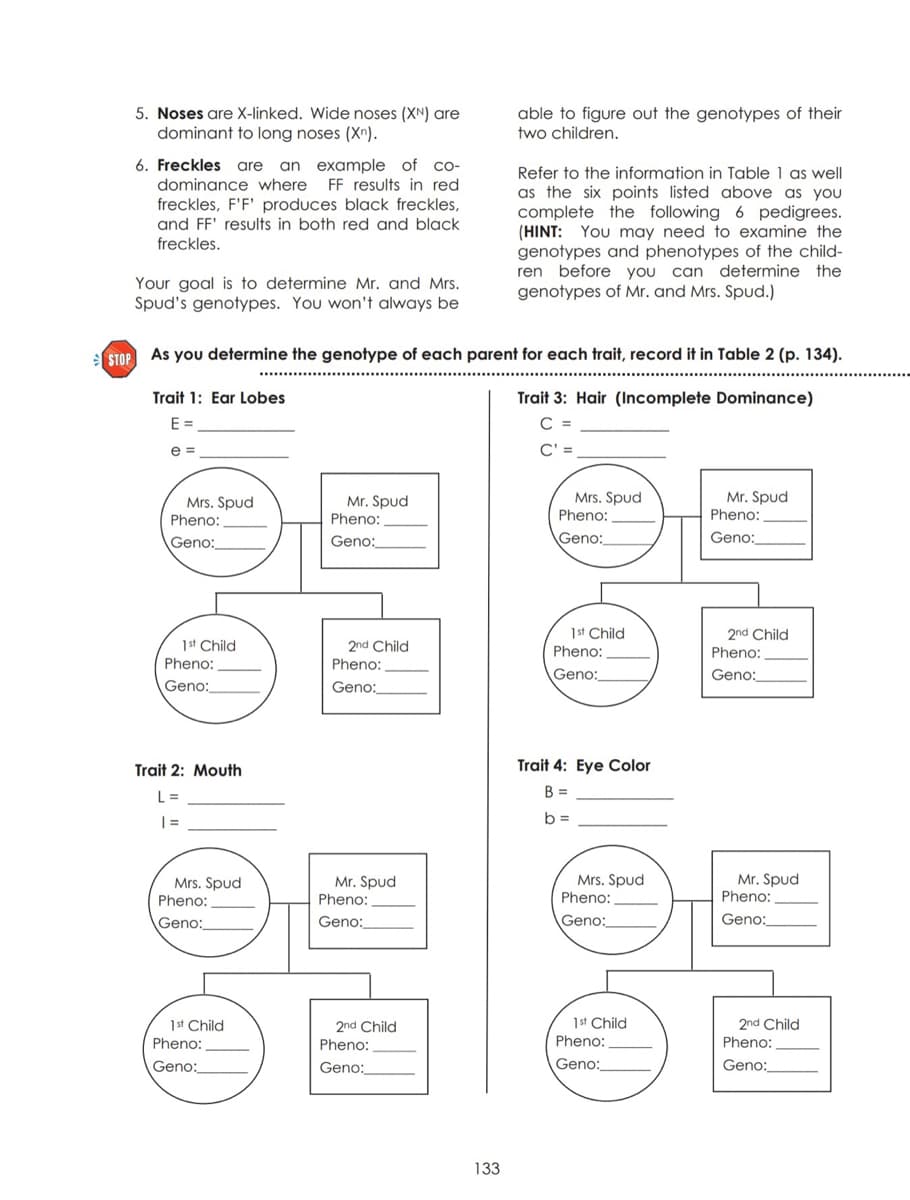
Transcribed Image Text:5. Noses are X-linked. Wide noses (XN) are
dominant to long noses (X^).
able to figure out the genotypes of their
two children.
an example of co-
FF results in red
6. Freckles
are
Refer to the information in Table 1 as well
dominance where
as the six points listed above as you
complete the following 6 pedigrees.
(HINT: You may need to examine the
genotypes and phenotypes of the child-
ren before you can determine the
genotypes of Mr. and Mrs. Spud.)
freckles, F'F' produces black freckles,
and FF' results in both red and black
freckles.
Your goal is to determine Mr. and Mrs.
Spud's genotypes. You won't always be
STOP As you determine the genotype of each parent for each trait, record it in Table 2 (p. 134).
Trait 1: Ear Lobes
Trait 3: Hair (Incomplete Dominance)
E =
e =
C' =
Mr. Spud
Mrs. Spud
Pheno:
Mr. Spud
Pheno:
Mrs. Spud
Pheno:
Pheno:
Geno:
Geno:
Geno:
Geno:_
1st Child
2nd Child
Pheno:
1st Child
2nd Child
Pheno:
Pheno:
Pheno:
Geno:
Geno:
Geno:
Geno:
Trait 2: Mouth
Trait 4: Eye Color
L =
B =
| =
b =
Mr. Spud
Pheno:
Mrs. Spud
Mrs. Spud
Pheno:
Mr. Spud
Pheno:
Pheno:
Geno:
Geno:
Geno:
Geno:
1st Child
2nd Child
1st Child
2nd Child
Pheno:
Pheno:
Pheno:
Pheno:
Geno:
Geno:
Geno:
Geno:
133
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305112100
Author:
Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305112100
Author:
Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning