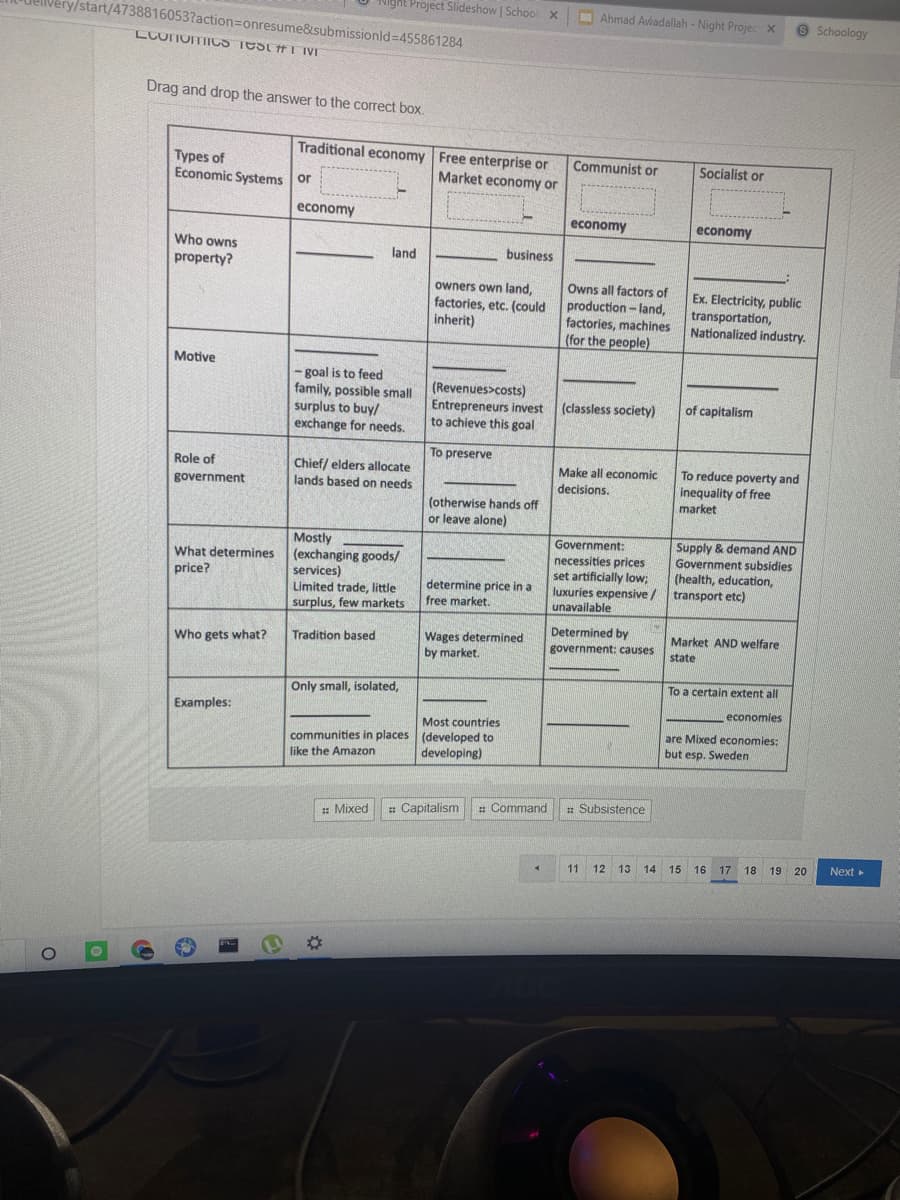
Drag and drop the answer to the correct box. Traditional economy Free enterprise or Market economy or Communist or Types of Economic Systems or Socialist or economy economy economy Who owns land business property? Owns all factors of production -land, factories, machines (for the people) owners own land, factories, etc. (could inherit) Ex. Electricity, public transportation, Nationalized industry. Motive - goal is to feed family, possible small surplus to buy/ exchange for needs. (Revenues>costs) Entrepreneurs invest to achieve this goal (classless society) of capitalism To preserve Role of Chief/ elders allocate lands based on needs To reduce poverty and inequality of free Make all economic government decisions. (otherwise hands off or leave alone) market Supply & demand AND Government subsidies (health, education, Government: Mostly (exchanging goods/ services) Limited trade, little surplus, few markets necessities prices set artificially low; luxuries expensive/ transport etc) unavailable What determines price? determine price in a free market. Determined by Wages determined by market. Market AND welfare Who gets what? Tradition based government: causes state To a certain extent all Only small, isolated, Examples: economies Most countries
Drag and drop the answer to the correct box. Traditional economy Free enterprise or Market economy or Communist or Types of Economic Systems or Socialist or economy economy economy Who owns land business property? Owns all factors of production -land, factories, machines (for the people) owners own land, factories, etc. (could inherit) Ex. Electricity, public transportation, Nationalized industry. Motive - goal is to feed family, possible small surplus to buy/ exchange for needs. (Revenues>costs) Entrepreneurs invest to achieve this goal (classless society) of capitalism To preserve Role of Chief/ elders allocate lands based on needs To reduce poverty and inequality of free Make all economic government decisions. (otherwise hands off or leave alone) market Supply & demand AND Government subsidies (health, education, Government: Mostly (exchanging goods/ services) Limited trade, little surplus, few markets necessities prices set artificially low; luxuries expensive/ transport etc) unavailable What determines price? determine price in a free market. Determined by Wages determined by market. Market AND welfare Who gets what? Tradition based government: causes state To a certain extent all Only small, isolated, Examples: economies Most countries
Chapter1: Making Economics Decisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1QTC
Related questions
Question
100%
Transcribed Image Text:Night Project Slideshow | Schoolx
O Ahmad Awadallah - Night Projec x
very/start/47388160537action=onresume&submissionid%-D455861284
6
Schoology
LCONONTIICS TESL HI IVI
Drag and drop the answer to the correct box.
Traditional economy Free enterprise or
Communist or
Types of
Economic Systems or
Socialist or
Market economy or
economy
economy
economy
Who owns
land
business
property?
owners own land,
factories, etc. (could
inherit)
Owns all factors of
production - land,
factories, machines
(for the people)
Ex. Electricity, public
transportation,
Nationalized industry.
Motive
- goal is to feed
family, possible small
surplus to buy/
exchange for needs.
(Revenues>costs)
Entrepreneurs invest
to achieve this goal
(classless society)
of capitalism
To preserve
Role of
Chief/ elders allocate
lands based on needs
To reduce poverty and
inequality of free
market
Make all economic
government
decisions,
(otherwise hands off
or leave alone)
Mostly
What determines (exchanging goods/
services)
Limited trade, little
surplus, few markets
Supply & demand AND
Government subsidies
(health, education,
Government:
necessities prices
set artificially low;
luxuries expensive /
price?
determine price in a
free market.
transport etc)
unavailable
Determined by
Wages determined
by market.
Tradition based
Market AND welfare
Who gets what?
government: causes
state
To a certain extent all
Only small, isolated,
Examples:
economies
Most countries
are Mixed economies:
communities in places (developed to
developing)
but esp. Sweden
like the Amazon
# Capitalism
: Command
: Subsistence
: Mixed
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Next
11
12
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-…
Economics
ISBN:
9781259290619
Author:
Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education