Government-imposed taxes cause reductions in the activity that is being taxed, which has important implications for revenue collections. To understand the effect of such a tax, consider the monthly market for gin, which is shown on the following graph. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. Graph Input Tool Market for Gin 100 I Quantity (Bottles) 48 90 Supply Demand Price (Dollars per bottle) Supply Price (Dollars per bottle) 80 60.00 40.00 70 Таx 20.00 (Dollars per bottle) 60 50 40 30 Demand 20 10 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96 108 120 QUANTITY (Bottles) Suppose the government imposes a $20-per-bottle tax on suppliers. At this tax amount, the equilibrium quantity of gin is bottles, and the government collects in tax revenue. Now calculate the government's tax revenue if it sets a tax of $0, $20, $40, $50, $60, $80, or $100 per bottle. (Hint: To find the equilibrium quant after the tax, adjust the "Quantity" field until the Tax equals the value of the per-unit tax.) Using the data you generate, plot a Laffer curve by using the green points (triangle symbol) to plot total tax revenue at each of those tax levels. Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically. PRICE (Dollars per bottle)
Government-imposed taxes cause reductions in the activity that is being taxed, which has important implications for revenue collections. To understand the effect of such a tax, consider the monthly market for gin, which is shown on the following graph. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. Graph Input Tool Market for Gin 100 I Quantity (Bottles) 48 90 Supply Demand Price (Dollars per bottle) Supply Price (Dollars per bottle) 80 60.00 40.00 70 Таx 20.00 (Dollars per bottle) 60 50 40 30 Demand 20 10 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96 108 120 QUANTITY (Bottles) Suppose the government imposes a $20-per-bottle tax on suppliers. At this tax amount, the equilibrium quantity of gin is bottles, and the government collects in tax revenue. Now calculate the government's tax revenue if it sets a tax of $0, $20, $40, $50, $60, $80, or $100 per bottle. (Hint: To find the equilibrium quant after the tax, adjust the "Quantity" field until the Tax equals the value of the per-unit tax.) Using the data you generate, plot a Laffer curve by using the green points (triangle symbol) to plot total tax revenue at each of those tax levels. Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically. PRICE (Dollars per bottle)
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies and Tactics (MindTap Course List)
14th Edition
ISBN:9781305506381
Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Chapter4: Estimating Demand
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7E
Related questions
Question
I need help with my economics homework.

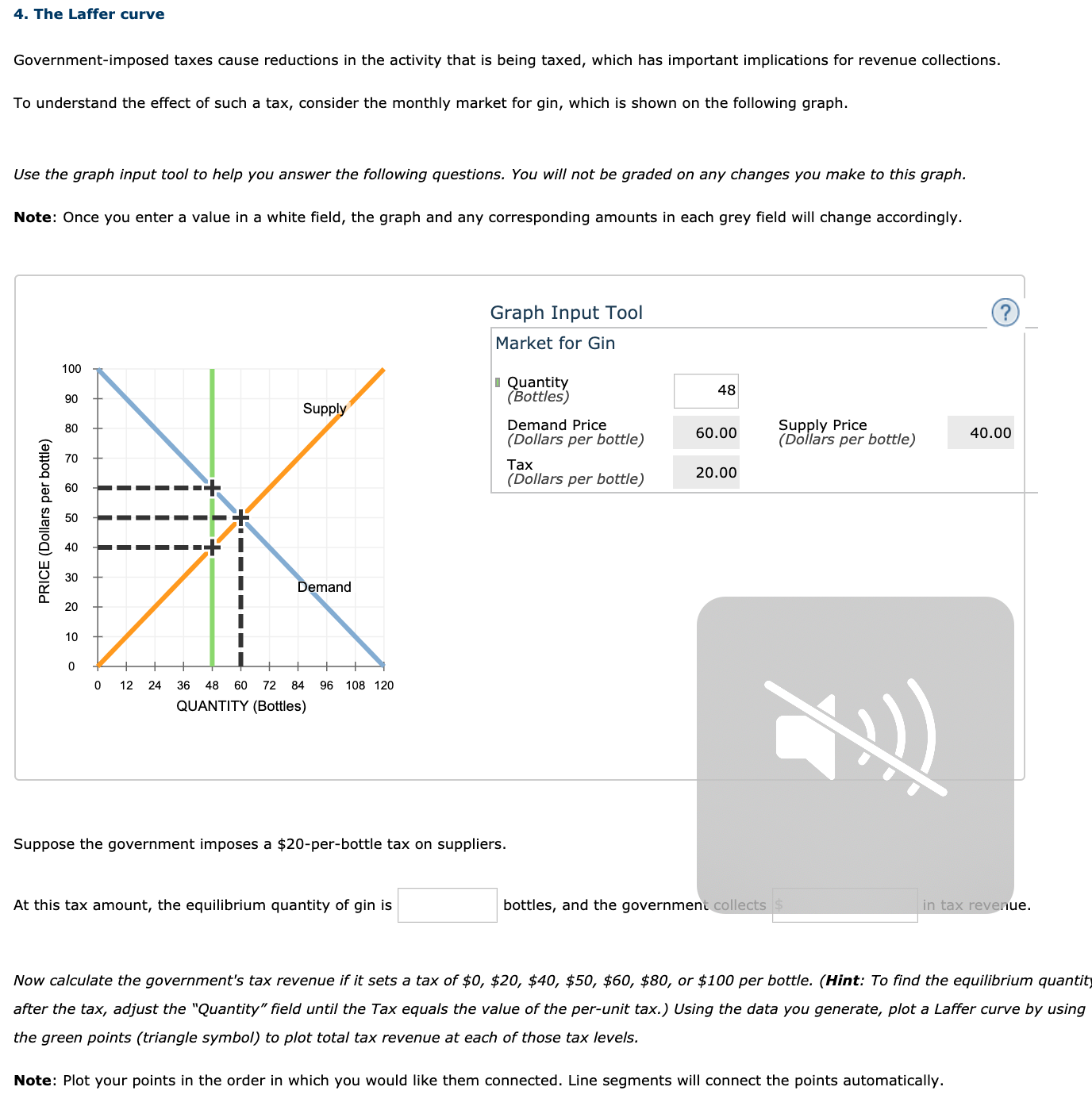
Transcribed Image Text:Government-imposed taxes cause reductions in the activity that is being taxed, which has important implications for revenue collections.
To understand the effect of such a tax, consider the monthly market for gin, which is shown on the following graph.
Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph.
Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly.
Graph Input Tool
Market for Gin
100
I Quantity
(Bottles)
48
90
Supply
Demand Price
(Dollars per bottle)
Supply Price
(Dollars per bottle)
80
60.00
40.00
70
Таx
20.00
(Dollars per bottle)
60
50
40
30
Demand
20
10
12 24
36
48
60
72
84
96 108 120
QUANTITY (Bottles)
Suppose the government imposes a $20-per-bottle tax on suppliers.
At this tax amount, the equilibrium quantity of gin is
bottles, and the government collects
in tax revenue.
Now calculate the government's tax revenue if it sets a tax of $0, $20, $40, $50, $60, $80, or $100 per bottle. (Hint: To find the equilibrium quant
after the tax, adjust the "Quantity" field until the Tax equals the value of the per-unit tax.) Using the data you generate, plot a Laffer curve by using
the green points (triangle symbol) to plot total tax revenue at each of those tax levels.
Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically.
PRICE (Dollars per bottle)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning