Experiment #1 From Antoinette de Senna's Master's thesis on "Screening of biological control organisms for the management of phytopathogenic fungi and foodborne pathogens on produce". Objective: To screen three LAB (Lactobacillus plantarum, Pediecoccus acidilactici, and Pediococcus pentosaceus) for antimicrobial activity against the foodborne pathogens Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella, and Escherichia coli. Methods: 1 ml of the pathogen was placed into a petri dish. Then. 15-20 mi molten tryptic soy agar (TSA) tempered to 50°C was added. When the TSA solidified, a loopful of LAB was spotted onto the agar. Plates were incubated at 35°C for 24 hours then the zone of inhibition was measured from the boarder of the bacterial colony to the perimeter of the clkaring. Results: E col OIS7H7 Questions: 1. What is the independent variable? 2. What is the dependent variable? P. pontonv
Experiment #1 From Antoinette de Senna's Master's thesis on "Screening of biological control organisms for the management of phytopathogenic fungi and foodborne pathogens on produce". Objective: To screen three LAB (Lactobacillus plantarum, Pediecoccus acidilactici, and Pediococcus pentosaceus) for antimicrobial activity against the foodborne pathogens Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella, and Escherichia coli. Methods: 1 ml of the pathogen was placed into a petri dish. Then. 15-20 mi molten tryptic soy agar (TSA) tempered to 50°C was added. When the TSA solidified, a loopful of LAB was spotted onto the agar. Plates were incubated at 35°C for 24 hours then the zone of inhibition was measured from the boarder of the bacterial colony to the perimeter of the clkaring. Results: E col OIS7H7 Questions: 1. What is the independent variable? 2. What is the dependent variable? P. pontonv
Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap Course List)
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781111306663
Author:Margaret Rodriguez, Paul Price
Publisher:Margaret Rodriguez, Paul Price
Chapter13: Gram-positive Bacilli
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1UTM
Related questions
Question
I need help anwering questions 6-10 only. Thanks.

Transcribed Image Text:3. Suggest a control for this experiment?
4. What is the optimal temperature range for Listeria monocyogenes? Is L. monocyogenes a
psychrophile, psychrophile, mesophile, or themophile?
5. What the optimal pH range for Lactobacillus plantarum? Is Lb. plantarum an acidophile,
neutraphile, or alkalophile?
6. What is the toxin produced by E. coli O157:H7 that was encode by phage as a
consequence of lysogenic conversion? Explain the medical importance.
7. Which bacterial culture (Lb. plantarum, P. acidilactici, or P. pentosaceus) was most
effective against L. monocytogenes and Salmonella? Explain why.
8. What are the limitations of using an agar disk diffusion assay to assess the
effectiveness of an antiseptic, disinfectant, or, in this case, a biological control agent
on the growth of bacteria of interest?
9. LAB produce organic acids that have shown to be effective against controlling the
growth of foodborne pathogens. What specific organic acid is produced by LAB during
fermentation?
10. What is the logical next step to validate the efficacy of the biological control agent?
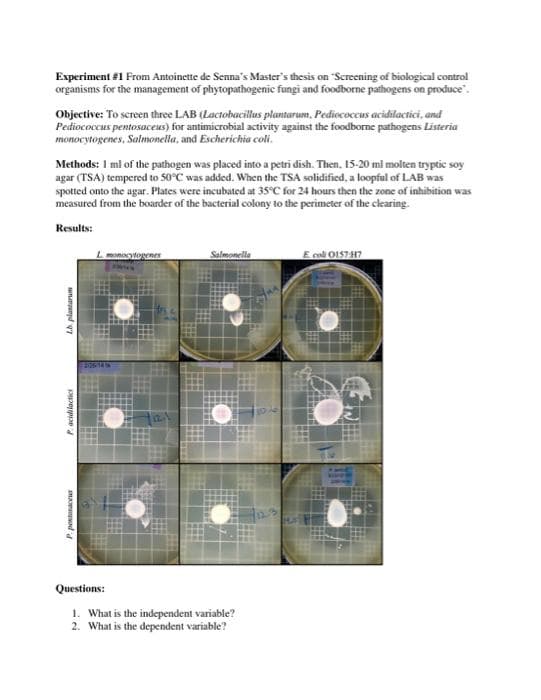
Transcribed Image Text:Experiment #1 From Antoinette de Senna's Master's thesis on "Screening of biological control
organisms for the management of phytopathogenic fungi and foodborne pathogens on produce".
Objective: To screen three LAB (Lactobacillus plantarum, Pediococcus acidilactici, and
Pediococcus pentosaceus) for antimicrobial activity against the foodborne pathogens Listeria
monocytogenes, Salmonella, and Escherichia coli.
Methods: 1 ml of the pathogen was placed into a petri dish. Then, 15-20 ml molten tryptic soy
agar (TSA) tempered to 50°C was added. When the TSA solidified, a loopful of LAB was
spotted onto the agar. Plates were incubated at 35°C for 24 hours then the zone of inhibition was
measured from the boarder of the bacterial colony to the perimeter of the clearing.
Results:
Lmonocytogenes
Salmonella
E col O157-H7
Questions:
1. What is the independent variable?
2. What is the dependent variable?
Pacidilactici
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781111306663
Author:
Margaret Rodriguez, Paul Price
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781111306663
Author:
Margaret Rodriguez, Paul Price
Publisher:
Cengage Learning