Locust Software sells computer training packages to its business customers at a price of $101. The cost of production (in present value terms) is $99. Locust sells its packages on terms of net 30 and estimates that about 7% of all orders will be uncollectible. An order comes in for 30 units. The interest rate is 1.3% per month. Required: a-1. Calculate the profit or loss if this is a one-time order and sale will not be made unless credit is extended a-2. Should the firm extend credit if this is a one-time order? b. What is the break-even probability of collection? c-1. Now suppose that if the customer pays this month's bill, they will place an identical order in each month indefinitely and can be safely assumed to pose no risk of default.Calculate the present value of the sale. c-2. Should credit be extended? d. What is the break-even probability of collection in the repeat-sales case? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A1 A2 and Req C1 C2 and B D c-1. Now suppose that if the customer pays this month's bill, they will place an identical order in each month indefinitely and can be safely assumed to pose no risk of default.Calculate the present value of the sale. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) c-2. Should credit be extended? d. What is the break-even probability of collection in the repeat-sales case? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter your answer as a percent rounded to 1 decimal place.) Show less A c-1. Present value c-2. Should credit be extended? d. Break-even probability % < Req A1 A2 and B Req C1 C2 and D Locust Software sells computer training packages to its business customers at a price of $101. The cost of production (in present value terms) is $99. Locust sells its packages on terms of net 30 and estimates that about 7% of all orders will be uncollectible. An order comes in for 30 units. The interest rate is 1.3% per month. Required: a-1. Calculate the profit or loss if this is a one-time order and sale will not be made unless credit is extended a-2. Should the firm extend credit if this is a one-time order? b. What is the break-even probability of collection? c-1. Now suppose that if the customer pays this month's bill, they will place an identical order in each month indefinitely and can be safely assumed to pose no risk of default.Calculate the present value of the sale. c-2. Should credit be extended? d. What is the break-even probability of collection in the repeat-sales case? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A1 A2 and Req C1 C2 and B D c-1. Now suppose that if the customer pays this month's bill, they will place an identical order in each month indefinitely and can be safely assumed to pose no risk of default.Calculate the present value of the sale. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) c-2. Should credit be extended? d. What is the break-even probability of collection in the repeat-sales case? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter your answer as a percent rounded to 1 decimal place.) Show less A c-1. Present value c-2. Should credit be extended? d. Break-even probability % < Req A1 A2 and B Req C1 C2 and D
Locust Software sells computer training packages to its business customers at a price of $101. The cost of production (in present value terms) is $99. Locust sells its packages on terms of net 30 and estimates that about 7% of all orders will be uncollectible. An order comes in for 30 units. The interest rate is 1.3% per month. Required: a-1. Calculate the profit or loss if this is a one-time order and sale will not be made unless credit is extended a-2. Should the firm extend credit if this is a one-time order? b. What is the break-even probability of collection? c-1. Now suppose that if the customer pays this month's bill, they will place an identical order in each month indefinitely and can be safely assumed to pose no risk of default.Calculate the present value of the sale. c-2. Should credit be extended? d. What is the break-even probability of collection in the repeat-sales case? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A1 A2 and Req C1 C2 and B D c-1. Now suppose that if the customer pays this month's bill, they will place an identical order in each month indefinitely and can be safely assumed to pose no risk of default.Calculate the present value of the sale. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) c-2. Should credit be extended? d. What is the break-even probability of collection in the repeat-sales case? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter your answer as a percent rounded to 1 decimal place.) Show less A c-1. Present value c-2. Should credit be extended? d. Break-even probability % < Req A1 A2 and B Req C1 C2 and D Locust Software sells computer training packages to its business customers at a price of $101. The cost of production (in present value terms) is $99. Locust sells its packages on terms of net 30 and estimates that about 7% of all orders will be uncollectible. An order comes in for 30 units. The interest rate is 1.3% per month. Required: a-1. Calculate the profit or loss if this is a one-time order and sale will not be made unless credit is extended a-2. Should the firm extend credit if this is a one-time order? b. What is the break-even probability of collection? c-1. Now suppose that if the customer pays this month's bill, they will place an identical order in each month indefinitely and can be safely assumed to pose no risk of default.Calculate the present value of the sale. c-2. Should credit be extended? d. What is the break-even probability of collection in the repeat-sales case? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A1 A2 and Req C1 C2 and B D c-1. Now suppose that if the customer pays this month's bill, they will place an identical order in each month indefinitely and can be safely assumed to pose no risk of default.Calculate the present value of the sale. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) c-2. Should credit be extended? d. What is the break-even probability of collection in the repeat-sales case? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter your answer as a percent rounded to 1 decimal place.) Show less A c-1. Present value c-2. Should credit be extended? d. Break-even probability % < Req A1 A2 and B Req C1 C2 and D
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Business Decision-Making
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337115773
Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Chapter8: Tactical Decision-making And Relevant Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 41E
Related questions
Question
I need the second Req please! Thank you.
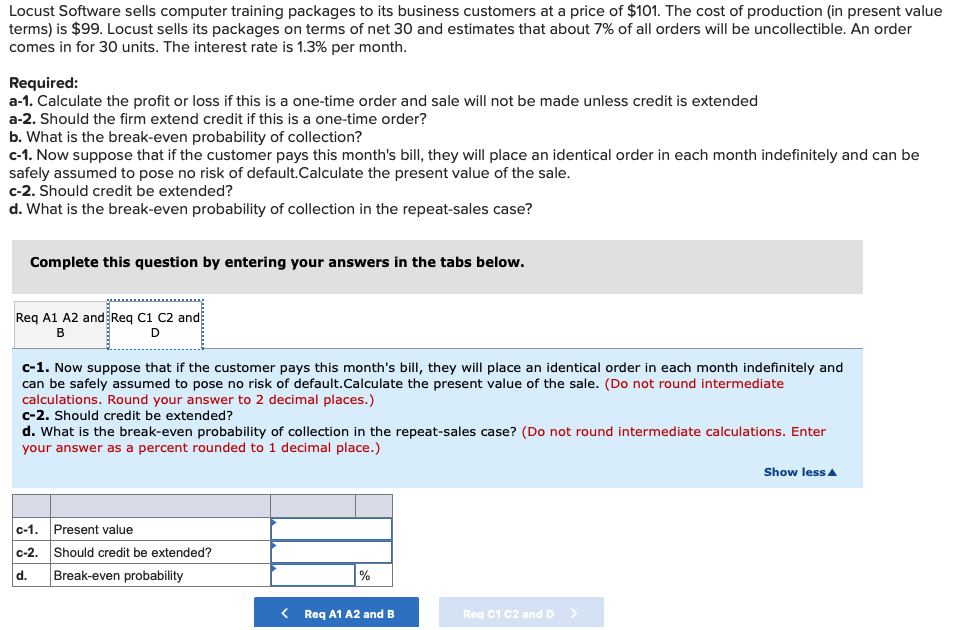
Transcribed Image Text:Locust Software sells computer training packages to its business customers at a price of $101. The cost of production (in present value
terms) is $99. Locust sells its packages on terms of net 30 and estimates that about 7% of all orders will be uncollectible. An order
comes in for 30 units. The interest rate is 1.3% per month.
Required:
a-1. Calculate the profit or loss if this is a one-time order and sale will not be made unless credit is extended
a-2. Should the firm extend credit if this is a one-time order?
b. What is the break-even probability of collection?
c-1. Now suppose that if the customer pays this month's bill, they will place an identical order in each month indefinitely and can be
safely assumed to pose no risk of default.Calculate the present value of the sale.
c-2. Should credit be extended?
d. What is the break-even probability of collection in the repeat-sales case?
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Req A1 A2 and Req C1 C2 and
B
D
c-1. Now suppose that if the customer pays this month's bill, they will place an identical order in each month indefinitely and
can be safely assumed to pose no risk of default.Calculate the present value of the sale. (Do not round intermediate
calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)
c-2. Should credit be extended?
d. What is the break-even probability of collection in the repeat-sales case? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter
your answer as a percent rounded to 1 decimal place.)
Show less A
c-1. Present value
c-2. Should credit be extended?
d.
Break-even probability
%
< Req A1 A2 and B
Req C1 C2 and D
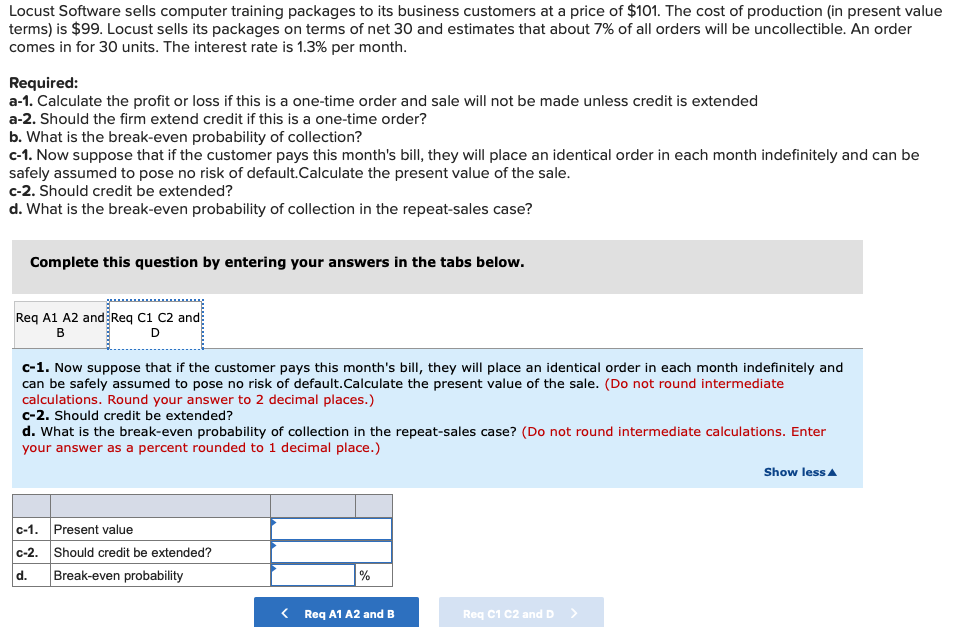
Transcribed Image Text:Locust Software sells computer training packages to its business customers at a price of $101. The cost of production (in present value
terms) is $99. Locust sells its packages on terms of net 30 and estimates that about 7% of all orders will be uncollectible. An order
comes in for 30 units. The interest rate is 1.3% per month.
Required:
a-1. Calculate the profit or loss if this is a one-time order and sale will not be made unless credit is extended
a-2. Should the firm extend credit if this is a one-time order?
b. What is the break-even probability of collection?
c-1. Now suppose that if the customer pays this month's bill, they will place an identical order in each month indefinitely and can be
safely assumed to pose no risk of default.Calculate the present value of the sale.
c-2. Should credit be extended?
d. What is the break-even probability of collection in the repeat-sales case?
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Req A1 A2 and Req C1 C2 and
B
D
c-1. Now suppose that if the customer pays this month's bill, they will place an identical order in each month indefinitely and
can be safely assumed to pose no risk of default.Calculate the present value of the sale. (Do not round intermediate
calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)
c-2. Should credit be extended?
d. What is the break-even probability of collection in the repeat-sales case? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter
your answer as a percent rounded to 1 decimal place.)
Show less A
c-1. Present value
c-2. Should credit be extended?
d.
Break-even probability
%
< Req A1 A2 and B
Req C1 C2 and D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning