Does 10K running time decrease when the runner listens to music? Nine runners were timed as they ran a 10K with and without listening to music. The running times in minutes are shown below. Running Time With 48 58 45 49 41 45 47 40 55 Music Without 54 57 45 48 45 43 50 43 55 Music Assume a Normal distribution. What can be concluded at the the a = 0.05 level of significance? For this study, we should use Hest for the difference betvieen two independent population means a. The null and altemative hypotheses would be: Hạ: ud (please enter a decimal) H1: ud (Please enter a decimal) b. The test statistic (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) c. The p-value = (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) d. The p-value is e. Based on this, we should fail to reject the null hypothesis. f. Thus, the final conclusion is that . The results are statistically insignificant at a = 0.05, so there is insufficient evidence to conclude that the population mean running time with music is less than the population mean running time without music. O The results are statistically significant at a = 0.05, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the nine runners finished in less time on average with music compared to running without music.
Does 10K running time decrease when the runner listens to music? Nine runners were timed as they ran a 10K with and without listening to music. The running times in minutes are shown below. Running Time With 48 58 45 49 41 45 47 40 55 Music Without 54 57 45 48 45 43 50 43 55 Music Assume a Normal distribution. What can be concluded at the the a = 0.05 level of significance? For this study, we should use Hest for the difference betvieen two independent population means a. The null and altemative hypotheses would be: Hạ: ud (please enter a decimal) H1: ud (Please enter a decimal) b. The test statistic (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) c. The p-value = (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) d. The p-value is e. Based on this, we should fail to reject the null hypothesis. f. Thus, the final conclusion is that . The results are statistically insignificant at a = 0.05, so there is insufficient evidence to conclude that the population mean running time with music is less than the population mean running time without music. O The results are statistically significant at a = 0.05, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the nine runners finished in less time on average with music compared to running without music.
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
Only questions B & C- thank you :)
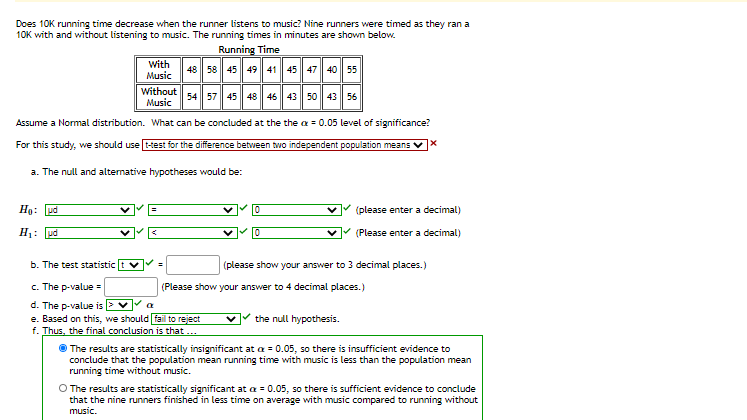
Transcribed Image Text:Does 10K running time decrease when the runner listens to music? Nine runners were timed as they ran a
10K with and without listening to music. The running times in minutes are shown below.
Running Time
With
Music
| 48 58 45 49 41 45 47 40 55
Without
Music
54 57 45 48 46 43 50 43 56
Assume a Normal distribution. What can be concluded at the the a = 0.05 level of significance?
For this study, we should use test for the difference between two independent population means
a. The null and altemative hypotheses would be:
Ho: ud
(please enter a decimal)
H: pd
(Please enter a decimal)
b. The test statistic t v
(please show your answer to 3 decimal places.)
%3D
c. The p-value =
d. The p-value is E ♥
e. Based on this, we should fail to reject
f. Thus, the final conclusion is that ...
(Please show your answer to 4 decimal places. )
the null hypothesis.
The results are statistically insignificant at a = 0.05, so there is insufficient evidence to
conclude that the population mean running time with music is less than the population mean
running time without music.
O The results are statistically significant at a = 0.05, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude
that the nine runners finished in less time on average with music compared to running without
music.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman