Classify each of the reactions according to one of the four reaction types summarized in the table below. Reaction Spontaneous Process? Туре AH°(system) AS" (system) (Standard Conditions) 1 Exothermic, < 0 Positive, >0 Spontaneous at all temperatures. AS°(universe) > 0. 2 Exothermic, < 0 Negative, <0 Depends on relative magnitudes of AH' and AS*. Spontaneous at lower temperatures. 3 Endothermic, > 0 Positive, > 0 Depends on relative magnitudes of AH° and AS*. Spontaneous at higher temperatures. Endothermic, > 0 Negative, <0 Not spontaneous at any temperature. AS"(universe) < 0. 4 C,H12O6 (s) + 6 O2(g) → 6 CO2(g) + 6 H,0(t) a. A‚H° = -673 kJ/mol-rxn A,s' = 60.4 J/K -· mol-rxn Spontaneous at all temperatures. O Spontaneous at lower temperatures. Spontaneous at higher temperatures. O Not spontaneous at any temperature. b. FeO(s) + C(graphite) → Fe(s) + CO(g) A‚H' = 153.2 kJ/mol-rxn A,S' = 160.4 J/K · mol-rxn Spontaneous at all temperatures. Spontaneous at lower temperatures. Spontaneous at higher temperatures. O Not spontaneous at any temperature.
Classify each of the reactions according to one of the four reaction types summarized in the table below. Reaction Spontaneous Process? Туре AH°(system) AS" (system) (Standard Conditions) 1 Exothermic, < 0 Positive, >0 Spontaneous at all temperatures. AS°(universe) > 0. 2 Exothermic, < 0 Negative, <0 Depends on relative magnitudes of AH' and AS*. Spontaneous at lower temperatures. 3 Endothermic, > 0 Positive, > 0 Depends on relative magnitudes of AH° and AS*. Spontaneous at higher temperatures. Endothermic, > 0 Negative, <0 Not spontaneous at any temperature. AS"(universe) < 0. 4 C,H12O6 (s) + 6 O2(g) → 6 CO2(g) + 6 H,0(t) a. A‚H° = -673 kJ/mol-rxn A,s' = 60.4 J/K -· mol-rxn Spontaneous at all temperatures. O Spontaneous at lower temperatures. Spontaneous at higher temperatures. O Not spontaneous at any temperature. b. FeO(s) + C(graphite) → Fe(s) + CO(g) A‚H' = 153.2 kJ/mol-rxn A,S' = 160.4 J/K · mol-rxn Spontaneous at all temperatures. Spontaneous at lower temperatures. Spontaneous at higher temperatures. O Not spontaneous at any temperature.
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter16: Thermodynamics: Directionality Of Chemical Reactions
Section16.3: Measuring Dispersal Of Energy: Entropy
Problem 16.3CE
Related questions
Question
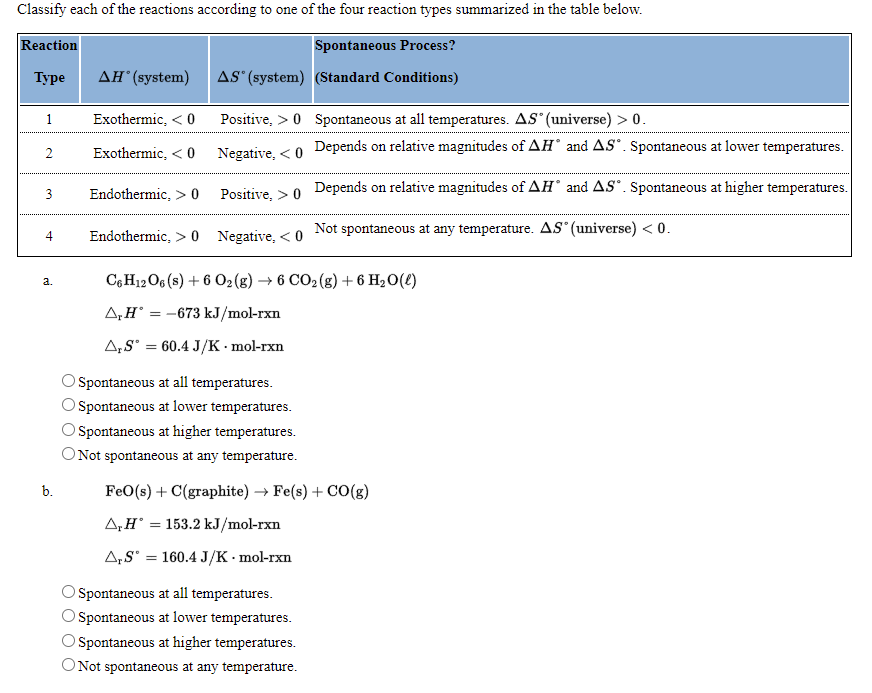
Transcribed Image Text:Classify each of the reactions according to one of the four reaction types summarized in the table below.
Reaction
Spontaneous Process?
Турe
ΔΗ' (system)
AS" (system) (Standard Conditions)
1
Exothermic, < 0
Positive, > 0 Spontaneous at all temperatures. AS (universe) > 0.
Exothermic, < 0
Negative, < 0 Depends on relative magnitudes of AH° and AS°. Spontaneous at lower temperatures.
2
Endothermic, > 0
Positive, > 0 Depends on relative magnitudes of AH and AS°. Spontaneous at higher temperatures.
3
4
Endothermic, > 0 Negative, < 0 Not spontaneous at any temperature. AS" (universe) <0.
C,H12 O6 (s) + 6 O2(g) → 6 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O(L)
a.
A,H° = -673 kJ/mol-rxn
A,S° = 60.4 J/K · mol-rxn
O Spontaneous at all temperatures.
O Spontaneous at lower temperatures.
Spontaneous at higher temperatures.
ONot spontaneous at any temperature.
b.
FeO(s) + C(graphite) → Fe(s) + CO(g)
A,H° = 153.2 kJ/mol-rxn
A,S' = 160.4 J/K · mol-rxn
O Spontaneous at all temperatures.
O Spontaneous at lower temperatures.
Spontaneous at higher temperatures.
ONot spontaneous at any temperature.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning