Hurricane damage: In August and September 2005, Hurricanes Katrina and Rita caused extraordinary flooding in New Orleans. Louisiana. Many homes were severely damaged or destroyed, and of those that survived, many required extensive cleaning. It was thought that cleaning flood-damaged homes might present a health hazard due to the large amounts of mold present in many of the homes. In a sample of 3 70 residents of Orleans Parish who had participated in the cleaning of one or more homes, 28 had experienced symptoms of wheezing, and in a sample of 173 residents who had not participated in the cleaning, 30 reported wheezing symptoms (numbers read from a graph). Can you conclude that there is a difference betvween the proportion of residents with wheezing symptoms who cleaned flood-damaged homes and those who did not participate in the cleaning? Let P. denote the proportion of residents with wheezing symptoms who had cleaned flood-damaged homes and p, denote the proportion of residents with wheezing symptoms who had not cleaned flood-damanged homes. Use the a = 0.01 level of significance and the P-value method with the TI-84 Plus calculator. Part 1 of 4 State the null and alternate hypotheses. H P - P H P1 * P2 This hypothesis test is a two-tailed test. Part: 1/4 Part 2 of 4 Find the P-value. Round the answer to four decimal places. P-value =
Hurricane damage: In August and September 2005, Hurricanes Katrina and Rita caused extraordinary flooding in New Orleans. Louisiana. Many homes were severely damaged or destroyed, and of those that survived, many required extensive cleaning. It was thought that cleaning flood-damaged homes might present a health hazard due to the large amounts of mold present in many of the homes. In a sample of 3 70 residents of Orleans Parish who had participated in the cleaning of one or more homes, 28 had experienced symptoms of wheezing, and in a sample of 173 residents who had not participated in the cleaning, 30 reported wheezing symptoms (numbers read from a graph). Can you conclude that there is a difference betvween the proportion of residents with wheezing symptoms who cleaned flood-damaged homes and those who did not participate in the cleaning? Let P. denote the proportion of residents with wheezing symptoms who had cleaned flood-damaged homes and p, denote the proportion of residents with wheezing symptoms who had not cleaned flood-damanged homes. Use the a = 0.01 level of significance and the P-value method with the TI-84 Plus calculator. Part 1 of 4 State the null and alternate hypotheses. H P - P H P1 * P2 This hypothesis test is a two-tailed test. Part: 1/4 Part 2 of 4 Find the P-value. Round the answer to four decimal places. P-value =
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8CR
Related questions
Question
Please help
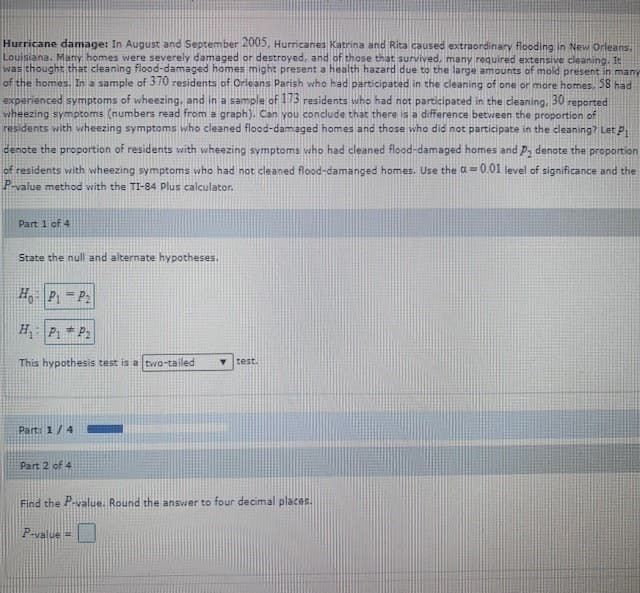
Transcribed Image Text:Hurricane damage: In August and September 2005, Hurricanes Katrina and Rita caused extraordinary flooding in New Orleans.
Louisiana. Many homes were severely damaged or destroyed, and of those that survived, many required extensive cleaning. It
was thought that cleaning flood-damaged homes might present a health hazard due to the large amounts of mold present in many
of the homes. In a sample of 3 70 residents of Orleans Parish who had participated in the cleaning of one or more homes, 28 had
experienced symptoms of wheezing, and in a sample of 173 residents who had not participated in the cleaning,
vwheezing symptoms (numbers read from a graph). Can you conclude that there is a difference betvween the proportion of
residents with wheezing symptoms who cleaned flood-damaged homes and those who did not participate in the cleaning? Let P
denote the proportion of residents with wheezing symptoms who had cleaned flood-damaged homes and p, denote the proportion
30
reported
of residents with wheezing symptoms who had not cleaned flood-damanged homes. Use the a= 0.01 level of significance and the
P-value method with the TI-84 Plus calculator.
Part 1 of 4
State the null and alternate hypotheses.
H P = P:
H P1 * P2
This hypothesis test is a two-tailed
test.
Part: 1/4
Part 2 of 4
Find the P-value. Round the answer to four decimal places.
P-value =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning