Consider the reaction 2 NO (g) + H2 (g) = N20 (g) + H2O (g) with AH° = + 36 kJ. In which direction, left or right, will the equilibrium shift if the following changes are made? 1. NO is added 2. the system is cooled 3. Hz is removed 4. pressure is increased 5. N20 is added 6. H2 is removed
Consider the reaction 2 NO (g) + H2 (g) = N20 (g) + H2O (g) with AH° = + 36 kJ. In which direction, left or right, will the equilibrium shift if the following changes are made? 1. NO is added 2. the system is cooled 3. Hz is removed 4. pressure is increased 5. N20 is added 6. H2 is removed
Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Chapter8: Gases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 94E: Xenon and fluorine will react to form binary compounds when a mixture of these two gases is heated...
Related questions
Question
Answer only items 1-6. Please provide a brief explanation.
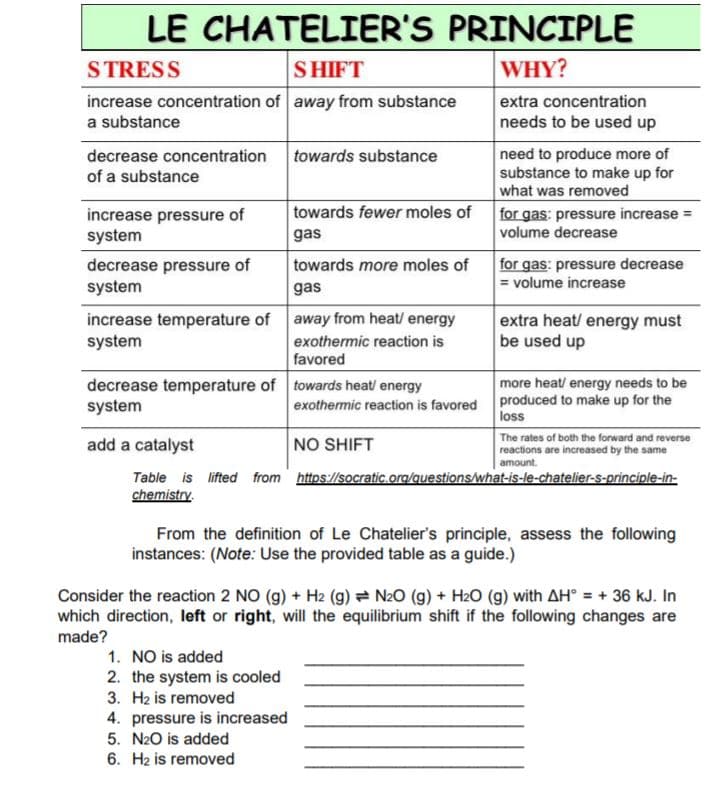
Transcribed Image Text:LE CHATELIER'S PRINCIPLE
STRESS
SHIFT
WHY?
increase concentration of away from substance
extra concentration
a substance
needs to be used up
need to produce more of
substance to make up for
decrease concentration
towards substance
of a substance
what was removed
towards fewer moles of
increase pressure of
system
for gas: pressure increase =
volume decrease
gas
decrease pressure of
system
towards more moles of
for gas: pressure decrease
= volume increase
gas
increase temperature of away from heat/ energy
system
extra heat/ energy must
be used up
exothermic reaction is
favored
more heat/ energy needs to be
decrease temperature of towards heat energy
system
exothermic reaction is favored produced to make up for the
loss
The rates of both the forward and reverse
reactions are increased by the same
amount.
add a catalyst
NO SHIFT
Table is lifted from https://socratic.org/questions/what-is-le-chatelier-S-principle-in-
chemistry.
From the definition of Le Chatelier's principle, assess the following
instances: (Note: Use the provided table as a guide.)
Consider the reaction 2 NO (g) + H2 (g) = N2O (g) + H2O (g) with AH° = + 36 kJ. In
which direction, left or right, will the equilibrium shift if the following changes are
made?
1. NO is added
2. the system is cooled
3. Hz is removed
4. pressure is increased
5. N20 is added
6. H2 is removed
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning