Hydrazine and 1,1-dimethylhydrazine both react spontaneously with Oz and can be used as rocket fuels. N3H4() + O2(g) → N2(g) + 2 H2O(g) N,Hạ (CH,)2() +4 0:(8) + 2 CO: (8) + 4 Hạ0(g) + N2(8) The molar enthalpy of formation of N3H,(() is +50.6 kl mol, and that of N3H2 (CH,)2(0) is +48.9 kJ mol. Use these values, with other A,H values in the table below. Compound A H (kJ/mol) H,O(g) CO(8) -241.83 -393.509 Calculate the specific heat of the reaction hydrazine with oxygen. A,H = -16.7 V kig hydrazine Correct To calculate molar enthalpy of the reaction, the sum of molar standard enthalpies of formation of reactants should be subtracted from molar standard enthalpies of formation of products: A,H" (kJ/mol) = 2 mol x (-241.83 kJ/mol) – 1 mol x x 50.6 kJ/mol = -534.3 kJ/mol Convert the value from (kJ mol) to (kJg): 1 mol (N,H4) 32.05 g (N,H,) A,H" (kJ/g) = -534.3 kJ/mol x = -16.67 kJ/g Calculate specific heat of the reaction 1,1-dimethyikydrazine with onygen. A,H' = 30.06 v kig 1,1-dimethyilhydrazine Correct To calculate molar enthalpy of the reaction, the sum of molar standard enthalpies of formation of reactants should be subtracted from molar standard enthalpies of formation of products: A,H" (kJ/mol) = 2 mol x (-393.509 kJ/mol) + 4 mol x x (-241.83 kJ/mol) – 1 mol x 48.9 kJ/mol --1803.2 kJ/mol Convert the value from (kJ mol) to (kg): 1 mol (N3 H3 (CH3)2) 60.10 g (N;H2 (CH,)2) -30.00 kJ/g A,H" (kJ/g) = -1803.2 kJ/mol x Decide whether the reaction of hydrazine or 1,1-dimethyihydrazine with oxygen provides more energy per gram. O Hydrazine gives more heat per gram when reacting with oxygen. O1,1-Dimethylhydrazine gives more heat per gram when reacting with oxygen. O The compounds give almost the same heat per gram when reacting with oxygen.
Hydrazine and 1,1-dimethylhydrazine both react spontaneously with Oz and can be used as rocket fuels. N3H4() + O2(g) → N2(g) + 2 H2O(g) N,Hạ (CH,)2() +4 0:(8) + 2 CO: (8) + 4 Hạ0(g) + N2(8) The molar enthalpy of formation of N3H,(() is +50.6 kl mol, and that of N3H2 (CH,)2(0) is +48.9 kJ mol. Use these values, with other A,H values in the table below. Compound A H (kJ/mol) H,O(g) CO(8) -241.83 -393.509 Calculate the specific heat of the reaction hydrazine with oxygen. A,H = -16.7 V kig hydrazine Correct To calculate molar enthalpy of the reaction, the sum of molar standard enthalpies of formation of reactants should be subtracted from molar standard enthalpies of formation of products: A,H" (kJ/mol) = 2 mol x (-241.83 kJ/mol) – 1 mol x x 50.6 kJ/mol = -534.3 kJ/mol Convert the value from (kJ mol) to (kJg): 1 mol (N,H4) 32.05 g (N,H,) A,H" (kJ/g) = -534.3 kJ/mol x = -16.67 kJ/g Calculate specific heat of the reaction 1,1-dimethyikydrazine with onygen. A,H' = 30.06 v kig 1,1-dimethyilhydrazine Correct To calculate molar enthalpy of the reaction, the sum of molar standard enthalpies of formation of reactants should be subtracted from molar standard enthalpies of formation of products: A,H" (kJ/mol) = 2 mol x (-393.509 kJ/mol) + 4 mol x x (-241.83 kJ/mol) – 1 mol x 48.9 kJ/mol --1803.2 kJ/mol Convert the value from (kJ mol) to (kg): 1 mol (N3 H3 (CH3)2) 60.10 g (N;H2 (CH,)2) -30.00 kJ/g A,H" (kJ/g) = -1803.2 kJ/mol x Decide whether the reaction of hydrazine or 1,1-dimethyihydrazine with oxygen provides more energy per gram. O Hydrazine gives more heat per gram when reacting with oxygen. O1,1-Dimethylhydrazine gives more heat per gram when reacting with oxygen. O The compounds give almost the same heat per gram when reacting with oxygen.
Chemistry: Matter and Change
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Chapter15: Energy And Chemical Change
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 112A: sample of natural gas is analyzed and found to be88.4% methane (CH4) and 11.6% ethane (C2H6) bymass....
Related questions
Question
*please answer question C
the other answer is needed to answer c
| c |
Decide whether the reaction of hydrazine or 1,1-dimethylhydrazine with oxygen provides more energy per gram. a)Hydrazine gives more heat per gram when reacting with oxygen. b)1,1-Dimethylhydrazine gives more heat per gram when reacting with oxygen. c)The compounds give almost the same heat per gram when reacting with oxygen. |
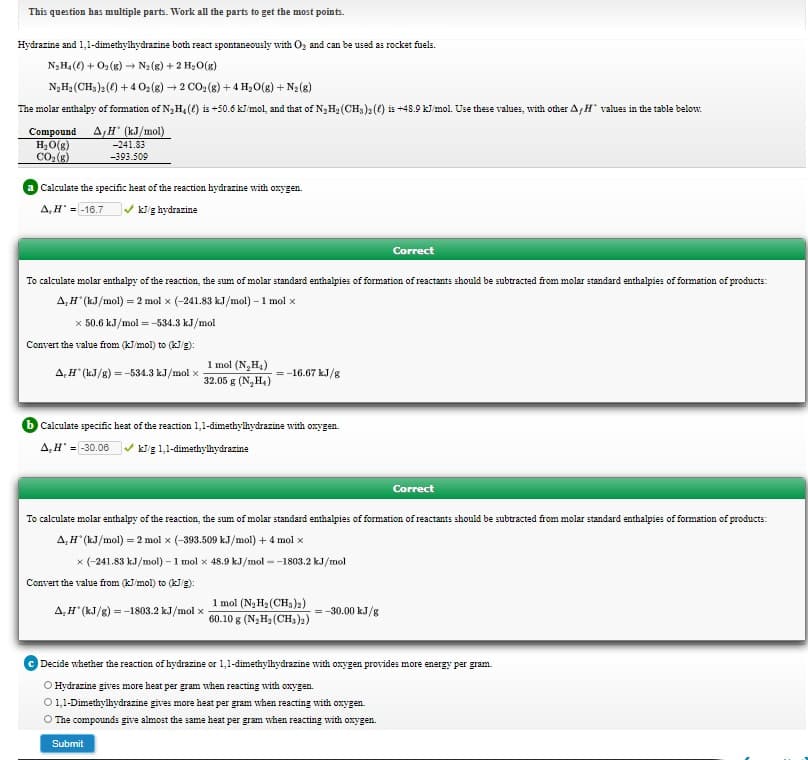
Transcribed Image Text:Hydrazine and 1,1-dimethylhydrazine both react spontaneously with Oz and can be used as rocket fuels.
N3H4() + O2(g) → N2(g) + 2 H2O(g)
N,Hạ (CH,)2() +4 0:(8) + 2 CO: (8) + 4 Hạ0(g) + N2(8)
The molar enthalpy of formation of N3H,(() is +50.6 kl mol, and that of N3H2 (CH,)2(0) is +48.9 kJ mol. Use these values, with other A,H values in the table below.
Compound A H (kJ/mol)
H,O(g)
CO(8)
-241.83
-393.509
Calculate the specific heat of the reaction hydrazine with oxygen.
A,H = -16.7
V kig hydrazine
Correct
To calculate molar enthalpy of the reaction, the sum of molar standard enthalpies of formation of reactants should be subtracted from molar standard enthalpies of formation of products:
A,H" (kJ/mol) = 2 mol x (-241.83 kJ/mol) – 1 mol x
x 50.6 kJ/mol = -534.3 kJ/mol
Convert the value from (kJ mol) to (kJg):
1 mol (N,H4)
32.05 g (N,H,)
A,H" (kJ/g) = -534.3 kJ/mol x
= -16.67 kJ/g
Calculate specific heat of the reaction 1,1-dimethyikydrazine with onygen.
A,H' = 30.06 v kig 1,1-dimethyilhydrazine
Correct
To calculate molar enthalpy of the reaction, the sum of molar standard enthalpies of formation of reactants should be subtracted from molar standard enthalpies of formation of products:
A,H" (kJ/mol) = 2 mol x (-393.509 kJ/mol) + 4 mol x
x (-241.83 kJ/mol) – 1 mol x 48.9 kJ/mol --1803.2 kJ/mol
Convert the value from (kJ mol) to (kg):
1 mol (N3 H3 (CH3)2)
60.10 g (N;H2 (CH,)2)
-30.00 kJ/g
A,H" (kJ/g) = -1803.2 kJ/mol x
Decide whether the reaction of hydrazine or 1,1-dimethyihydrazine with oxygen provides more energy per gram.
O Hydrazine gives more heat per gram when reacting with oxygen.
O1,1-Dimethylhydrazine gives more heat per gram when reacting with oxygen.
O The compounds give almost the same heat per gram when reacting with oxygen.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning