For the reaction 2CH,(9) -== C,H2(9) + 3H2(g) K = 0.140 mol L at 1727 °C. What is K, for the reaction at this temperature? Enter your answer numerically. > View Available Hint(s) K, = 3870 bar Prevlous Anewere Correct Part B What is the unitless themodynamic equilibrium constant K for the reaction in part A? Express your answer numerically. > View Available Hint(s) Templates Symbols undo regio teset keyboard shortouts Help K = 21.8
For the reaction 2CH,(9) -== C,H2(9) + 3H2(g) K = 0.140 mol L at 1727 °C. What is K, for the reaction at this temperature? Enter your answer numerically. > View Available Hint(s) K, = 3870 bar Prevlous Anewere Correct Part B What is the unitless themodynamic equilibrium constant K for the reaction in part A? Express your answer numerically. > View Available Hint(s) Templates Symbols undo regio teset keyboard shortouts Help K = 21.8
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter12: Chemical Equilibrium
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 113QRT
Related questions
Question
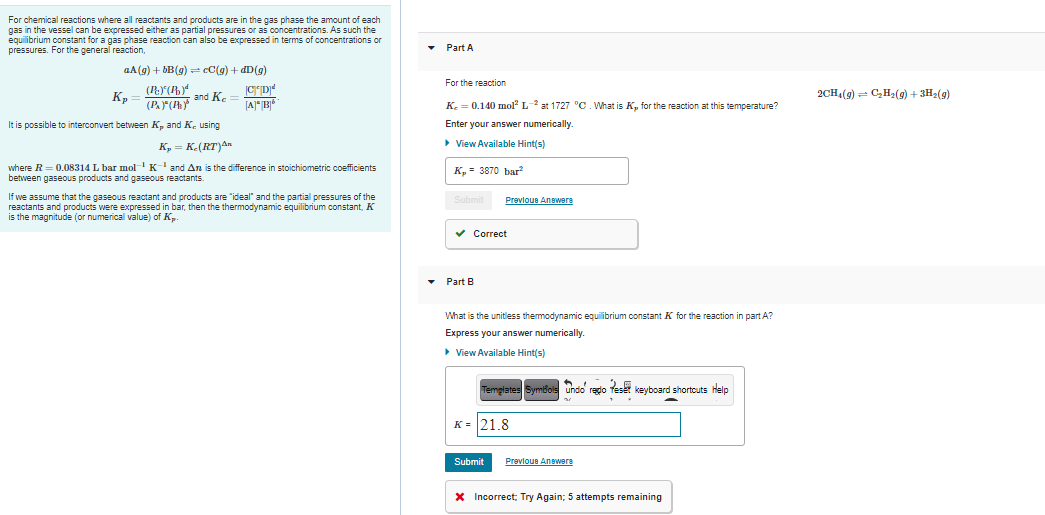
Transcribed Image Text:For chemical reactions where all reactants and products are in the gas phase the amount of each
gas in the vessel can be expressed either as partial pressures or as concentrations. As such the
equilibrium constant for a gas phase reaction can also be expressed in terms of concentrations or
pressures. For the general reaction,
Part A
aA(g) + bB(g) - cC(g) + dD(g)
For the reaction
K,
and K.
2CH(g) = C,H2(9) + 3H2(9)
(P.(Ay
K. = 0.140 mol L- at 1727 °C. What is K, for the reaction at this temperature?
It is possible to interconvert between K, and K. using
Enter your answer numerically.
K, = K-(RT)An
> View Available Hint(s)
where R = 0.08314 L bar molKand An is the difference in stoichiometric coefficients
between gaseous products and gaseous reactants.
к, 3 3870 bar?
If we assume that the gaseous reactant and products are "ideal" and the partial pressures of the
reactants and products were expressed in bar, then the thermodynamic equilibrium constant, K
is the magnitude (or numerical value) of Kp.
Prevlous Answere
v Correct
• Part B
What is the unitless themodynamic equilibrium constant
for the reaction in part A?
Express your answer numerically.
• View Available Hint(s)
Templates Symbols undo redo Teset keyboard shortcuts Help
K = 21.8
Submit
Previoun Anewere
X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining
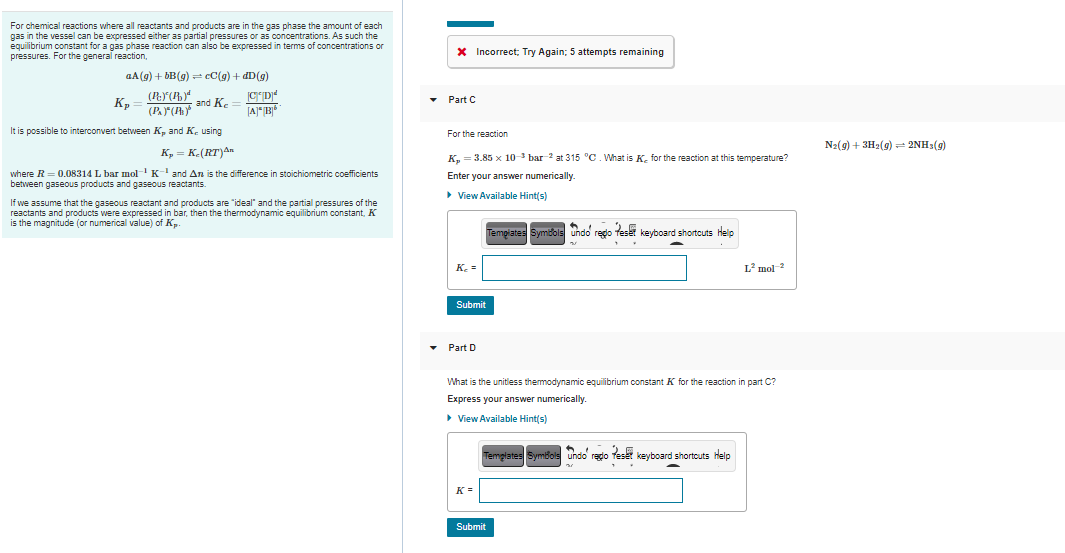
Transcribed Image Text:For chemical reactions where all reactants and products are in the gas phase the amount of each
gas in the vessel can be expressed either as partial pressures or as concentrations. As such the
equilibrium constant for a gas phase reaction can also be expressed in terms of concentrations or
pressures. For the general reaction,
Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining
aA (g) + bB(g) = cC(g) + dD(g)
and Ke
• Part C
JA"B
It is possible to interconvert between K, and K. using
For the reaction
N2(9) + 3H2(9) = 2NH3(9)
K, = K-(RT)An
K, = 3.85 x 10-3 bar 2 at 315 °C. What is K. for the reaction at this temperature?
where R = 0.08314 L bar mol Kand An is the difference in stoichiometric coefficients
between gaseous products and gaseous reactants.
Enter your answer numerically.
> View Available Hint(s)
If we assume that the gaseous reactant and products are "ideal" and the partial pressures of the
reactants and products were expressed in bar, then the thermodynamic equilibrium constant, K
is the magnitude (or numerical value) of K.
Tempiates Symdols undo rego
o fes keyboard shortcuts Help
K. =
L mol 2
Submit
• Part D
What is the unitless themodynamic equilibrium constant K for the reaction in part C?
Express your answer numerically.
> View Available Hint(s)
Templates
Sumfol
undo redo Tese keyboard shortcuts Help
K=
Submit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax