For the following unbalanced equation, calculate how many moles of the second reactant would be required to react completely with 0.310 moles of the first reactant. Co(s) + F2(9) → COF3(s) |mol F2 Submit b For the following unbalanced equation, calculate how many moles of the second reactant would be required to react completely with 0.192 moles of the first reactant. Al(s) + H2SO, (ag) → Al (SO,)s(s) + H2 (9) |mol H,SO4 For the following unbalanced equation, calculate how many moles of the second reactant would be required to react completely with 0.424 moles of the first reactant. K(s) + H30(1) → KOH(ag) + H2(9) |mol H20 d For the following unbalanced equation, calculate how many moles of the second reactant would be required to react completely with 0.588 moles of the first reactant. Cu(s) + O2 (9) → CugO(s) mol O2
For the following unbalanced equation, calculate how many moles of the second reactant would be required to react completely with 0.310 moles of the first reactant. Co(s) + F2(9) → COF3(s) |mol F2 Submit b For the following unbalanced equation, calculate how many moles of the second reactant would be required to react completely with 0.192 moles of the first reactant. Al(s) + H2SO, (ag) → Al (SO,)s(s) + H2 (9) |mol H,SO4 For the following unbalanced equation, calculate how many moles of the second reactant would be required to react completely with 0.424 moles of the first reactant. K(s) + H30(1) → KOH(ag) + H2(9) |mol H20 d For the following unbalanced equation, calculate how many moles of the second reactant would be required to react completely with 0.588 moles of the first reactant. Cu(s) + O2 (9) → CugO(s) mol O2
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter9: Chemical Quantities
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 43QAP: Consider the equation: 2A+B5C. If 10.0 g of A reacts with 5.00 g of B. how is the limiting reactant...
Related questions
Question
|
For the following balanced chemical equation, calculate how many moles of products would be produced if |
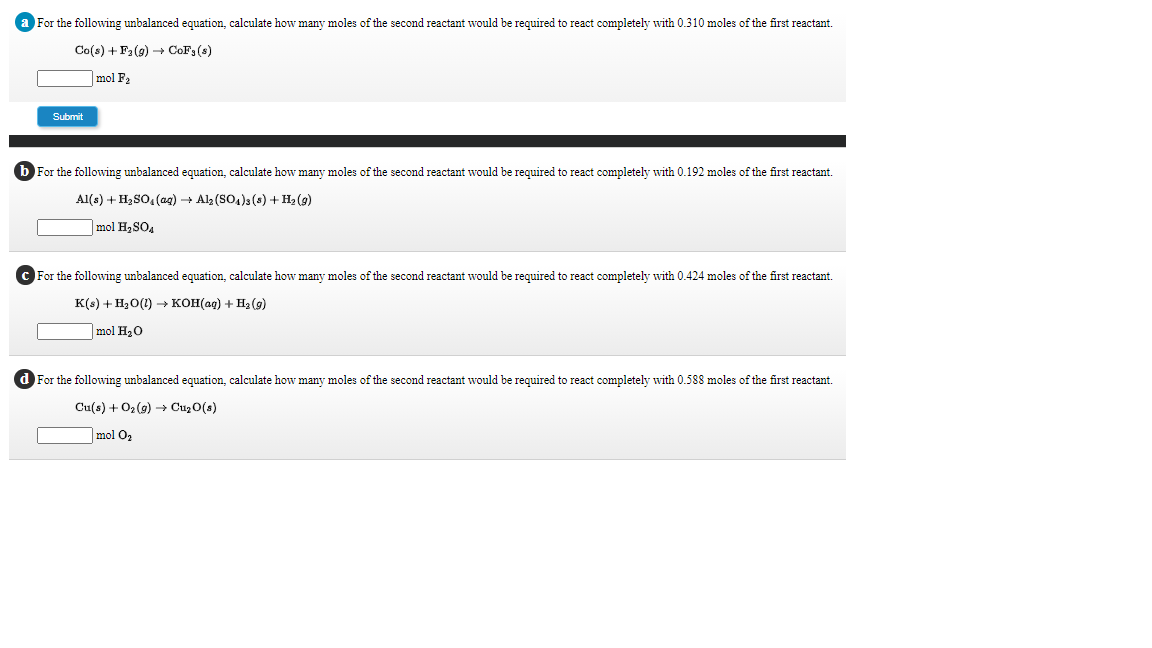
Transcribed Image Text:For the following unbalanced equation, calculate how many moles of the second reactant would be required to react completely with 0.310 moles of the first reactant.
Co(s) + F2(9) → CoF;(s)
mol F2
Submit
b For the following unbalanced equation, calculate how many moles of the second reactant would be required to react completely with 0.192 moles of the first reactant.
Al(s) + H2SO, (ag) + Alz (SO4)3(s) + H2 (9)
mol H, SO,
For the following unbalanced equation, calculate how many moles of the second reactant would be required to react completely with 0.424 moles of the first reactant.
К() + Н,о() — кон(ад) + Hа (9)
mol H20
d For the following unbalanced equation, calculate how many moles of the second reactant would be required to react completely with 0.588 moles of the first reactant.
Cu(s) + 02 (g) -→ CuzO(s)
mol O2
![For the following balanced chemical equation, calculate how many grams of the products would be produced by complete reaction of 0.285 mol of the first reactant.
AGNO, (ag) + LIOH(ag) → AGOH(s) + LINO3 (ag)
]g AgOH
g LINOS
Submit
b For the following balanced chemical equation, calculate how many grams of the products would be produced by complete reaction of 0.105 mol of the first reactant.
Al3 (SO,)s (ag) + 3CaCl, (ag) → 2AICl (ag) + 3CaSO,(s)
g AICI3
|g CaSO4
C For the following balanced chemical equation, calculate how many grams of the products would be produced by complete reaction of 0.155 mol of the first reactant.
CaCO: (s) + 2HCI(ag) + CaCl2 (ag) + CO2 (g) + H0(1)
g CaCl2
g CO2
g H20](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F41533dd6-be05-40da-a627-190380aa1e53%2F92e80e51-9d1f-4d8c-b6d0-a617c8ac9b09%2Ft4815p_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:For the following balanced chemical equation, calculate how many grams of the products would be produced by complete reaction of 0.285 mol of the first reactant.
AGNO, (ag) + LIOH(ag) → AGOH(s) + LINO3 (ag)
]g AgOH
g LINOS
Submit
b For the following balanced chemical equation, calculate how many grams of the products would be produced by complete reaction of 0.105 mol of the first reactant.
Al3 (SO,)s (ag) + 3CaCl, (ag) → 2AICl (ag) + 3CaSO,(s)
g AICI3
|g CaSO4
C For the following balanced chemical equation, calculate how many grams of the products would be produced by complete reaction of 0.155 mol of the first reactant.
CaCO: (s) + 2HCI(ag) + CaCl2 (ag) + CO2 (g) + H0(1)
g CaCl2
g CO2
g H20
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199023
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199030
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning