3.14 A single-phase 50-kVA, 2400/240-volt, 60-Hz distribution transformer is used as a step-down transformer at the load end of a 2400-volt feeder whose series impedance is (1.0 + j2.0) ohms. The equivalent series impedance of the transformer is (1.0 + j2.5) ohms referred to the high- voltage (primary) side. The transformer is delivering rated load at a 0.8 power factor lagging and at a rated secondary voltage. Neglecting the transformer exciting current, determine (a) the voltage at the transformer primary terminals, (b) the voltage at the sending end of the feeder, and (c) the real and reactive power delivered to the sending end of the feeder.
3.14 A single-phase 50-kVA, 2400/240-volt, 60-Hz distribution transformer is used as a step-down transformer at the load end of a 2400-volt feeder whose series impedance is (1.0 + j2.0) ohms. The equivalent series impedance of the transformer is (1.0 + j2.5) ohms referred to the high- voltage (primary) side. The transformer is delivering rated load at a 0.8 power factor lagging and at a rated secondary voltage. Neglecting the transformer exciting current, determine (a) the voltage at the transformer primary terminals, (b) the voltage at the sending end of the feeder, and (c) the real and reactive power delivered to the sending end of the feeder.
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305632134
Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Chapter3: Power Transformers
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3.14P: A single-phase 50-kVA,2400/240-volt,60-Hz distribution transformer is used as a step-down...
Related questions
Question
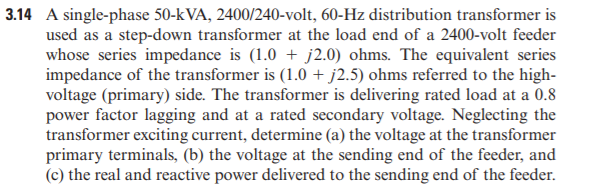
Transcribed Image Text:3.14 A single-phase 50-kVA, 2400/240-volt, 60-Hz distribution transformer is
used as a step-down transformer at the load end of a 2400-volt feeder
whose series impedance is (1.0 + j2.0) ohms. The equivalent series
impedance of the transformer is (1.0 + j2.5) ohms referred to the high-
voltage (primary) side. The transformer is delivering rated load at a 0.8
power factor lagging and at a rated secondary voltage. Neglecting the
transformer exciting current, determine (a) the voltage at the transformer
primary terminals, (b) the voltage at the sending end of the feeder, and
(c) the real and reactive power delivered to the sending end of the feeder.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course …
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305632134
Author:
J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course …
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305632134
Author:
J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:
Cengage Learning