Consider a system employing interrupt-driven I/O for a particular device that trans- fers data at an average of 8 KB/s on a continuous basis. a. Assume that interrupt processing takes about 100 μs (i.e., the time to jump to the interrupt service routine (ISR), execute it, and return to the main program). De- termine what fraction of processor time is consumed by this I/O device if it inter- rupts for every byte. b. Now assume that the device has two 16-byte buffers and interrupts the processor when one of the buffers is full. Naturally, interrupt processing takes longer, be- cause the ISR must transfer 16 bytes. While executing the ISR, the processor takes about 8 us for the transfer of each byte. Determine what fraction of processor time is consumed by this I/O device in this case. c. Now assume that the processor is equipped with a block transfer I/O instruction such as that found on the Z8000. This permits the associated ISR to transfer each byte of a block in only 2 µs. Determine what fraction of processor time is con- sumed by this I/O device in this case.
Consider a system employing interrupt-driven I/O for a particular device that trans- fers data at an average of 8 KB/s on a continuous basis. a. Assume that interrupt processing takes about 100 μs (i.e., the time to jump to the interrupt service routine (ISR), execute it, and return to the main program). De- termine what fraction of processor time is consumed by this I/O device if it inter- rupts for every byte. b. Now assume that the device has two 16-byte buffers and interrupts the processor when one of the buffers is full. Naturally, interrupt processing takes longer, be- cause the ISR must transfer 16 bytes. While executing the ISR, the processor takes about 8 us for the transfer of each byte. Determine what fraction of processor time is consumed by this I/O device in this case. c. Now assume that the processor is equipped with a block transfer I/O instruction such as that found on the Z8000. This permits the associated ISR to transfer each byte of a block in only 2 µs. Determine what fraction of processor time is con- sumed by this I/O device in this case.
Chapter4: Processor Technology And Architecture
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2PE: If a microprocessor has a cycle time of 0.5 nanoseconds, what’s the processor clock rate? If the...
Related questions
Question
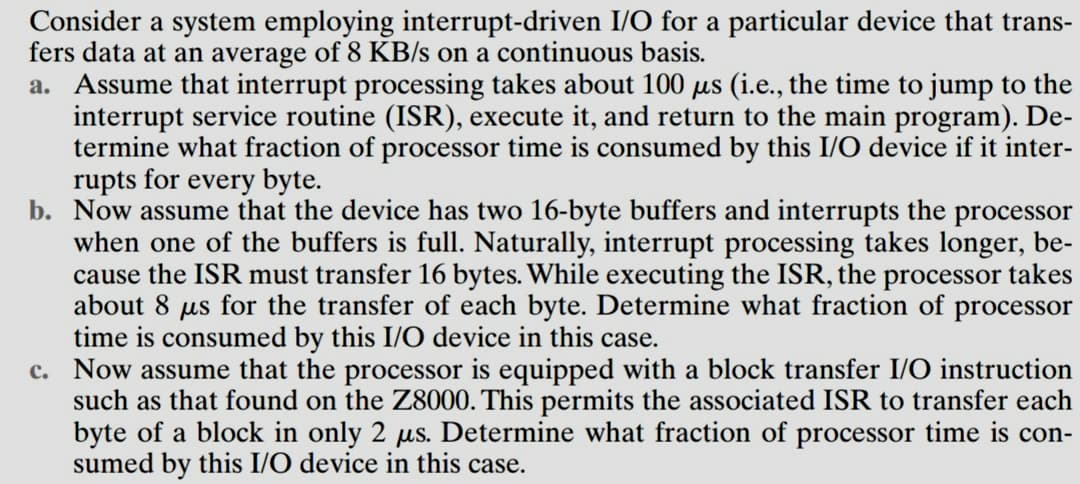
Transcribed Image Text:Consider a system employing interrupt-driven I/O for a particular device that trans-
fers data at an average of 8 KB/s on a continuous basis.
a. Assume that interrupt processing takes about 100 µs (i.e., the time to jump to the
interrupt service routine (ISR), execute it, and return to the main program). De-
termine what fraction of processor time is consumed by this I/O device if it inter-
rupts for every byte.
b. Now assume that the device has two 16-byte buffers and interrupts the processor
when one of the buffers is full. Naturally, interrupt processing takes longer, be-
cause the ISR must transfer 16 bytes. While executing the ISR, the processor takes
about 8 us for the transfer of each byte. Determine what fraction of processor
time is consumed by this I/O device in this case.
c. Now assume that the processor is equipped with a block transfer I/O instruction
such as that found on the Z8000. This permits the associated ISR to transfer each
byte of a block in only 2 µs. Determine what fraction of processor time is con-
sumed by this I/O device in this case.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Systems Architecture
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781305080195
Author:
Stephen D. Burd
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Systems Architecture
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781305080195
Author:
Stephen D. Burd
Publisher:
Cengage Learning