For each price in the following table, calculate the firm's optimal quantity of units to produce, and determine the profit or loss if it produces at that quantity, using the data from the graph to identify its total variable cost. Assume that if the firm is indiffferent between producing and shutting down, it will produce. (Hint: You can select the purple points (damond symbols] on the graph to see precise information on average variable cost.) Price Total Revenue Fixed Cost Quantity (Pans) Variable Cost Profit (Dollars per pan) (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) 25.00 1,600,000 70.00 1,600,000 100.00 1,600,000 If the firm shuts down, it must incur its fixed costs (FC) in the short run. In this case, the firm's fixed cost is $1,600,000 per day. In other words, if it shuts down, the firm would suffer losses of $1,600,000 per day until its fxed costs end (such as the expiration of a building lease). This firm's shutdown price-that is, the price below which it is optimal for the firm to shut down-is per pan.
For each price in the following table, calculate the firm's optimal quantity of units to produce, and determine the profit or loss if it produces at that quantity, using the data from the graph to identify its total variable cost. Assume that if the firm is indiffferent between producing and shutting down, it will produce. (Hint: You can select the purple points (damond symbols] on the graph to see precise information on average variable cost.) Price Total Revenue Fixed Cost Quantity (Pans) Variable Cost Profit (Dollars per pan) (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) 25.00 1,600,000 70.00 1,600,000 100.00 1,600,000 If the firm shuts down, it must incur its fixed costs (FC) in the short run. In this case, the firm's fixed cost is $1,600,000 per day. In other words, if it shuts down, the firm would suffer losses of $1,600,000 per day until its fxed costs end (such as the expiration of a building lease). This firm's shutdown price-that is, the price below which it is optimal for the firm to shut down-is per pan.
Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
14th Edition
ISBN:9781337794992
Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Chapter7: Production, Inputs, And Cost: Building Blocks For Supply Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1DQ
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Homework (Ch 14)
Back to Assignment
Attempts
Keep the Highest/2
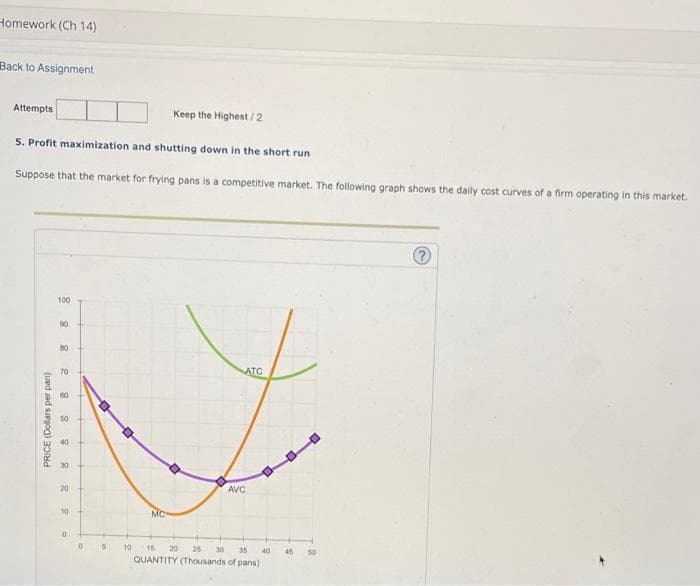
5. Profit maximization and shutting down in the short run
Suppose that the market for frying pans is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market.
100
90
80
70
ATC
50
40
30
20
AVC
10
MC
10
15
20
25 30
35
40
45
50
QUANTITY (Thousands of pans)
PRICE (Dollars per pan)
![20
AVC
10
MC
15
t0
15
20 25
30
35
40
45
50
QUANTITY (Thousands of pans)
For each price in the following table, calculate the firm's optimal quantity of units to produce, and determine the profit or loss if it produces at that
quantity, using the data from the graph to identify its total variable cost. Assume that if the firm is indifferent between producing and shutting down,
it will produce. (Hint: You can select the purple points (diamond symbols] on the graph to see precise information on average variable cost.)
Price
Quantity
(Pans)
Total Revenue
Fixed Cost
Variable Cost
Profit
(Dollars per pan)
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
25.00
1,600,000
70.00
1,600,000
100.00
1,600,000
If the firm shuts down, it must incur its foxed costs (FC) in the short run. In this case, the firm's fxed cost is $1,600,000 per day. In other words, if it
shuts down, the firm would suffer losses of $1,600,000 per day until its fixed costs end (such as the expiration of a building lease).
This firm's shutdown price-that is, the price below which it is optimal for the firm to shut down-is
per pan.
Grade It Now
Savee Continue
Continue without saving](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F1f36f778-24d5-4069-ac57-b05e49ea1e9f%2F5e71e33a-c15a-4596-bea2-fbd14bcf8700%2Fb3vnxjc_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:20
AVC
10
MC
15
t0
15
20 25
30
35
40
45
50
QUANTITY (Thousands of pans)
For each price in the following table, calculate the firm's optimal quantity of units to produce, and determine the profit or loss if it produces at that
quantity, using the data from the graph to identify its total variable cost. Assume that if the firm is indifferent between producing and shutting down,
it will produce. (Hint: You can select the purple points (diamond symbols] on the graph to see precise information on average variable cost.)
Price
Quantity
(Pans)
Total Revenue
Fixed Cost
Variable Cost
Profit
(Dollars per pan)
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
25.00
1,600,000
70.00
1,600,000
100.00
1,600,000
If the firm shuts down, it must incur its foxed costs (FC) in the short run. In this case, the firm's fxed cost is $1,600,000 per day. In other words, if it
shuts down, the firm would suffer losses of $1,600,000 per day until its fixed costs end (such as the expiration of a building lease).
This firm's shutdown price-that is, the price below which it is optimal for the firm to shut down-is
per pan.
Grade It Now
Savee Continue
Continue without saving
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning