Calculate the equilibrium constant for the following reaction carried out in 1 M perchloric acid: 2Fe³+ + 2I- = 2FE²+ +I_(aq) See appendix H in the textbook for standard reduction potentials.
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the following reaction carried out in 1 M perchloric acid: 2Fe³+ + 2I- = 2FE²+ +I_(aq) See appendix H in the textbook for standard reduction potentials.
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
3rd Edition
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Chapter18: Electrochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 18.68QE
Related questions
Question
100%
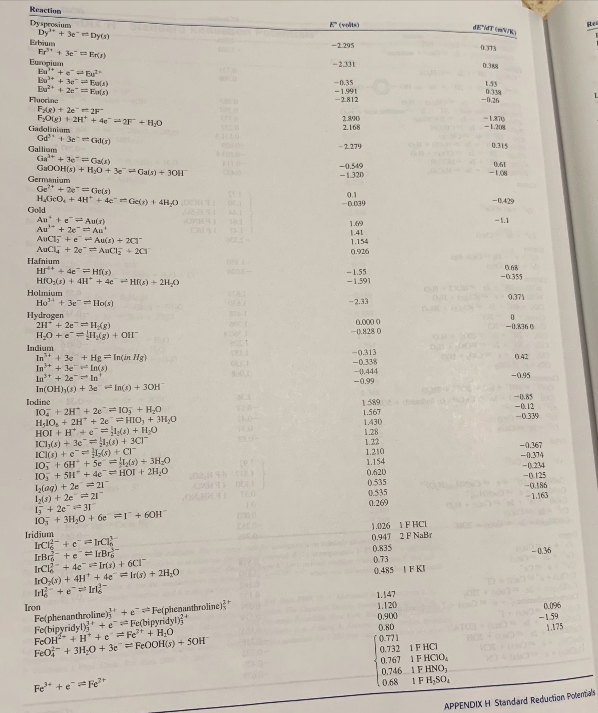
Transcribed Image Text:Reaction
Dysprosium
Dy + 3e Dy
E (volts)
EMT K)
Re
Erbium
Fr + 3e" Er)
Europium
Eu +e Eu
Eu + 3e"Eula)
Eu + 2e Eats)
-2.295
-2.331
0.38
-0.35
-1.991
1.53
0.338
-0.26
Fluorine
-2.812
FAR) + 2e 2
FOlg) + 2H* + 4e 2F+ H0
2.800
2.168
Ciadolinium
Gd + 3e" Gdr)
-1.20
Gallium
Ga+ 3e=Gala)
GaOOH(s) + H,0 + 3e Gals) + 301
Germanium
Ge* + 2e = Ge(s)
HGeO, + 4H + 4c"Ge() + 4H0
-2.279
0.315
-0.549
0.61
-1320
0.1
-0.039
-0429
Gold
Au +e Auls)
Au" + 2e Au'
AuCl, +e - Au(s) + 2CI
AuCl, + 2e= AuCl + 201
149
-1.1
1.41
1.154
0.926
Hafnium
HI* + 4e - Hs)
HIO:(s) + 4H" + 4e -HRs) + 2H,)
-1.55
-1.591
068
-0.355
Holmium
Ho+ 3e =Ho(s)
-2.33
0.371
Hydrogen
2H* + 2e H(g)
H0 +e=IH,(g) + OII"
Indium
In* + 3e + Hg In(in lg)
In* + 3e In(s)
In* + 2e In'
In(OH),() + 3e In(s) + 30H
Iodine
1O, + 2H + 2e 10, + H0
HIO, + 2H + 2e= HIO, + 3H,0
HOI + H + e=1(4) + H,O
ICI,(s) + 3c= 1,() + 3CI"
ICI() +e=L(s) + CI
10, + 6H + Se s) + 3H-O
I0, + 51" + 4e= HOI + 2H,0
Ilag) + 2e21
I(s) + 2e= 21
5 + 2e 31
10, + 3H,0 + 6e1 + 60H
Iridium
IC +e- IrCl
IrBr +e= IrBr
IrC + 4e Irts) + 6CI
IrO,(r) + 4H* + 4e Irls) + 2H,0
0.000 0
-0.828 0
-0.8360
-0.313
-0.338
-0.444
-0.99
042
-095
1589
1.567
1.430
1.28
--0.85
-0.12
-039
1.22
1.210
1.154
0.620
0535
0.535
-0.367
-0.374
-0.234
-0.125
-0.186
-1.163
0.269
1.026 IF HCI
0.947 2 FNaBr
0.835
-036
0.73
0.485 IFKI
1.147
Iron
Felphenanthroline) +e Felphenanthroline
Fe(bipyridyl), + e Fe(bipyridyl)"
FEOH" + H* +e Fe + H;0
Feo-+ 3H-0 + 3e = FE0OH(s) + SOH
1.120
0,096
0.900
-159
1.175
0.80
(0.771
0.732 1F HCI
0.767 1F HCI0,
0.746 IF HNO,
Fe" +e Fe
0.68
1F H,SO,
APPENDIX H Standard Reduction Polentials
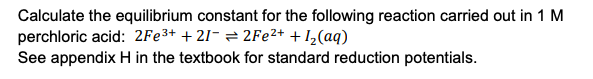
Transcribed Image Text:Calculate the equilibrium constant for the following reaction carried out in 1 M
perchloric acid: 2Fe3+ + 21- = 2FE²+ + I½(aq)
See appendix H in the textbook for standard reduction potentials.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning