Find the reaction order (n), reaction rate constant (k) and reaction rate general form using integral method. Integral method steps:1. Assume a first order reaction (n= 1) 2. Integrate the reaction rate to find CA and time linear relation 3. Plot CA versus time to see if you get a straight line. If not, the assumption is not correct andassume a second order reaction (n=2), and repeat same procedure till linear plot achieved I want full answer with all solution steps plz
Find the reaction order (n), reaction rate constant (k) and reaction rate general form using integral method. Integral method steps:1. Assume a first order reaction (n= 1) 2. Integrate the reaction rate to find CA and time linear relation 3. Plot CA versus time to see if you get a straight line. If not, the assumption is not correct andassume a second order reaction (n=2), and repeat same procedure till linear plot achieved I want full answer with all solution steps plz
Chapter8: Polyfunctional Acids And Bases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9P
Related questions
Question
Find the reaction order (n), reaction rate constant (k) and reaction rate general form using integral method.
Integral method steps:1. Assume a first order reaction (n= 1)
2. Integrate the reaction rate to find CA and time linear relation
3. Plot CA versus time to see if you get a straight line. If not, the assumption is not correct andassume a second order reaction (n=2), and repeat same procedure till linear plot achieved
I want full answer with all solution steps plz
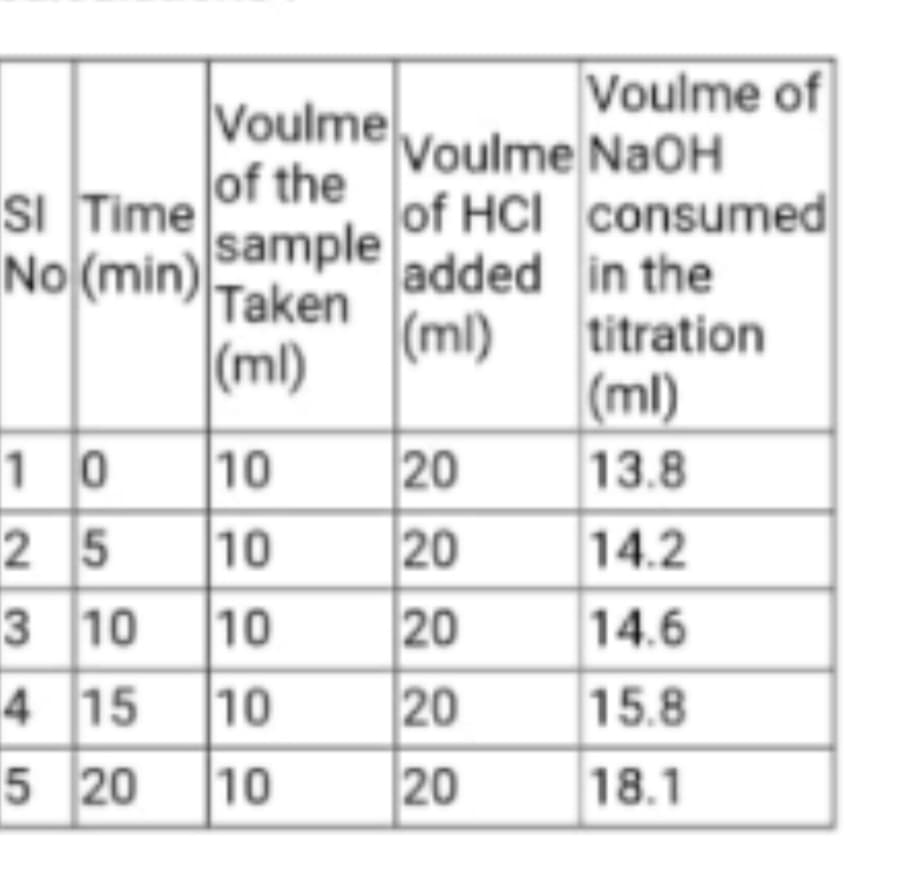
Transcribed Image Text:Voulme of
Voulme Voulme NaOH
of the
sI Time
No (min) sample
(ml)
of HCI consumed
Taken
added in the
(ml)
titration
|(ml)
10 10
25 10
20
13.8
20
14.2
3 10
10
20
14.6
4 15 10
20
15.8
5 20
10
20
18.1
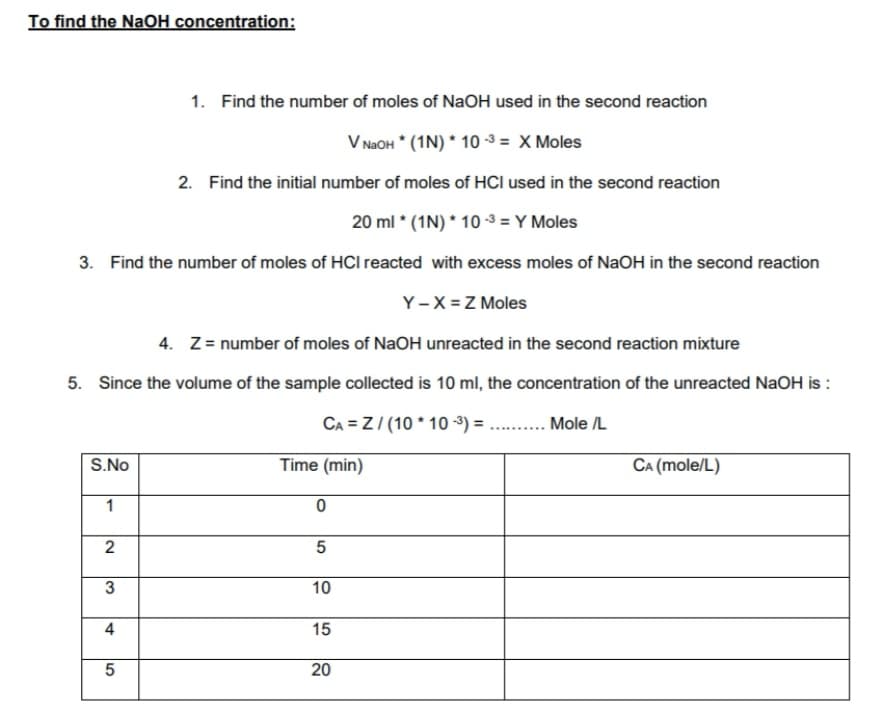
Transcribed Image Text:To find the NaOH concentration:
1. Find the number of moles of NaOH used in the second reaction
V NAOH * (1N) * 10 -3 = X Moles
2. Find the initial number of moles of HCI used in the second reaction
20 ml * (1N) * 10 -3 = Y Moles
3. Find the number of moles of HCI reacted with excess moles of NaOH in the second reaction
Y-X = Z Moles
4. Z= number of moles of NaOH unreacted in the second reaction mixture
5. Since the volume of the sample collected is 10 ml, the concentration of the unreacted NaOH is :
CA = Z/ (10 * 10 -3) = .. .
Mole /L
S.No
Time (min)
CA (mole/L)
1
5
3
10
15
20
2.
4,
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you







Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning