cars in Japan is given as: Japanese demand = 10,000 - 0.001(Price of U.S. cars in yen). imilarly, the demand for Japanese-made cars in the United States is: U.S. demand = 30,000-0.2(Price of Japanese cars in dollars). he domestic price of a U.S-made car is $20,000, and the domestic price of a Japanese-made car is ¥2,500,000. ustructions: If imports exceed exports, enter a negative value (-) for net export. If the nominal exchange rate is 100 yen per dollar, then the real exchange rate in terms of cars from the perspective of the United cates is and net exports of cars to Japan is The nominal exchange rate is 125 yen per dollar, then the real exchange rate in terms of cars from the perspective of the United ates is and net exports of cars to Japan is Which of following correctly describes the effect(s) of an appreciation of the dollar on U.S. net exports of automobiles (to the panese market): US. exports will decrease while U.S. imports will increase in response to the appreciation of the dollar. OU.S. exports will decrease while U.S. Imports will stay the same in response to the appreciation of the dollar. O Both U.S. exports and U.S. imports will decrease in response to the appreciation of the dollar. OUS. exports will increase while U.S. Imports will decrease in response to the appreciation of the dollar.
cars in Japan is given as: Japanese demand = 10,000 - 0.001(Price of U.S. cars in yen). imilarly, the demand for Japanese-made cars in the United States is: U.S. demand = 30,000-0.2(Price of Japanese cars in dollars). he domestic price of a U.S-made car is $20,000, and the domestic price of a Japanese-made car is ¥2,500,000. ustructions: If imports exceed exports, enter a negative value (-) for net export. If the nominal exchange rate is 100 yen per dollar, then the real exchange rate in terms of cars from the perspective of the United cates is and net exports of cars to Japan is The nominal exchange rate is 125 yen per dollar, then the real exchange rate in terms of cars from the perspective of the United ates is and net exports of cars to Japan is Which of following correctly describes the effect(s) of an appreciation of the dollar on U.S. net exports of automobiles (to the panese market): US. exports will decrease while U.S. imports will increase in response to the appreciation of the dollar. OU.S. exports will decrease while U.S. Imports will stay the same in response to the appreciation of the dollar. O Both U.S. exports and U.S. imports will decrease in response to the appreciation of the dollar. OUS. exports will increase while U.S. Imports will decrease in response to the appreciation of the dollar.
Chapter20: Elasticity: Demand And Supply
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6E
Related questions
Question
2
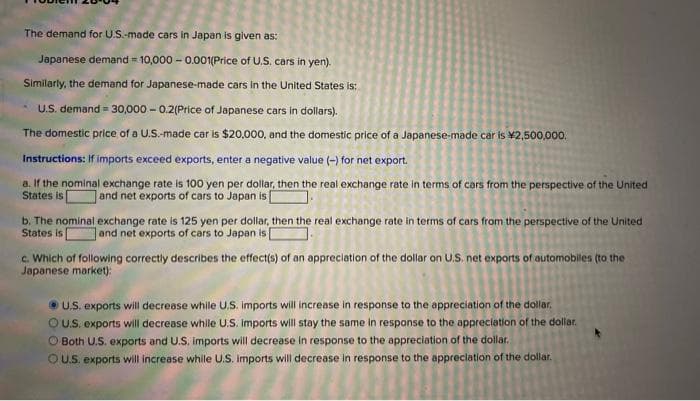
Transcribed Image Text:The demand for U.S.-made cars in Japan is given as:
Japanese demand = 10,000 - 0.001(Price of U.S. cars in yen).
Similarly, the demand for Japanese-made cars in the United States is:
U.S. demand = 30,000 - 0.2(Price of Japanese cars in dollars).
The domestic price of a U.S.-made car is $20,000, and the domestic price of a Japanese-made car is ¥2,500,000.
Instructions: If imports exceed exports, enter a negative value (-) for net export.
a. If the nominal exchange rate is 100 yen per dollar, then the real exchange rate in terms of cars from the perspective of the United
States is
and net exports of cars to Japan is
b. The nominal exchange rate is 125 yen per dollar, then the real exchange rate in terms of cars from the perspective of the United
States is
Jand net exports of cars to Japan is [
c. Which of following correctly describes the effects) of an appreciation of the dollar on U.S. net exports of automobiles (to the
Japanese market):
• U.S. exports will decrease while U.S. Imports will increase in response to the appreciation of the dollar,
OUS. exports will decrease while U.S. Imports will stay the same in response to the appreciation of the dollar.
O Both U.S. exports and U.S. imports will decrease in response to the appreciation of the dollar.
OU.S. exports will increase while U.S. Imports will decrease in response to the appreclation of the dollar.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

