Cost of Goods Manufactured, using Variable Costing and Absorption Costing On March 31, the end of the first year of operations, Barnard Inc., manufactured 3,300 units and sold 2,800 units. The following income statement was prepared, based on the variable costing concept: Sales Variable cost of goods sold: Variable cost of goods manufactured Inventory, March 31 Barnard Inc. Variable Costing Income Statement For the Year Ended March 31, 2011 Total variable cost of goods sold Manufacturing margin Total variable selling and administrative expenses Contribution margin Fixed costs: Fixed manufacturing costs Fixed selling and administrative expenses Total fixed costs Operating income Variable costing Absorption costing $508,200 (77,000) $231,000 72,800 $896,000 (431,200) $464,800 (106,400) $358,400 (303,800) $54,600 Determine the unit cost of goods manufactured, based on (a) the variable costing concept and (b) the absorption costing concept.
Cost of Goods Manufactured, using Variable Costing and Absorption Costing On March 31, the end of the first year of operations, Barnard Inc., manufactured 3,300 units and sold 2,800 units. The following income statement was prepared, based on the variable costing concept: Sales Variable cost of goods sold: Variable cost of goods manufactured Inventory, March 31 Barnard Inc. Variable Costing Income Statement For the Year Ended March 31, 2011 Total variable cost of goods sold Manufacturing margin Total variable selling and administrative expenses Contribution margin Fixed costs: Fixed manufacturing costs Fixed selling and administrative expenses Total fixed costs Operating income Variable costing Absorption costing $508,200 (77,000) $231,000 72,800 $896,000 (431,200) $464,800 (106,400) $358,400 (303,800) $54,600 Determine the unit cost of goods manufactured, based on (a) the variable costing concept and (b) the absorption costing concept.
Managerial Accounting
15th Edition
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Chapter7: Variable Costing For Management
analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3BE: Variable costingsales exceed production The beginning inventory is 52,800 units. All of the units...
Related questions
Question
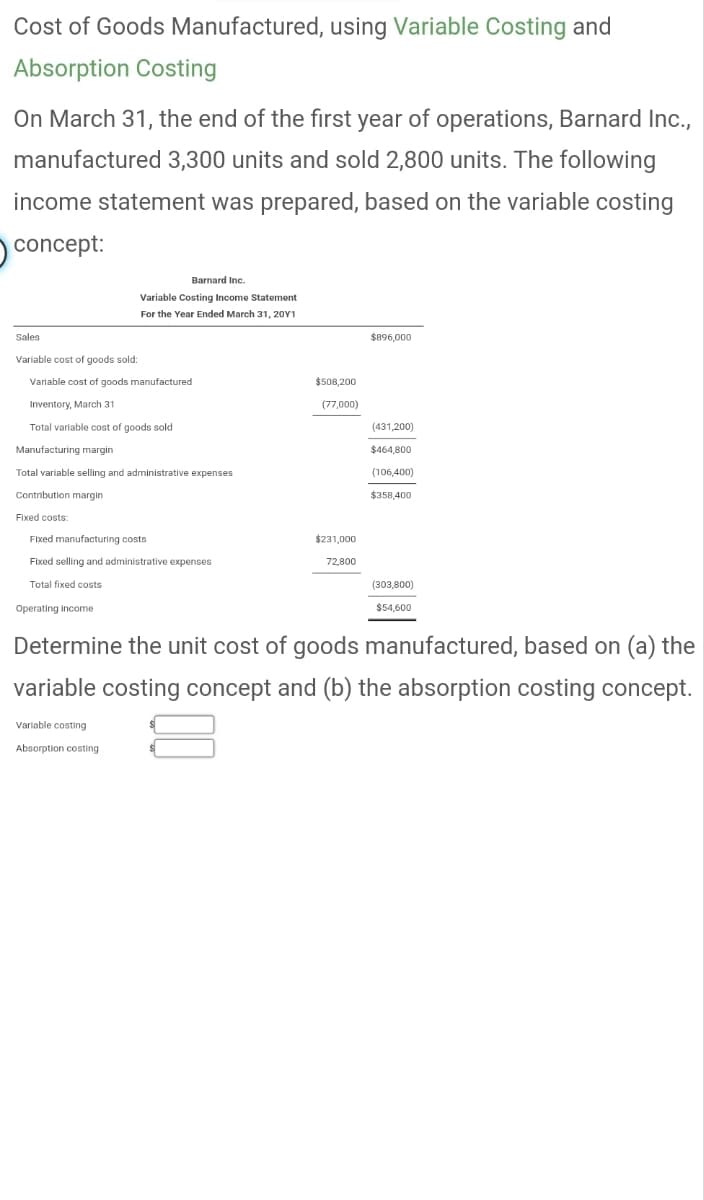
Transcribed Image Text:Cost of Goods Manufactured, using Variable Costing and
Absorption Costing
On March 31, the end of the first year of operations, Barnard Inc.,
manufactured 3,300 units and sold 2,800 units. The following
income statement was prepared, based on the variable costing
concept:
Sales
Variable cost of goods sold:
Variable cost of goods manufactured
Inventory, March 31
Total variable cost of goods sold
Manufacturing margin
Total variable selling and administrative expenses
Contribution margin
Fixed costs:
Barnard Inc.
Variable Costing Income Statement
For the Year Ended March 31, 20Y1
Fixed manufacturing costs
Fixed selling and administrative expenses
Total fixed costs
Operating income
Variable costing
Absorption costing
$508,200
(77,000)
$231,000
72,800
$896,000
(431,200)
$464,800
(106,400)
$358,400
(303,800)
$54,600
Determine the unit cost of goods manufactured, based on (a) the
variable costing concept and (b) the absorption costing concept.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning