Hultquist Corporation has two manufacturing departments--Forming and Customizing. The company used the following data at the beginning of the period to calculate predetermined overhead rates: Estimated total machine-hours (MHs) Estimated total fixed manufacturing overhead cost Estimated variable manufacturing overhead cost per MH Forming Customizing 7,000 $14,700 $ 2.00 Total 10, e00 $22,800 3,000 $8,100 $ 4.00 During the period, the company started and completed two jobs--Job C and Job L. Data concerning those two jobs follow: Job C Job L Direct materials Direct labor cost Forming machine-hours Customizing machine-hours $14,800 $ 8,500 $21,700 $ 8,600 2,500 2,500 4,500 500 Required: a. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours. Calculate that overhead rate. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) b. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours. Calculate the amount of manufacturing overhead applied to Job L. (Do not round intermediate calculations.) C. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours. Calculate the total manufacturing cost assigned to Job L. (Do not round intermediate calculations.) d. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours and uses a markup of 20% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices. Calculate the selling price for Job L. (Do not round intermediate calculations.) e. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both departments. What is the departmental predetermined overhead rate in the Forming department? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) f. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments. What is the departmental predetermined overhead rate in the Customizing department? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) g. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments. How much manufacturing overhead will be applied to Job L? (Do not round intermediate calculations.) h. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments. Further assume that the company uses a markup of 20% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices. Calculate the selling price for Job L. (Do not round intermediate calculations.)
Hultquist Corporation has two manufacturing departments--Forming and Customizing. The company used the following data at the beginning of the period to calculate predetermined overhead rates: Estimated total machine-hours (MHs) Estimated total fixed manufacturing overhead cost Estimated variable manufacturing overhead cost per MH Forming Customizing 7,000 $14,700 $ 2.00 Total 10, e00 $22,800 3,000 $8,100 $ 4.00 During the period, the company started and completed two jobs--Job C and Job L. Data concerning those two jobs follow: Job C Job L Direct materials Direct labor cost Forming machine-hours Customizing machine-hours $14,800 $ 8,500 $21,700 $ 8,600 2,500 2,500 4,500 500 Required: a. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours. Calculate that overhead rate. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) b. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours. Calculate the amount of manufacturing overhead applied to Job L. (Do not round intermediate calculations.) C. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours. Calculate the total manufacturing cost assigned to Job L. (Do not round intermediate calculations.) d. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours and uses a markup of 20% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices. Calculate the selling price for Job L. (Do not round intermediate calculations.) e. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both departments. What is the departmental predetermined overhead rate in the Forming department? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) f. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments. What is the departmental predetermined overhead rate in the Customizing department? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) g. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments. How much manufacturing overhead will be applied to Job L? (Do not round intermediate calculations.) h. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments. Further assume that the company uses a markup of 20% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices. Calculate the selling price for Job L. (Do not round intermediate calculations.)
Principles of Cost Accounting
17th Edition
ISBN:9781305087408
Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Chapter4: Accounting For Factory Overhead
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 14P: Abbey Products Company is studying the results of applying factory overhead to production. The...
Related questions
Question
100%
info in images. pls help with d through h soon! i will give a thumbs up! :)
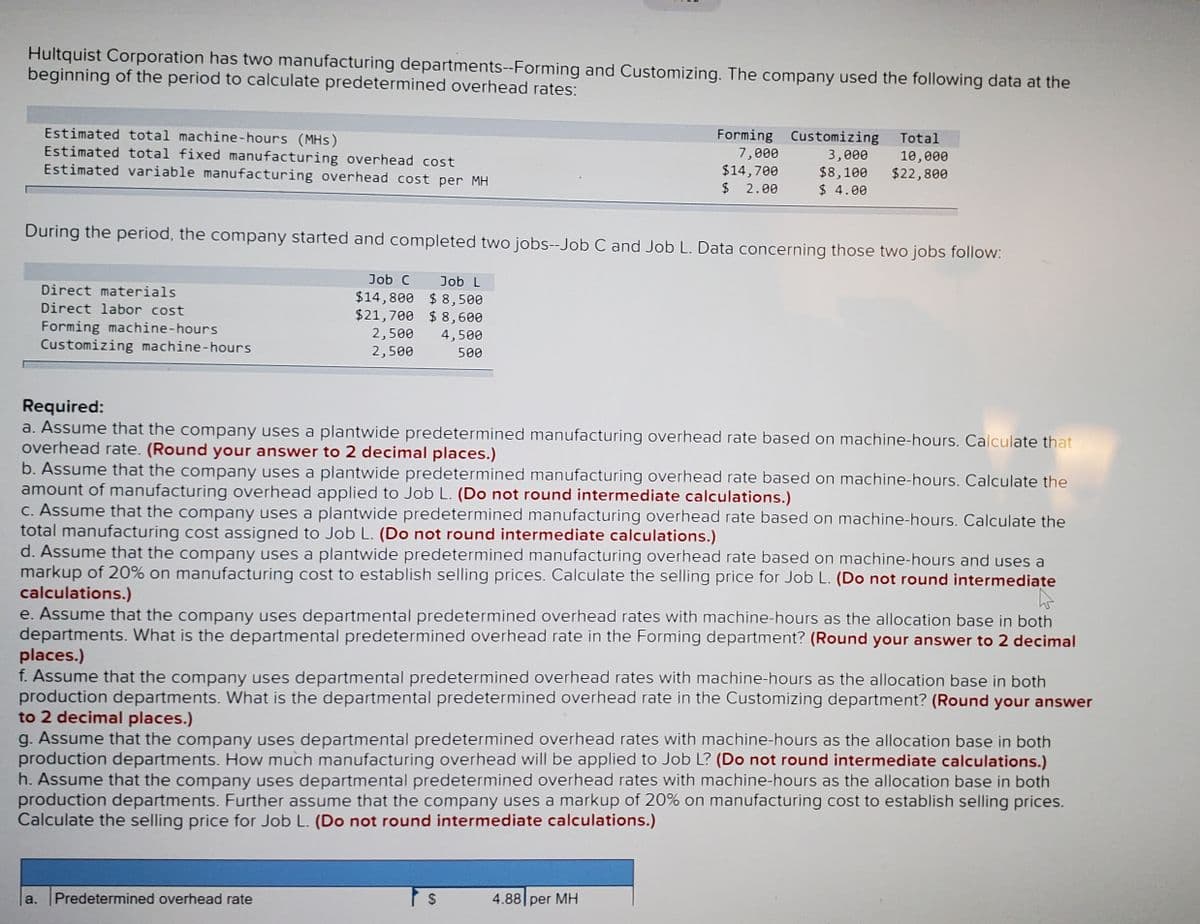
Transcribed Image Text:Hultquist Corporation has two manufacturing departments--Forming and Customizing. The company used the following data at the
beginning of the period to calculate predetermined overhead rates:
Estimated total machine-hours (MHs)
Estimated total fixed manufacturing overhead cost
Estimated variable manufacturing overhead cost per MH
Forming Customizing
Total
7,000
$14,700
$ 2.00
3,000
$8,100
$ 4.00
10,000
$22,800
During the period, the company started and completed two jobs--Job C and Job L. Data concerning those two jobs follow:
Job C
Job L
$14,800 $ 8,500
$21,700 $ 8,600
Direct materials
Direct labor cost
Forming machine-hours
Customizing machine-hours
2,500
2,500
4,500
500
Required:
a. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours. Calculate that
overhead rate. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)
b. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours. Calculate the
amount of manufacturing overhead applied to Job L. (Do not round intermediate calculations.)
C. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours. Calculate the
total manufacturing cost assigned to Job L. (Do not round intermediate calculations.)
d. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours and uses a
markup of 20% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices. Calculate the selling price for Job L. (Do not round intermediate
calculations.)
e. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both
departments. What is the departmental predetermined overhead rate in the Forming department? (Round your answer to 2 decimal
places.)
f. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both
production departments. What is the departmental predetermined overhead rate in the Customizing department? (Round your answer
to 2 decimal places.)
g. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both
production departments. How much manufacturing overhead will be applied to Job L? (Do not round intermediate calculations.)
h. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both
production departments. Further assume that the company uses a markup of 20% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices.
Calculate the selling price for Job L. (Do not round intermediate calculations.)
a.
Predetermined overhead rate
4.88 per MH
%24
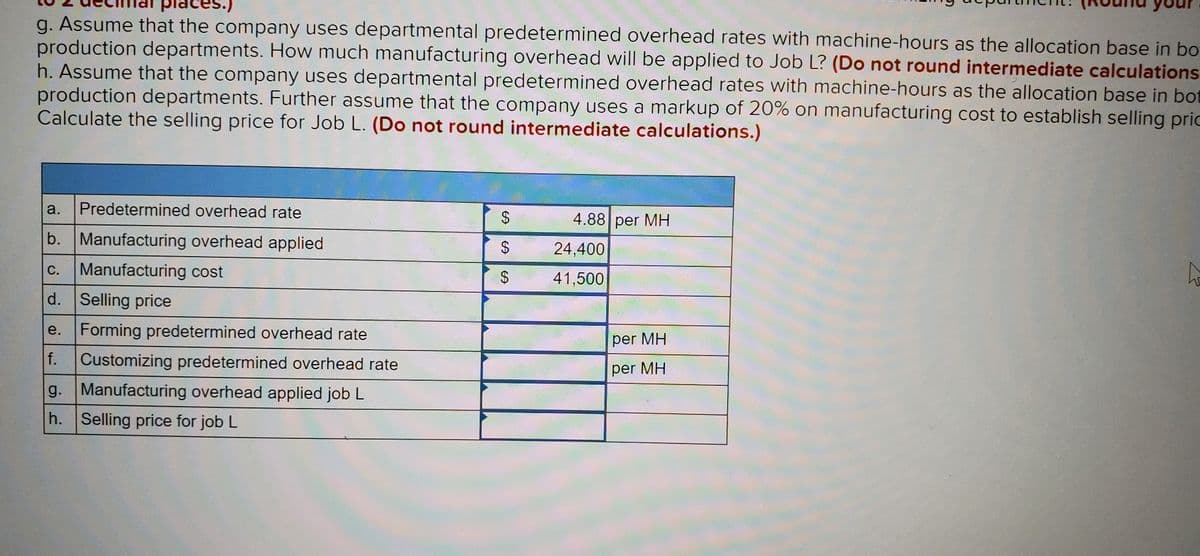
Transcribed Image Text:g. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in bo
production departments. How much manufacturing overhead will be applied to Job L? (Do not round intermediate calculations
h. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in bot
production departments. Further assume that the company uses a markup of 20% on manufacturing cost to establish selling pric
Calculate the selling price for Job L. (Do not round intermediate calculations.)
a.
Predetermined overhead rate
4.88 per MH
b. Manufacturing overhead applied
$.
24,400
c. Manufacturing cost
С.
41,500
d. Selling price
e.
Forming predetermined overhead rate
per MH
f.
Customizing predetermined overhead rate
per MH
g. Manufacturing overhead applied job L
h. Selling price for job L
%24
%24
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305087408
Author:
Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Excel Applications for Accounting Principles
Accounting
ISBN:
9781111581565
Author:
Gaylord N. Smith
Publisher:
Cengage Learning