Consider a frictionless track as shown in the figure below. A block of mass m, = 2.00 kg is released from point O from a height of h = 1.15 m. It makes a perfectly inelastic collision at point ® with a block of mass m, = 2.00 kg that is initially at rest. After the collision, the block of mass m, moves to the right and collides with a spring at point ©. The spring is attached to a wall and has a spring constant of 8.81 kN/m. h (a) Calculate the energy loss during the collision. Enter the magnitude. (b) Calculate the maximum compression of the spring. cm (c) Instead of an inelastic collision, consider a head-on elastic collision at point ®. During this specific elastic collision when the masses are equal, m, transfers its kinetic energy to m, and as a result, m, comes to rest. Calculate the maximum compression of the spring. cm
Consider a frictionless track as shown in the figure below. A block of mass m, = 2.00 kg is released from point O from a height of h = 1.15 m. It makes a perfectly inelastic collision at point ® with a block of mass m, = 2.00 kg that is initially at rest. After the collision, the block of mass m, moves to the right and collides with a spring at point ©. The spring is attached to a wall and has a spring constant of 8.81 kN/m. h (a) Calculate the energy loss during the collision. Enter the magnitude. (b) Calculate the maximum compression of the spring. cm (c) Instead of an inelastic collision, consider a head-on elastic collision at point ®. During this specific elastic collision when the masses are equal, m, transfers its kinetic energy to m, and as a result, m, comes to rest. Calculate the maximum compression of the spring. cm
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Chapter8: Potential Energy And Conservation Of Energy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 56P: In a “Top Fail” video (https://openstaxcollege.org/l/21topfailvideo), two women run at each other...
Related questions
Question
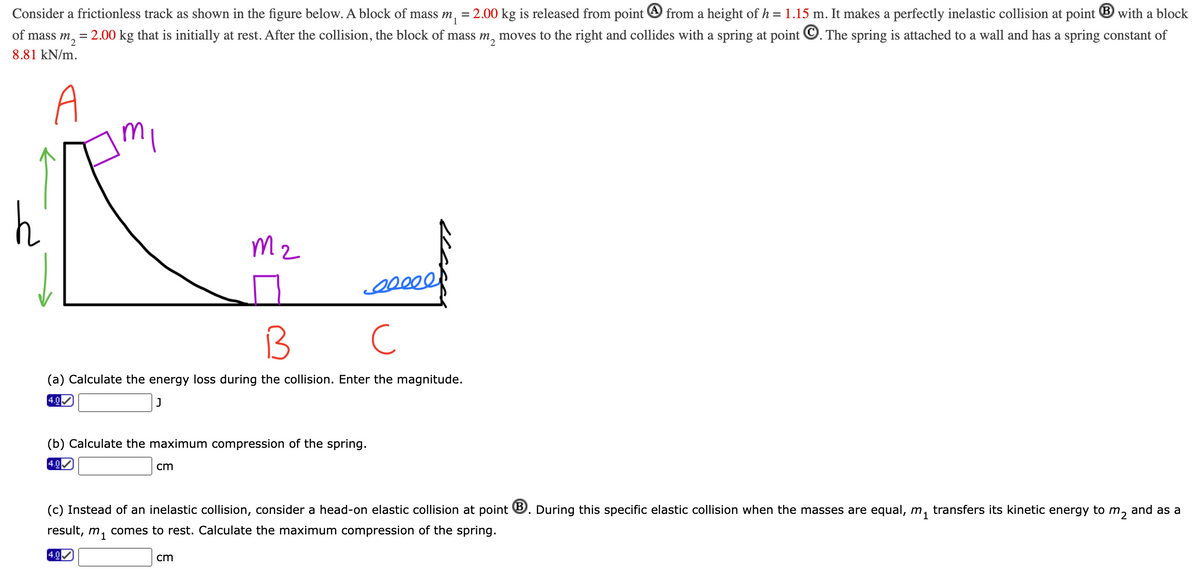
Transcribed Image Text:Consider a frictionless track as shown in the figure below. A block of mass m, = 2.00 kg is released from point O from a height of h = 1.15 m. It makes a perfectly inelastic collision at point ® with a block
of mass m, = 2.00 kg that is initially at rest. After the collision, the block of mass m, moves to the right and collides with a spring at point ©. The spring is attached to a wall and has a spring constant of
8.81 kN/m.
A
m
h
m2
B
(a) Calculate the energy loss during the collision. Enter the magnitude.
4.0
(b) Calculate the maximum compression of the spring.
4.0
cm
(c) Instead of an inelastic collision, consider a head-on elastic collision at point ®. During this specific elastic collision when the masses are equal, m,
transfers its kinetic energy to m, and as a
result, m, comes to rest. Calculate the maximum compression of the spring.
4.0
cm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning