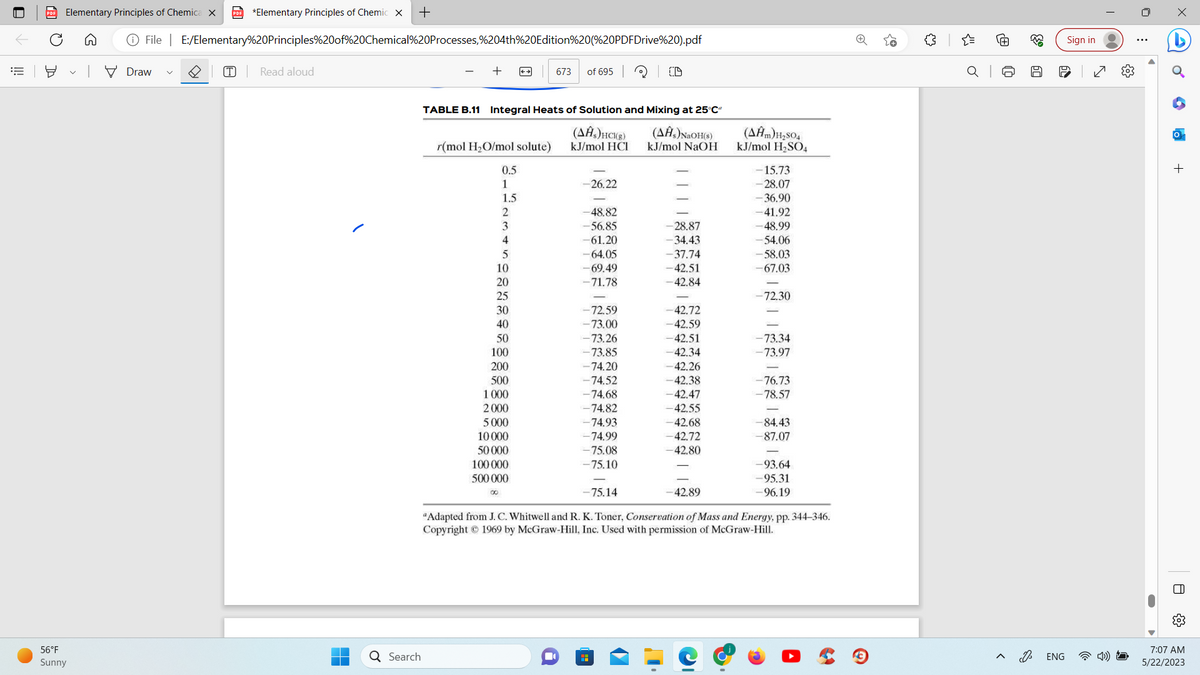
For the product solution, H₁ = 2.178 kJ/mol r= (44,400 mol H₂O)/(5480 mol HCI) = 8.10 HCl(g. 25°C) +8.10 H₂O(1, 25°C), HCl(aq, 25°C)- Table 8.11 AH, = AĤ,(25°C, r = 8.1) HCl(aq, 40°C) -67.4 kJ/mol HCI The heat capacities of aqueous hydrochloric acid solutions are listed on p. 2-183 of Perry's Chemical Engineers' Handbook (see Footnote 5) as a function of the mole fraction of HCI in the solution, which in our problem is
For the product solution, H₁ = 2.178 kJ/mol r= (44,400 mol H₂O)/(5480 mol HCI) = 8.10 HCl(g. 25°C) +8.10 H₂O(1, 25°C), HCl(aq, 25°C)- Table 8.11 AH, = AĤ,(25°C, r = 8.1) HCl(aq, 40°C) -67.4 kJ/mol HCI The heat capacities of aqueous hydrochloric acid solutions are listed on p. 2-183 of Perry's Chemical Engineers' Handbook (see Footnote 5) as a function of the mole fraction of HCI in the solution, which in our problem is
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
100%
How was -67.4 kJ/mol HCl obtained? I do not see it on the table.
Transcribed Image Text:||!
PDF Elementary Principles of Chemica X PDF *Elementary Principles of Chemic X +
56°F
Sunny
File | E:/Elementary%20Principles%20of%20Chemical%20Processes,%204th%20Edition%20(%20PDFDrive%20).pdf
Draw
T Read aloud
Q Search
r(mol H₂O/mol solute)
0.5
1
1.5
2
3
4
5
TABLE B.11 Integral Heats of Solution and Mixing at 25°C²
(AĤs) NaOH(s)
kJ/mol NaOH
10
20
25
30
40
50
100
200
500
1000
2000
5000
10 000
50 000
100 000
500 000
673 of 695
■
(AĤs) HCK(g)
kJ/mol HCI
-26.22
-48.82
-56.85
-61.20
-64.05
-69.49
-71.78
-72.59
-73.00
-73.26
-73.85
-74.20
-74.52
-74.68
-74.82
-74.93
-74.99
-75.08
-75.10
CD
-75.14
28.87
-34.43
-37.74
-42.51
-42.84
42.72
-42.59
-42.51
42.34
-42.26
-42.38
-42.47
-42.55
-42.68
-42.72
-42.80
-42.89
(AĤm) H₂SO4
kJ/mol H₂SO4
-15.73
-28.07
- 36.90
-41.92
- 48.99
- 54.06
-58.03
-67.03
-72.30
-73.34
-73.97
-76.73
-78.57
-84.43
-87.07
-93.64
-95.31
-96.19
"Adapted from J. C. Whitwell and R. K. Toner, Conservation of Mass and Energy, pp. 344-346.
Copyright © 1969 by McGraw-Hill, Inc. Used with permission of McGraw-Hill.
{"
J
63
60
D
ENG
Sign in
(0)
+
O
7:07 AM
5/22/2023

Transcribed Image Text:||!
PDF Elementary Principles of Chemica X PDF *Elementary Principles of Chemic X +
56°F
Sunny
File | E:/Elementary%20Principles%20of%20Chemical%20Processes,%204th%20Edition%20(%20PDFDrive%20).pdf
Draw
(T) Read aloud
+
References: HC1, H₂0 at 25°C and 1 atm
Substance
A in
H₁kJ/mol HCI
0
HCl(g)
H₂O(1)
HCl(aq)
Calculate H₁ and ₂:
For the product solution,
Q Search
nin
5480 mol/HCL
44,400 mol H₂O
L
Energy Balance:
466 of 695
0.73 kcal
kg. °C
HCI(g, 2C) → HCl(g, 100°C)
100°C
Ĥ₁ = AĤ =
C₂1
H₁ = 2.178 kJ/mol
5480 mol HCl/h
(5480+ 44,400) mol/h
AHb
o
r = (44,400 mol H₂O)/(5480 mol HCI) = 8.10
AĤa
AHb
HCl(g, 25°C) + 8.10 H₂O(1, 25°C). HCl(aq, 25°C)→→→ HCl(aq, 40°C)
ΔΗ = ΔΗ,(25°C, r = 8.1)
-67.4 kJ/mol HCI
Table B.11.
The heat capacities of aqueous hydrochloric acid solutions are listed on p. 2-183 of Perry's Chemical
Engineers' Handbook (see Footnote 5) as a function of the mole fraction of HCI in the solution, which in our
problem is
1000 kg solution
5480 mol HCI
40°C
Q = AH = = Σñ‚á - Σñ‚¡
Codt
J25°C
for HCl(g) from Table B.2
J25°C
OD
nout
5480 mol HCI H₂kJ/mol HCI)
ty
H
d
4.184 kJ
kcal
= 0.110 mol HCl/mol
Ĥ out
0.557
Cp dT = 8.36(kJ/mol HCI
clau
kJ
mol HCI-C
Ĥ₂ = AĤ₁ + AĤb = (-67.4+8.36) kJ/mol HCl = -59.0 kJ/mol HCl
{"
Ơ
Ⓡ
J
63
50
D
ENG
Sign in
(0)
+
O
7:27 AM
5/22/2023
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The