For the following reaction (Table 20.1): FAD +2 cyt c (Fe*2) +2 H* → FADH2 + 2 cyt c (Fe+3) a The cytochrome couple is the acceptor because it has the higher (more positive) reduction potential. Consider the oxidation of Succinate by molecular oxygen as carried out via the electron transport pathway: Succinate + 1/202→ Fumarate + H20 b If E,' (Fumarate/Succinate) = +0.031 V and E,' (1/20,/H20) = +0.816 V AG,' = -151.5 kJ/mol In different organisms Sucrose can be cleaved either by hydrolysis or by phosphorolysis. The ATP yield per mole of Sucrose metabolized by hydrolysis is 5 (2 from each Glucose and 3 from Fructose). For the oxidation of NADH by molecular oxygen as carried out via the electron transport pathway: If Eo' (NAD*/NADH) = d -0.32 V and E, (1/20,/H20) = +0.816 V the AG,' for the reaction is -219 kJ/mol Glucose labelled in carbon number one with radioactive carbon and taken through the oxidative reactions of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway will give rise to radioactive Ribulose 5-phosphate e If Sucrose is subjected to phosphorolysis the ATP yield per mole of Sucrose metabolized is 4 (2 from each Glucose and f Fructose) Starting with Glucose 6-phosphate labelled in carbon number 2 with radioactive carbon and taken through the oxidative g phase of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway and the first transaldolase reaction gives rise to a 7-carbon intermediate labeled with radioactive carbon in carbon number 1 Three ATP equivalents are consumed in the conversion of Dihydroxyacetone phosphate to a glycosyl residue of glycogen i An individual with Glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency suffers from chronic hypoglycemia
For the following reaction (Table 20.1): FAD +2 cyt c (Fe*2) +2 H* → FADH2 + 2 cyt c (Fe+3) a The cytochrome couple is the acceptor because it has the higher (more positive) reduction potential. Consider the oxidation of Succinate by molecular oxygen as carried out via the electron transport pathway: Succinate + 1/202→ Fumarate + H20 b If E,' (Fumarate/Succinate) = +0.031 V and E,' (1/20,/H20) = +0.816 V AG,' = -151.5 kJ/mol In different organisms Sucrose can be cleaved either by hydrolysis or by phosphorolysis. The ATP yield per mole of Sucrose metabolized by hydrolysis is 5 (2 from each Glucose and 3 from Fructose). For the oxidation of NADH by molecular oxygen as carried out via the electron transport pathway: If Eo' (NAD*/NADH) = d -0.32 V and E, (1/20,/H20) = +0.816 V the AG,' for the reaction is -219 kJ/mol Glucose labelled in carbon number one with radioactive carbon and taken through the oxidative reactions of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway will give rise to radioactive Ribulose 5-phosphate e If Sucrose is subjected to phosphorolysis the ATP yield per mole of Sucrose metabolized is 4 (2 from each Glucose and f Fructose) Starting with Glucose 6-phosphate labelled in carbon number 2 with radioactive carbon and taken through the oxidative g phase of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway and the first transaldolase reaction gives rise to a 7-carbon intermediate labeled with radioactive carbon in carbon number 1 Three ATP equivalents are consumed in the conversion of Dihydroxyacetone phosphate to a glycosyl residue of glycogen i An individual with Glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency suffers from chronic hypoglycemia
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Chapter1: Biochemistry: An Evolving Science
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
which staments are false
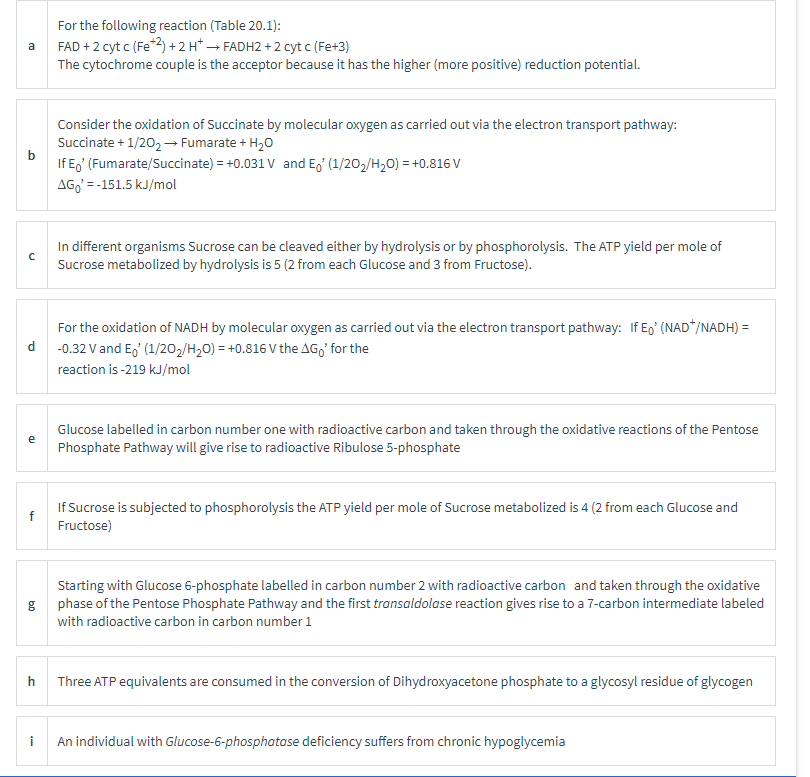
Transcribed Image Text:For the following reaction (Table 20.1):
FAD +2 cyt c (Fe*2) +2 H* → FADH2 + 2 cyt c (Fe+3)
a
The cytochrome couple is the acceptor because it has the higher (more positive) reduction potential.
Consider the oxidation of Succinate by molecular oxygen as carried out via the electron transport pathway:
Succinate + 1/202→ Fumarate + H20
b
If E,' (Fumarate/Succinate) = +0.031 V and E,' (1/20,/H20) = +0.816 V
AG,' = -151.5 kJ/mol
In different organisms Sucrose can be cleaved either by hydrolysis or by phosphorolysis. The ATP yield per mole of
Sucrose metabolized by hydrolysis is 5 (2 from each Glucose and 3 from Fructose).
For the oxidation of NADH by molecular oxygen as carried out via the electron transport pathway: If Eo' (NAD*/NADH) =
d
-0.32 V and E, (1/20,/H20) = +0.816 V the AG,' for the
reaction is -219 kJ/mol
Glucose labelled in carbon number one with radioactive carbon and taken through the oxidative reactions of the Pentose
Phosphate Pathway will give rise to radioactive Ribulose 5-phosphate
e
If Sucrose is subjected to phosphorolysis the ATP yield per mole of Sucrose metabolized is 4 (2 from each Glucose and
f
Fructose)
Starting with Glucose 6-phosphate labelled in carbon number 2 with radioactive carbon and taken through the oxidative
g phase of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway and the first transaldolase reaction gives rise to a 7-carbon intermediate labeled
with radioactive carbon in carbon number 1
Three ATP equivalents are consumed in the conversion of Dihydroxyacetone phosphate to a glycosyl residue of glycogen
i
An individual with Glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency suffers from chronic hypoglycemia
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781319114671
Author:
Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781464126116
Author:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul…
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781118918401
Author:
Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:
WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781319114671
Author:
Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781464126116
Author:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul…
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781118918401
Author:
Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:
WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305961135
Author:
Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological …
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9780134015187
Author:
John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:
PEARSON