Explain why each substance below is soluble or not by picking one of the following explanations below: Table Sugar A. A. Structure is non-polar and cannot hydrogen bond with water. * Honey • Cornstarch B. B. Structure is polar and can hydrogen bond with water * White milk C. C. The non-polar hydrocarbon portion overshadows the polar portion. * Potato Celery D. D. There are not enough reducing ends or exposed aldehydes to be oxidized. E. E. Structure is non-polar and can form dispersion forces with water F. F. Structure is too large to be reduced but forms dipole-dipole interaction
Explain why each substance below is soluble or not by picking one of the following explanations below: Table Sugar A. A. Structure is non-polar and cannot hydrogen bond with water. * Honey • Cornstarch B. B. Structure is polar and can hydrogen bond with water * White milk C. C. The non-polar hydrocarbon portion overshadows the polar portion. * Potato Celery D. D. There are not enough reducing ends or exposed aldehydes to be oxidized. E. E. Structure is non-polar and can form dispersion forces with water F. F. Structure is too large to be reduced but forms dipole-dipole interaction
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Chapter1: Biochemistry: An Evolving Science
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
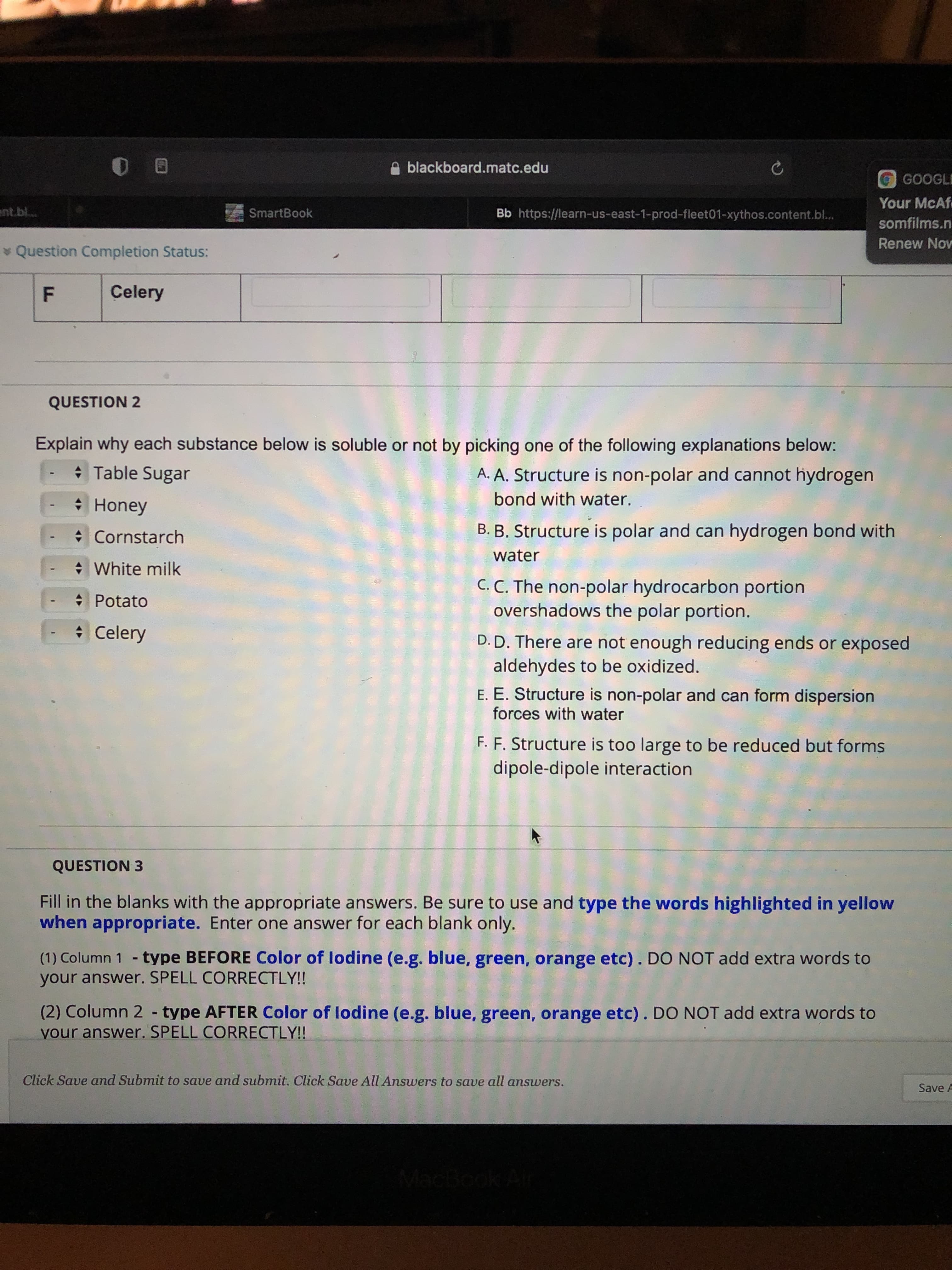
Transcribed Image Text:Explain why each substance below is soluble or not by picking one of the following explanations below:
Table Sugar
A. A. Structure is non-polar and cannot hydrogen
bond with water.
* Honey
• Cornstarch
B. B. Structure is polar and can hydrogen bond with
water
* White milk
C. C. The non-polar hydrocarbon portion
overshadows the polar portion.
* Potato
Celery
D. D. There are not enough reducing ends or exposed
aldehydes to be oxidized.
E. E. Structure is non-polar and can form dispersion
forces with water
F. F. Structure is too large to be reduced but forms
dipole-dipole interaction

Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781319114671
Author:
Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781464126116
Author:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul…
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781118918401
Author:
Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:
WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781319114671
Author:
Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781464126116
Author:
David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul…
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781118918401
Author:
Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:
WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305961135
Author:
Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological …
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9780134015187
Author:
John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:
PEARSON