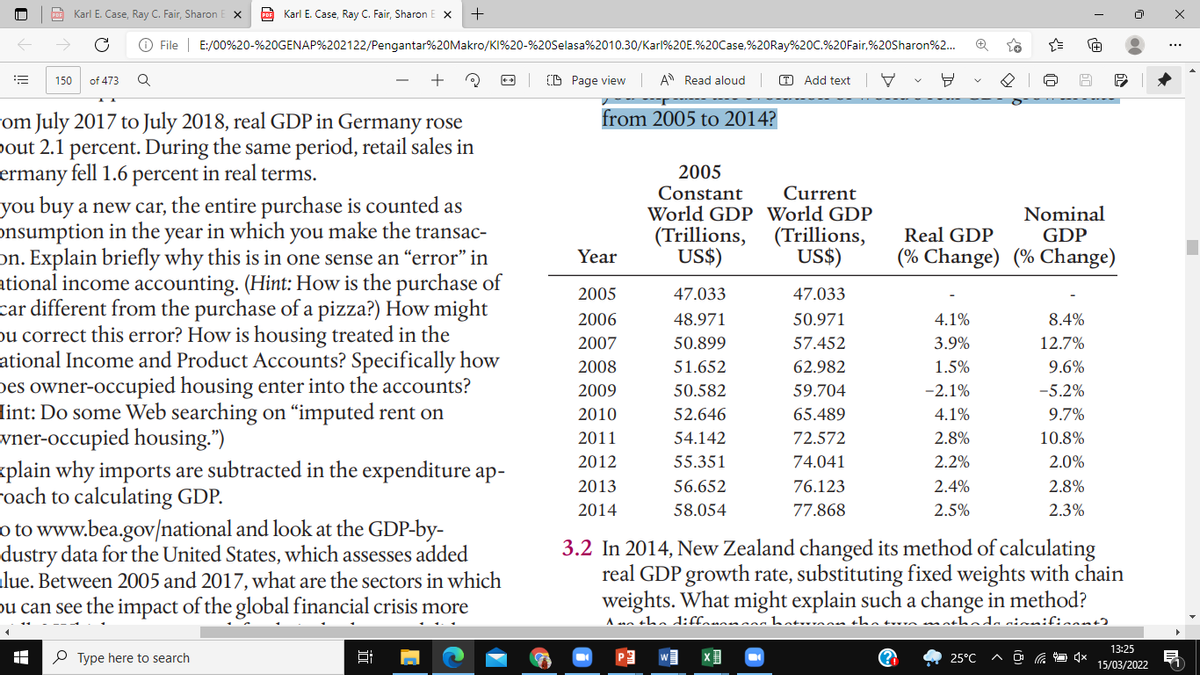
he following table shows World Bank estimates for world GDP from 2005 to 2014, both in nominal and real terms (real GDP is calculated using a fixed weights method, using 2005 as a base year). How do you explain the discrepancy between nominal and real GDP in 2014? How do you explain the evolution of world’s real GDP growth rate from 2005 to 2014?
he following table shows World Bank estimates for world GDP from 2005 to 2014, both in nominal and real terms (real GDP is calculated using a fixed weights method, using 2005 as a base year). How do you explain the discrepancy between nominal and real GDP in 2014? How do you explain the evolution of world’s real GDP growth rate from 2005 to 2014?
Microeconomics A Contemporary Intro
10th Edition
ISBN:9781285635101
Author:MCEACHERN
Publisher:MCEACHERN
Chapter13: Capital, Interest, Entrepreneurship, And Corporate Finance
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13PAE
Related questions
Question
The following table shows World Bank estimates for world GDP from 2005 to 2014, both in nominal and real terms (real GDP is calculated using a fixed weights method, using 2005 as a base year). How do you explain the discrepancy between nominal and real GDP in 2014? How do you explain the evolution of world’s real GDP growth rate from 2005 to 2014?
Transcribed Image Text:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon
C Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon
+
O File | E:/00%20-%20GENAP%202122/Pengantar%20Makro/KI%20-%20Selasa%2010.30/Karl%20E.%20Case,%20Ray%20C.%20Fair,%20Sharon%2..
150
of 473
(D Page view A Read aloud
T Add text
from 2005 to 2014?
om July 2017 to July 2018, real GDP in Germany rose
pout 2.1 percent. During the same period, retail sales in
ermany fell 1.6 percent in real terms.
you buy a new car, the entire purchase is counted as
onsumption in the year in which you make the transac-
on. Explain briefly why this is in one sense an “error" in
ational income accounting. (Hint: How is the purchase of
car different from the purchase of a pizza?) How might
ou correct this error? How is housing treated in the
ational Income and Product Accounts? Specifically how
bes owner-occupied housing enter into the accounts?
Hint: Do some Web searching on “imputed rent on
wner-occupied housing.")
<plain why imports are subtracted in the expenditure ap-
roach to calculating GDP.
o to www.bea.gov/national and look at the GDP-by-
dustry data for the United States, which assesses added
lue. Between 2005 and 2017, what are the sectors in which
pu can see the impact of the global financial crisis more
2005
Current
World GDP World GDP
(Trillions,
US$)
Constant
Nominal
GDP
(Trillions,
US$)
Real GDP
Year
(% Change) (% Change)
2005
47.033
47.033
2006
48.971
50.971
4.1%
8.4%
2007
50.899
57.452
3.9%
12.7%
2008
51.652
62.982
1.5%
9.6%
2009
50.582
59.704
-2.1%
-5.2%
2010
52.646
65.489
4.1%
9.7%
2011
54.142
72.572
2.8%
10.8%
2012
55.351
74.041
2.2%
2.0%
2013
56.652
76.123
2.4%
2.8%
2014
58.054
77.868
2.5%
2.3%
3.2 In 2014, New Zealand changed its method of calculating
real GDP growth rate, substituting fixed weights with chain
weights. What might explain such a change in method?
A ma tha d:ffo
thotuo mathada ninnifinan4)
13:25
P Type here to search
25°C
15/03/2022
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning