Bob plays a game in which a dice is rolled until an odd number occurs. Bob wins 10 – x dollars if x rolls are needed for x = 1,2 but loses k = 10 dollars if x > 2. Calculate the probability that Bob loses money in this game. Calculate the expected value Bob’s winnings. Calculate the variance of Bob’s winnings. What should be the value of k for the game to be fair, i.e. for the expected value of the money earned to be equal to 0?
Bob plays a game in which a dice is rolled until an odd number occurs. Bob wins 10 – x dollars if x rolls are needed for x = 1,2 but loses k = 10 dollars if x > 2. Calculate the probability that Bob loses money in this game. Calculate the expected value Bob’s winnings. Calculate the variance of Bob’s winnings. What should be the value of k for the game to be fair, i.e. for the expected value of the money earned to be equal to 0?
College Algebra
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305115545
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Chapter9: Counting And Probability
Section9.3: Binomial Probability
Problem 2E: If a binomial experiment has probability p success, then the probability of failure is...
Related questions
Question
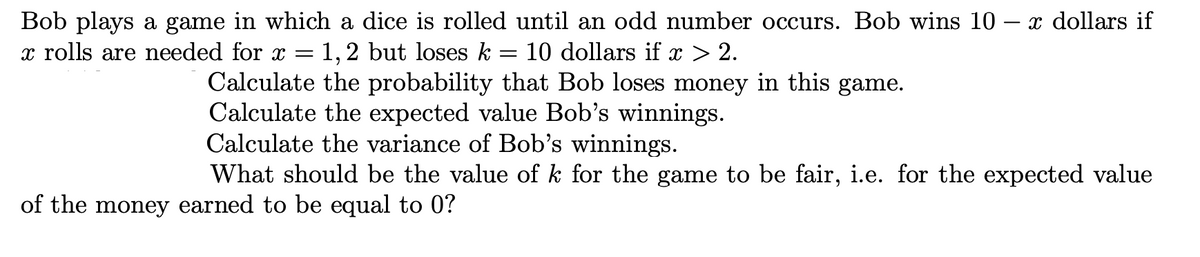
Transcribed Image Text:x dollars if
Bob plays a game in which a dice is rolled until an odd number occurs. Bob wins 10
x rolls are needed for x =
1,2 but loses k
10 dollars if x > 2.
Calculate the probability that Bob loses money in this game.
Calculate the expected value Bob's winnings.
Calculate the variance of Bob's winnings.
What should be the value of k for the game to be fair, i.e. for the expected value
of the money earned to be equal to 0?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning