Calculate accuracy and precision for each set of 5 aliquots. Assume that the density of water Is g/mL. Accuracy is how close a set of values measures to a standard value. Precision is a measur not of values is to one another and is measured by the deviation.
Calculate accuracy and precision for each set of 5 aliquots. Assume that the density of water Is g/mL. Accuracy is how close a set of values measures to a standard value. Precision is a measur not of values is to one another and is measured by the deviation.
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter1: Basic Concepts Of Chemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 21RPS: You and your lab partner are asked to determine the density of an aluminum bar. The mass is known...
Related questions
Question
100%
How do I solve for the percent value? The sample data calculated the answers but I have no idea how they obtained the percent error values. Calculate sample data #1 with detailed steps.
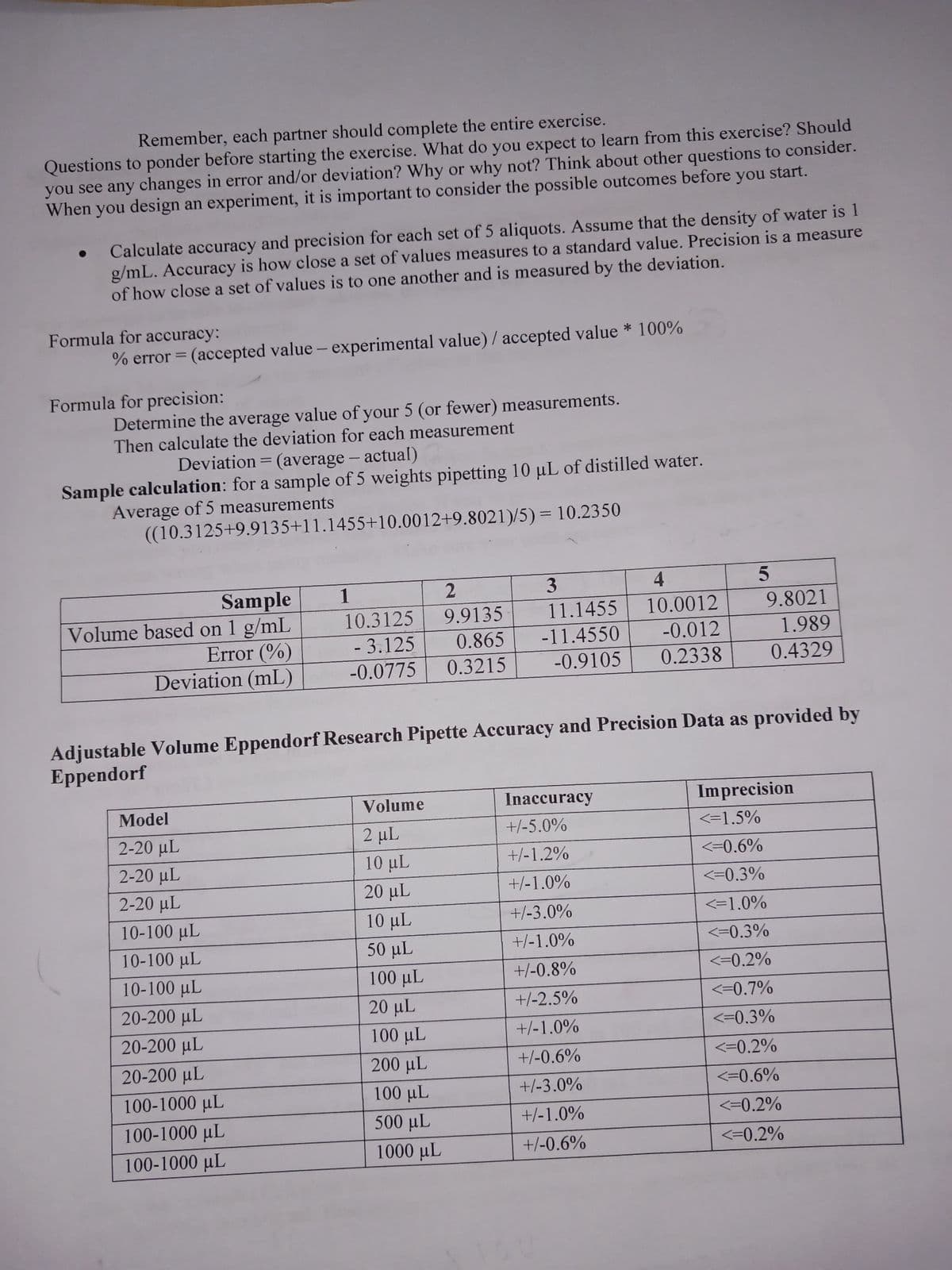
Transcribed Image Text:Remember, each partner should complete the entire exercise.
Questions to ponder before starting the exercise. What do you expect to learn from this exercise? Should
you see any changes in error and/or deviation? Why or why not? Think about other questions to consider.
When you design an experiment, it is important to consider the possible outcomes before you start.
Calculate accuracy and precision for each set of 5 aliquots. Assume that the density of water is 1
g/mL. Accuracy is how close a set of values measures to a standard value. Precision is a measure
of how close a set of values is to one another and is measured by the deviation.
% error = (accepted value - experimental value) / accepted value * 100%
Formula for accuracy:
Formula for precision:
Determine the average value of your 5 (or fewer) measurements.
Then calculate the deviation for each measurement
Deviation = (average - actual)
Sample calculation: for a sample of 5 weights pipetting 10 µL of distilled water.
Average of 5 measurements
((10.3125+9.9135+11.1455+10.0012+9.8021)/5) = 10.2350
Sample
Volume based on 1 g/mL
Error (%)
Deviation (mL)
Model
2-20 μL
2-20 μL
2-20 μL
10-100 μL
10-100 με
10-100 μL
20-200 μL
20-200 με
20-200 μL
1
2
10.3125 9.9135
- 3.125 0.865
-0.0775 0.3215
100-1000 μL
100-1000 μL
100-1000 μL
Adjustable Volume Eppendorf Research Pipette Accuracy and Precision Data as provided by
Eppendorf
Volume
2 µL
10 μL
20 µL
3
11.1455
-11.4550
-0.9105
10 μL
50 µL
100 μL
20 μL
100 μL
200 µL
100 μL
500 µL
1000 μL
4
10.0012
-0.012
0.2338
Inaccuracy
+/-5.0%
+/-1.2%
+/-1.0%
+/-3.0%
+/-1.0%
+/-0.8%
+/-2.5%
+/-1.0%
+/-0.6%
+/-3.0%
+/-1.0%
+/-0.6%
5
9.8021
1.989
0.4329
Imprecision
<=1.5%
<=0.6%
<=0.3%
<=1.0%
<=0.3%
<=0.2%
<=0.7%
<=0.3%
<=0.2%
<=0.6%
<=0.2%
<=0.2%
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning