Bower likes to plant trees in his front year. His neighbors also derive pleasure form the trees in his front year. That is, Bower's trees provide a positive externality for the neighborhood. His marginal private benefit and the marginal social benefit (his and that received by his neighbors combined) are represented on the graph below, along with the marginal cost of planting a tree. Prie, Cest (kole) $ 00 45.00 40.00 1.00 00 Mgial Ou 25.00 20.00 15.00 10.00 1.00 I 4 S68 Quanity (mber of wees) Suppose the neighborhood subsidies Bower's trees. That is, neighbors give him enough money to plant the socially optimal number of trees. What area on the graph would be equal to the net social gain resulting form the subsidy? OA OB Oc OA+B
Bower likes to plant trees in his front year. His neighbors also derive pleasure form the trees in his front year. That is, Bower's trees provide a positive externality for the neighborhood. His marginal private benefit and the marginal social benefit (his and that received by his neighbors combined) are represented on the graph below, along with the marginal cost of planting a tree. Prie, Cest (kole) $ 00 45.00 40.00 1.00 00 Mgial Ou 25.00 20.00 15.00 10.00 1.00 I 4 S68 Quanity (mber of wees) Suppose the neighborhood subsidies Bower's trees. That is, neighbors give him enough money to plant the socially optimal number of trees. What area on the graph would be equal to the net social gain resulting form the subsidy? OA OB Oc OA+B
Chapter14: Environmental Economics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7SQ
Related questions
Question
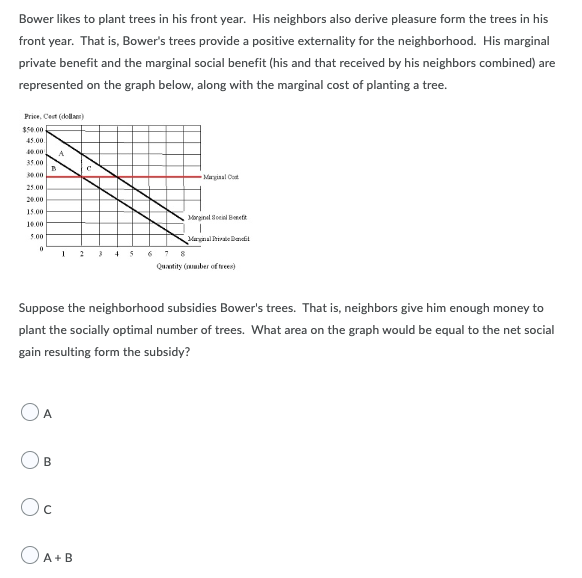
Transcribed Image Text:Bower likes to plant trees in his front year. His neighbors also derive pleasure form the trees in his
front year. That is, Bower's trees provide a positive externality for the neighborhood. His marginal
private benefit and the marginal social benefit (his and that received by his neighbors combined) are
represented on the graph below, along with the marginal cost of planting a tree.
Price, Cest (oll)
$S0.00
45.00.
40.00
A
35.00
0 00
Margiaal Cot
25.00
20.00
15.00
argnel Soeiel Benett
je 00
5.00
agnal hirde Bandfil
2
4 5
Quantity (mber of trees)
Suppose the neighborhood subsidies Bower's trees. That is, neighbors give him enough money to
plant the socially optimal number of trees. What area on the graph would be equal to the net social
gain resulting form the subsidy?
OA
В
Oc
O
A+ B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you



Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax



Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
