g. Interpret the p-value in the context of the study. O f the population mean IQ score for younger siblings is the same as the population mean. IQ Score for older siblings and if another 10 sibling pairs are given an IQ test then there would be a 2.28% chance that the mean IQ score for the 10 younger siblings would differ by at least 4.5 points from the mean IQ score for the 10 older siblings. O There is a 2.28% chance that the mean IQ score for the 10 younger siblings differs by at least 4.5 points from the mean IQ score for the 10 older siblings. O If the sample mean IQ score for the 10 younger siblings is the same as the sample mean IQ score for the 10 older siblings and if another 10 sibling pairs are given an IQ test then there would be a 2.28% chance of concluding that the mean IQ score for the 10 younger siblings differs by at least 4.5 points from the mean IQ score for the 10 older siblings. O There is a 2.28% chance of a Type I error. h. Interpret the level of significance in the context of the study. O If the population mean IQ score for younger siblings is the same as the population mean IQ Score for older siblings and if another 10 sibling pairs are given an J0 test, then there would be
g. Interpret the p-value in the context of the study. O f the population mean IQ score for younger siblings is the same as the population mean. IQ Score for older siblings and if another 10 sibling pairs are given an IQ test then there would be a 2.28% chance that the mean IQ score for the 10 younger siblings would differ by at least 4.5 points from the mean IQ score for the 10 older siblings. O There is a 2.28% chance that the mean IQ score for the 10 younger siblings differs by at least 4.5 points from the mean IQ score for the 10 older siblings. O If the sample mean IQ score for the 10 younger siblings is the same as the sample mean IQ score for the 10 older siblings and if another 10 sibling pairs are given an IQ test then there would be a 2.28% chance of concluding that the mean IQ score for the 10 younger siblings differs by at least 4.5 points from the mean IQ score for the 10 older siblings. O There is a 2.28% chance of a Type I error. h. Interpret the level of significance in the context of the study. O If the population mean IQ score for younger siblings is the same as the population mean IQ Score for older siblings and if another 10 sibling pairs are given an J0 test, then there would be
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:g. Interpret the p-value in the context of the study.
O f the population mean IQ score for younger siblings is the same as the population mean. IQ
Score for older siblings and if another 10 sibling pairs are given an
a 2.28% chance that the mean IQ score for the 10 younger siblings would differ by at least 4.5
points from the mean IQ score for the 10 older siblings.
test then there would be
O There is a 2.28% chance that the mean IQ score for the 10 younger siblings differs by at least
4.5 points from the mean IQ score for the 10 older siblings.
O If the sample mean IQ score for the 10 younger siblings is the same as the sample mean IQ
Score for the 10 older siblings and if another 10 sibling pairs are given an IQ test then there
would be a 2.28% chance of concluding that the mean IQ score for the 10 younger siblings
differs by at least 4.5 points from the mean IQ score for the 10 older siblings.
O There is a 2.28% chance of a Type I error.
h. Interpret the level of significance in the context of the study.
O If the population mean IQ score for younger siblings is the same as the population mean IQ
score for older siblings and if another 10 sibling pairs are given an IQ test, then there would be
a 1% chance that we would end up falsely concuding that the population mean IQ score for
younger siblings is not the same as the population mean IQ score for older siblings
O There is a 1% chance that you are so much smarter than your sibling that there is no need to
take an IQ test to make a comparison.
O If the population mean IQ score for younger siblings is the same as the population mean IQ
score for older siblings and if another 10 sibling pairs are given an IQ test, then there would be
a 1% chance that we would end up falsely concuding that the sample mean IQ scores for these
10 sibling pairs differ from each other.
O There is a 1% chance that the population mean IQ score is the same for younger and older
siblings.
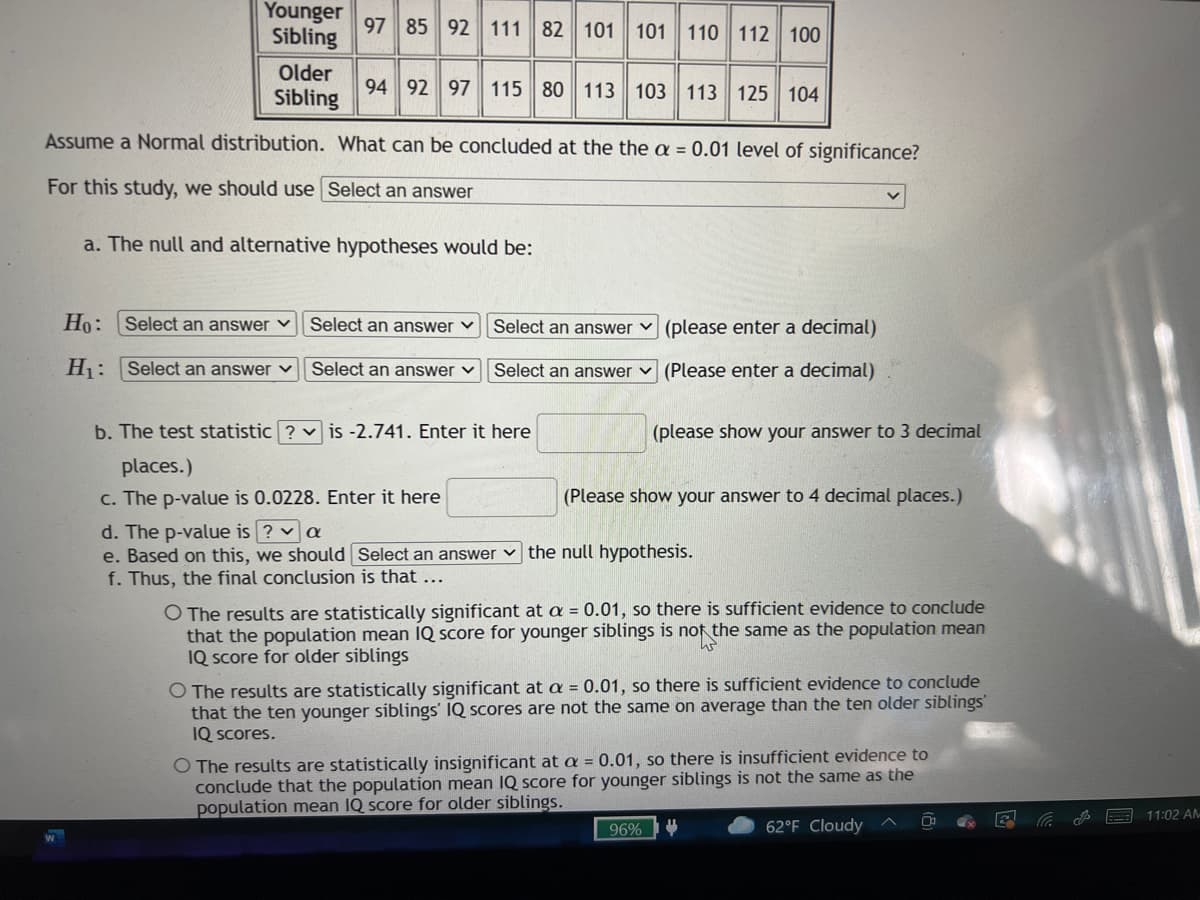
Transcribed Image Text:Younger
Sibling
97 85 92 111 82 101 101 110 112 100
Older
Sibling
94 92 97 115 80 113 103
113 125 104
Assume a Normal distribution. What can be concluded at the the a = 0.01 level of significance?
For this study, we should use Select an answer
a. The null and alternative hypotheses would be:
Ho:
Select an answer ♥
Select an answer v
Select an answer v (please enter a decimal)
H: Select an answer v
Select an answer v Select an answer v (Please enter a decimal)
b. The test statistic ? v is -2.741. Enter it here
(please show your answer to 3 decimal
places.)
c. The p-value is 0.0228. Enter it here
(Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.)
d. The p-value is ? v a
e. Based on this, we should Select an answer v the null hypothesis.
f. Thus, the final conclusion is that ...
O The results are statistically significant at a = 0.01, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude
that the population mean IQ score for younger siblings is not the same as the population mean
IQ Score for older siblings
O The results are statistically significant at a = 0.01, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude
that the ten younger siblings' IQ scores are not the same on average than the ten older siblings
IQ Scores.
O The results are statistically insignificant at a = 0.01, so there is insufficient evidence to
conclude that the population mean IQ score for younger siblings is not the same as the
population mean IQ score for older siblings.
11:02 AM
96%
62°F Cloudy
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman