If one person with the trait of Huntington's disease (H h) has 2 children with a partner who does not have a trait for the disease what is the chance that both children won't have the disease?
If one person with the trait of Huntington's disease (H h) has 2 children with a partner who does not have a trait for the disease what is the chance that both children won't have the disease?
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Michael Cummings
Chapter11: Genome Alterations: Mutation And Epigenetics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 16QP: Familial retinoblastoma, a rare autosomal dominant defect, arose in a large family that had no prior...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
If one person with the trait of Huntington's disease (H h) has 2 children with a partner who does not have a trait for the disease what is the chance that both children won't have the disease?
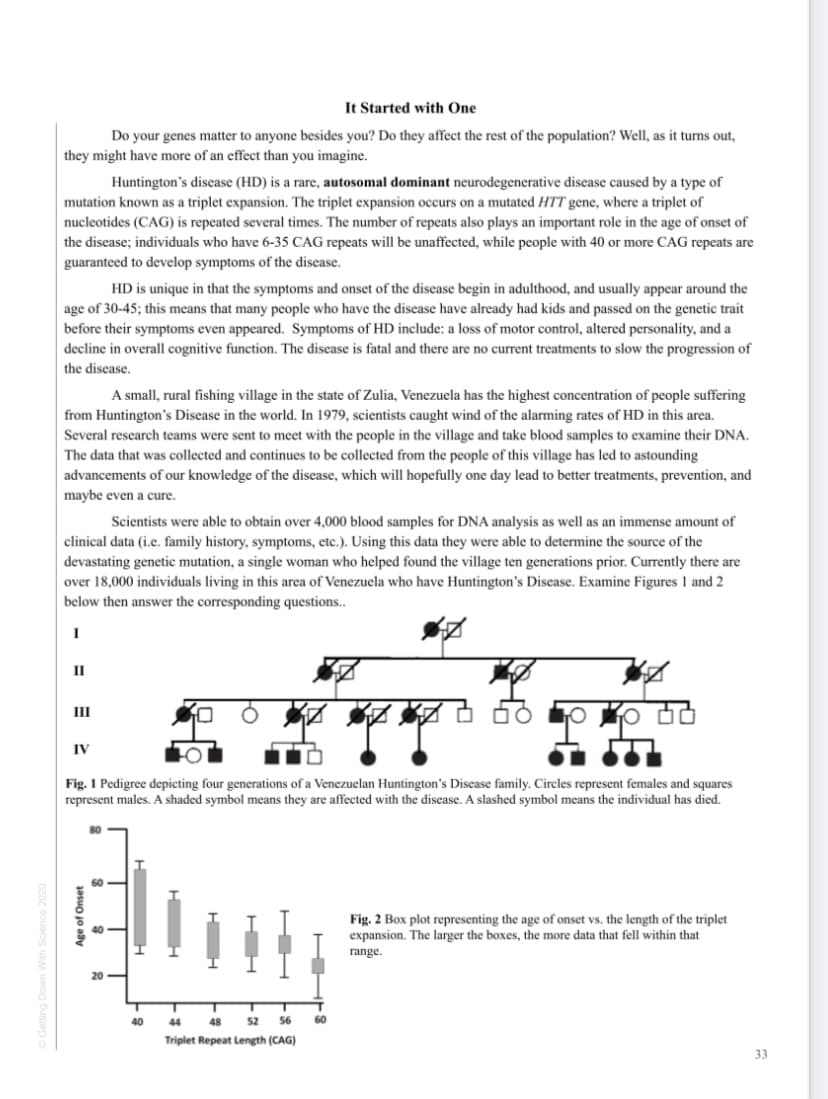
Transcribed Image Text:It Started with One
Do your genes matter to anyone besides you? Do they affect the rest of the population? Well, as it turns out,
they might have more of an effect than you imagine.
Huntington's disease (HD) is a rare, autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disease caused by a type of
mutation known as a triplet expansion. The triplet expansion occurs on a mutated HTT gene, where a triplet of
nucleotides (CAG) is repeated several times. The number of repeats also plays an important role in the age of onset of
the disease; individuals who have 6-35 CAG repeats will be unaffected, while people with 40 or more CAG repeats are
guaranteed to develop symptoms of the disease.
HD is unique in that the symptoms and onset of the disease begin in adulthood, and usually appear around the
age of 30-45; this means that many people who have the disease have already had kids and passed on the genetic trait
before their symptoms even appeared. Symptoms of HD include: a loss of motor control, altered personality, and a
decline in overall cognitive function. The disease is fatal and there are no current treatments to slow the progression of
the disease.
A small, rural fishing village in the state of Zulia, Venezuela has the highest concentration of people suffering
from Huntington's Disease in the world. In 1979, scientists caught wind of the alarming rates of HD in this area.
Several research teams were sent to meet with the people in the village and take blood samples to examine their DNA.
The data that was collected and continues to be collected from the people of this village has led to astounding
advancements of our knowledge of the disease, which will hopefully one day lead to better treatments, prevention, and
maybe even a cure.
Scientists were able to obtain over 4,000 blood samples for DNA analysis as well as an immense amount of
clinical data (i.e. family history, symptoms, etc.). Using this data they were able to determine the source of the
devastating genetic mutation, a single woman who helped found the village ten generations prior. Currently there are
over 18,000 individuals living in this area of Venezuela who have Huntington's Disease. Examine Figures 1 and 2
below then answer the corresponding questions..
II
II
IV
Fig. 1 Pedigree depicting four generations of a Venezuelan Huntington's Disease family. Circles represent females and squares
represent males. A shaded symbol means they are affected with the disease. A slashed symbol means the individual has died.
Fig. 2 Box plot representing the age of onset vs. the length of the triplet
expansion. The larger the boxes, the more data that fell within that
range.
40
44
48
52
56
60
Triplet Repeat Length (CAG)
33
Age of Onset
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning